-
Couldn't load subscription status.
- Fork 6
Azure SQL Execute Query
![]()
With this task, you can execute a SQL query on an Azure SQL Database, using an Azure Resource Manager Service Endpoint. The query will be executed with SQLCMD, and allow uses of variables.
You should have Setup an Azure Resource Manager Endpoint to use this task.
Your Build Agent should have the SQLPS capability, so you have to Install SQLPS on your Build Agent.

You will find the task in the "Deploy" category.
-
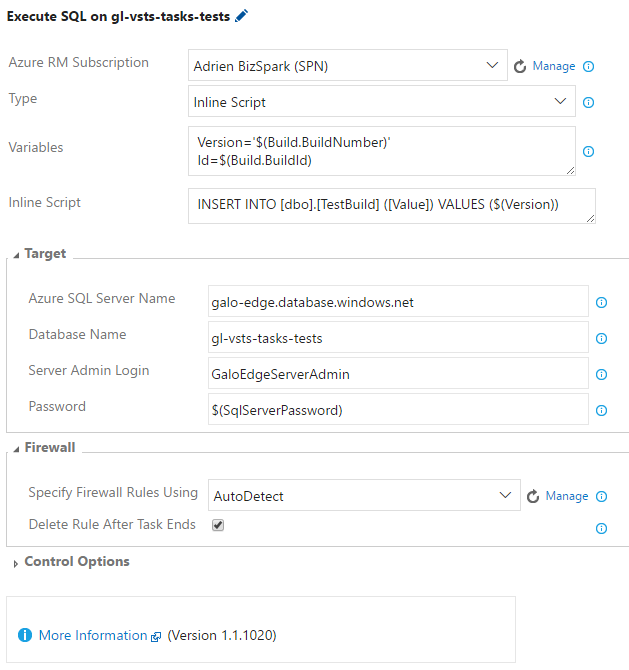
Azure RM Subscription - Specifies the Azure Resource Manager Service Endpoint to use.
-
Type - Type of the SQL script to execute on target: File Path, Inline Script or Predefined Script.
-
Script Path - Path of the script to execute. Should be fully qualified path or relative to the default working directory.
-
Inline Script - An in-place editable script.
-
Predefined Script - This task come with several predefined scripts of common tasks on SQL Azure.
-
Create User - Create an user on the target database. Must match an existing login. You must provide the
Loginvariable using the Variables input (i.e.Login=MyUserorLogin=$(MyUserBuildVariable))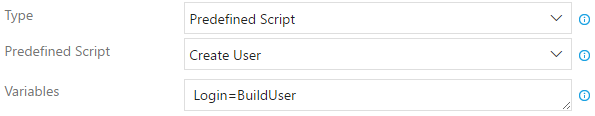
-
Add Role Member - Add a role member on the target database (with
sp_addrolemember). You must provide theLoginandRolevariables using the Variables input (i.e.Login=$(MyUserBuildVariable)andRole=$(MyRoleBuildVariable))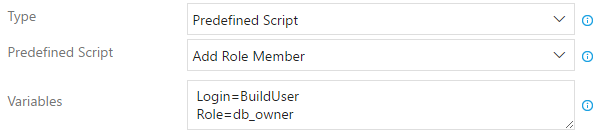
-
Create Database Owner - Combine the two previous script: create an user and add it to the
db_ownerrole on the target database. You must provide theLoginvariable using the Variables input (i.e.Login=$(MyUserBuildVariable))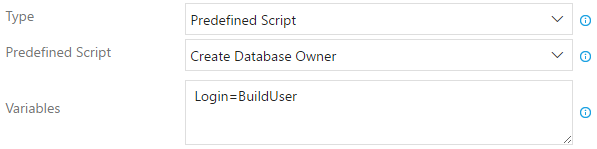
- Feel free to contribute to add your generic predefined scripts!
-
Add Role Member - Add a role member on the target database (with
-
-
Variables - Variables passed to the SQLCMD script with the -v option. Should be formatted like
Var1=Value1, with one variable per line. It can then be used with the SQLCMD$(Var1)syntax in the script. -
Predefined SQLCMD variables:
- WorkingDirectory: The current path of the script. Usefull with the SQLCMD
:rsyntax to link other SQL files. See CreateDbOwner.sql as an example.
- WorkingDirectory: The current path of the script. Usefull with the SQLCMD
- Azure SQL Server Name - Azure SQL Server name like, FabrikamSQL.database.windows.net,1433 or FabrikamSQL.database.windows.net.
- Database Name - Name of the Azure SQL Database.
- Login - The Azure SQL Server login, with the permissions required for your script.
-
Password - Password for the Azure SQL Server login provided. It can accept variable defined in Build / Release Definitions as
$(PasswordVariable). You may mark variable type as "secret" to secure it.
- Specify Firewall Rules Using - For the script to execute, the IP Address of the automation agent has to be added to the 'Allowed IP Addresses' in the Azure SQL Server's Firewall. Provide the IP Address range of the automation agents, or select auto-detect (it will find the external IP of your agent).
- Start IP Address - If you choose 'Allowed IP Addresses', the starting IP Address of the automation agent machine pool like 196.21.30.50.
- End IP Address - If you choose 'Allowed IP Addresses', the ending IP Address of the automation agent machine pool like 196.21.30.65.
- Delete Rule After Task Ends - If selected, then after the task ends, the IP Addresses specified here are deleted from the 'Allowed IP Addresses' list of the Azure SQL Server's Firewall.