This repository has been archived by the owner on Oct 31, 2024. It is now read-only.
-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 4
Commit
This commit does not belong to any branch on this repository, and may belong to a fork outside of the repository.
Updating documentation and adding support for containerd and crio
- Loading branch information
Showing
6 changed files
with
122 additions
and
215 deletions.
There are no files selected for viewing
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| Original file line number | Diff line number | Diff line change |
|---|---|---|
| @@ -0,0 +1,17 @@ | ||
| FROM ubuntu:20.04 | ||
| ENV DEBIAN_FRONTEND=noninteractive | ||
| WORKDIR / | ||
| RUN apt update ; apt-get install apt-transport-https ca-certificates -y ; update-ca-certificates | ||
| RUN apt-get update && \ | ||
| apt-get upgrade -y && \ | ||
| apt-get install --no-install-recommends -y \ | ||
| zip bison build-essential cmake flex git libedit-dev \ | ||
| libllvm12 llvm-12-dev libclang-12-dev python zlib1g-dev libelf-dev libfl-dev python3-setuptools \ | ||
| liblzma-dev arping netperf iperf linux-tools-generic python3-pip && rm -rf /var/lib/apt/lists/* | ||
| RUN rm /usr/bin/perf | ||
| RUN ln -s /usr/lib/linux-tools/*/perf /usr/bin/perf | ||
| RUN git clone https://github.com/iovisor/bcc.git | ||
| RUN mkdir bcc/build; cd bcc/build ; cmake .. ; make ; make install ; cmake -DPYTHON_CMD=python3 .. ; cd src/python/ ; make ; make install ; cd ../.. | ||
| COPY procmon/ . | ||
| COPY requirements.txt . | ||
| RUN pip install -r requirements.txt |
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| Original file line number | Diff line number | Diff line change |
|---|---|---|
| @@ -1,193 +1,80 @@ | ||
| # Workload Interference Detector | ||
|
|
||
| ## Introduction | ||
|
|
||
| Workload Interference Detector is a tool that leverages the Intel Performance Monitoring Units (PMU) to monitor and detect interference between workloads. Traditional PMU drivers that work in counting mode (i.e., emon, perf-stat) provide system level analysis with very little overhead. However, these drivers lack the ability to breakdown the system level metrics (CPI, cache misses, etc) at a process or application level. With eBPF, it is possible to associate the process context with the HW counter data, providing the ability to breakdown PMU metrics by process at a system level. Additionally, since eBPF runs filters in the kernel and uses perf in counting mode, this incurs very little overhead, allowing for real-time performance tracking. | ||
|
|
||
| ## Contents: | ||
|
|
||
| *_procmon_*: Dumps performance metrics per process in counting mode through eBPF functionality using perf interface. | ||
|
|
||
| *_dockermon_*: Shows the same performance metrics but on the container level (i.e. a single record for each container-core, or a single record for each container). It also has the option to export data to cloudwatch. Please check cloudwatch pricing: https://aws.amazon.com/cloudwatch/pricing/ | ||
|
|
||
| *_NN_detect_*: Monitors the performance for a given workload (process or container) and compares it to a reference-signature. If any of the performance metrics deviates by an amount > a user-specified threshold (10% by default), the workload is flagged as a noisy neighbor victim and a list of workloads that likely caused the performance degradation is shown. | ||
|
|
||
| ## Installation | ||
|
|
||
| 1. Install all distribution-specific requirements for [compiling BCC from source.](https://github.com/iovisor/bcc/blob/master/INSTALL.md#source) | ||
|
|
||
| 2. Test it using a quick example: | ||
| <div align="center"> | ||
|
|
||
| <div id="user-content-toc"> | ||
| <ul> | ||
| <summary><h1 style="display: inline-block;">Workload Interference Detector</h1></summary> | ||
| </ul> | ||
| </div> | ||
|
|
||
| [](https://github.com/intel/interferencedetector/blob/master/LICENSE) | ||
|
|
||
| [Requirements](#requirements) | [Usage](#usage) | [Demo](#demo) | [Notes](#notes) | ||
| </div> | ||
|
|
||
| Workload Interference Detector uses a combination of hardware events and ebpf to capture a wholistic signature of a workload's performance at very low overhead. | ||
| 1. instruction efficiency | ||
| - cycles | ||
| - instructions | ||
| - cycles per instruction | ||
| 2. disk IO | ||
| - local bandwidth (MB/s) | ||
| - remote bandwidth (MB/s) | ||
| - disk reads (MB/s) | ||
| - disk writes (MB/s) | ||
| 3. network IO | ||
| - network transmitted (MB/s) | ||
| - network received (MB/s) | ||
| 4. cache | ||
| - L1 instrutions misses per instruction | ||
| - L1 data hit ratio | ||
| - L1 data miss ratio | ||
| - L2 miss ratio | ||
| - L3 miss ratio | ||
| 5. scheduling | ||
| - scheduled count | ||
| - average queue length | ||
| - average queue latency (ms) | ||
|
|
||
| ## Requirements | ||
| 1. Linux Perf | ||
| 2. [BCC compiled from source.](https://github.com/iovisor/bcc/blob/master/INSTALL.md#source) | ||
| 3. `pip install -r requirements.txt` | ||
| 4. Access to PMU | ||
| - Bare-metal | ||
| - VM with vPMU exposed (uncore metrics like disk IO will be zero) | ||
| 5. Intel Xeon chip | ||
| - Skylake | ||
| - Cascade Lake | ||
| - Ice Lake | ||
| - Sapphire Rapids | ||
| 6. Python | ||
|
|
||
| ## Usage | ||
| 1. Monitor processes | ||
| ``` | ||
| cd procmon | ||
| sudo python3 procmon.py | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| 3. For monitoring docker containers, run the following command: | ||
| ``` | ||
| cd procmon | ||
| sudo python3 dockermon.py | ||
| 2. Monitor containers (can also export to cloudwatch) | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| 4. For monitoring the performance of a process, run the following command: | ||
| sudo python3 cmon.py | ||
| ``` | ||
| cd procmon | ||
| sudo python3 NN_detect.py --pid <process-pid> --ref_signature <processes's reference signature> --distance_ratio 0.15 | ||
| 3. Detect process or container interference. A list of workloads that likely caused the performance degradation is shown. | ||
| ``` | ||
| # process | ||
| sudo python3 NN_detect.py --pid <process-pid> --ref_signature <processes's reference signature> --distance_ratio 0.15 | ||
| 5. For monitoring the performance of a container, run the following command: | ||
| ``` | ||
| cd procmon | ||
| # container | ||
| sudo python3 NN_detect.py --cid <container id> --ref_signature <container's reference signature> --distance_ratio 0.15 | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| ## Demo | ||
|
|
||
| ## Usage and Example Output | ||
|
|
||
| ### Procmon | ||
| ``` | ||
| usage: procmon.py [-h] [-f SAMPLE_FREQ] [-p PID] [-c CPU] [-d DURATION] [-i INTERVAL] [--aggregate_cpus] [--aggregate_cgroup] [--acc] [-v] | ||
| eBPF based Core metrics by PID | ||
| options: | ||
| -h, --help show this help message and exit | ||
| -f SAMPLE_FREQ, --sample_freq SAMPLE_FREQ | ||
| Sample one in this many number of events | ||
| -p PID, --pid PID PID | ||
| -c CPU, --cpu CPU cpu number | ||
| -d DURATION, --duration DURATION | ||
| duration | ||
| -i INTERVAL, --interval INTERVAL | ||
| interval in seconds | ||
| --aggregate_cpus Aggregate all the counters across CPUs, the cpu field will be set to zero for all PIDs/Containers | ||
| --aggregate_cgroup Aggregate all the counters on cgroup level, every contaiiner will then have a single row | ||
| --acc collect events in accumulate mode. If not set, all counter cleared in each round | ||
| -v, --verbose show raw counters in every interval | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| ### Example output | ||
| ``` | ||
| Timestamp,PID,process,cgroupID,core,cycles,insts,cpi,l1i_mpi,l1d_hit_ratio,l1d_miss_ratio,l2_miss_ratio,l3_miss_ratio,local_bw,remote_bw,disk_reads,disk_writes,network_tx,network_rx,avg_q_len | ||
| 1676052270.426364,4203,mlc,6759,10,3034000000,5222000000,0.58,0.00,0.00,1.00,0.00,0.00,0.00,0.00,0.00,0.00,0.00,0.00,0.00 | ||
| 1676052270.426398,4257,python3,5534,60,169000000,57000000,2.96,0.06,0.00,1.00,0.00,0.00,0.00,0.00,0.00,0.00,0.00,0.00,0.00 | ||
| 1676052270.426417,4203,mlc,6759,8,3094000000,5225000000,0.59,0.00,0.00,1.00,0.00,0.00,0.00,0.00,0.00,0.00,0.00,0.00,2.00 | ||
| 1676052270.42643,4203,mlc,6759,7,3262000000,5225000000,0.62,0.00,0.00,1.00,0.00,0.00,0.00,0.00,0.00,0.00,0.00,0.00,2.00 | ||
| 1676052270.426441,4203,mlc,6759,9,2936000000,5220000000,0.56,0.00,0.00,1.00,0.00,0.00,0.00,0.00,0.00,0.00,0.00,0.00,2.00 | ||
| --------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | ||
| Timestamp,PID,process,cgroupID,core,cycles,insts,cpi,l1i_mpi,l1d_hit_ratio,l1d_miss_ratio,l2_miss_ratio,l3_miss_ratio,local_bw,remote_bw,disk_reads,disk_writes,network_tx,network_rx,avg_q_len | ||
| 1676052271.429533,4203,mlc,6759,10,3094000000,4808000000,0.64,0.00,0.00,1.00,0.19,0.33,4134.40,0.00,0.00,0.00,0.00,0.00,2.00 | ||
| 1676052271.429563,4257,python3,5534,60,9000000,8000000,1.12,0.00,0.00,0.00,0.00,0.00,0.00,0.00,0.00,0.00,0.00,0.00,0.00 | ||
| 1676052271.429583,2756,sshd,5534,52,1000000,1000000,1.00,0.00,0.00,0.00,0.00,0.00,0.00,0.00,0.00,0.00,1280.00,0.00,0.00 | ||
| 1676052271.429605,4203,mlc,6759,8,3094000000,4663000000,0.66,0.00,0.00,1.00,0.30,0.42,6323.20,0.00,0.00,0.00,0.00,0.00,2.00 | ||
| 1676052271.429619,4203,mlc,6759,7,3095000000,4653000000,0.67,0.00,0.00,1.00,0.30,0.42,6080.00,0.00,0.00,0.00,0.00,0.00,2.00 | ||
| 1676052271.429632,4203,mlc,6759,9,3095000000,4673000000,0.66,0.00,0.00,1.00,0.30,0.42,6323.20,0.00,0.00,0.00,0.00,0.00,2.00 | ||
| ``` | ||
| ### Dockermon | ||
| ``` | ||
| usage: dockermon.py [-h] [-v] [--collect_signatures] [-d DURATION] [--aggregate_on_core | --aggregate_on_containerID] | ||
| [--export_to_cloudwatch] [--cloudwatch_sampling_duration_in_sec CLOUDWATCH_SAMPLING_DURATION_IN_SEC] | ||
| Display procmon data on docker container level | ||
| options: | ||
| -h, --help show this help message and exit | ||
| -v, --verbose show raw verbose logging info. | ||
| --collect_signatures collect signatures of running containers and dump to: signatures.json | ||
| -d DURATION, --duration DURATION | ||
| Collection duration in seconds. Default is 0 (indefinitely) | ||
| --aggregate_on_core Show a single aggregated record for each containerID + core. This option is mutually exclusive with '-- | ||
| aggregate_on_containerID' | ||
| --aggregate_on_containerID | ||
| Show a single aggregated record for each containerID. This option is mutually exclusive with '-- | ||
| aggregate_on_core' | ||
| --export_to_cloudwatch | ||
| Export collected data to cloudwatch. Expects the following AWS parameters to be configured in `aws cli`: | ||
| aws_access_key_id, aws_secret_access_key, aws_region. | ||
| --cloudwatch_sampling_duration_in_sec CLOUDWATCH_SAMPLING_DURATION_IN_SEC | ||
| Duration between samples of data points sent to cloudwatch. Default is 10 (one sample every 10 seconds). The | ||
| minimum duration is 1 second. Note: this argument is only effective when --export_to_cloudwatch is set. | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| ### Example output | ||
| ``` | ||
| --------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | ||
| Timestamp,containerID,PID,process,cgroupID,core,cycles,insts,cpi,l1i_mpi,l1d_hit_ratio,l1d_miss_ratio,l2_miss_ratio,l3_miss_ratio,local_bw,remote_bw,disk_reads,disk_writes,network_tx,network_rx,avg_q_len | ||
| 1676052363.966291,f775ddd0c164,4700,mlc,6824,8,3241000000,1446000000,2.24,0.00,0.00,1.00,1.00,0.41,10771.20,0.00,0.00,0.00,0.00,0.00,2.00 | ||
| 1676052363.966381,f775ddd0c164,4700,mlc,6824,10,3240000000,1425000000,2.27,0.00,0.00,1.00,1.00,0.44,11249.92,0.00,0.00,0.00,0.00,0.00,0.00 | ||
| 1676052363.966419,f775ddd0c164,4700,mlc,6824,9,3240000000,1439000000,2.25,0.00,0.00,1.00,1.00,0.41,11249.92,0.00,0.00,0.00,0.00,0.00,2.00 | ||
| 1676052363.966453,f775ddd0c164,4700,mlc,6824,7,3238000000,1396000000,2.32,0.00,0.00,1.00,1.00,0.47,11010.56,0.00,0.00,0.00,0.00,0.00,2.00 | ||
| --------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | ||
| Timestamp,containerID,PID,process,cgroupID,core,cycles,insts,cpi,l1i_mpi,l1d_hit_ratio,l1d_miss_ratio,l2_miss_ratio,l3_miss_ratio,local_bw,remote_bw,disk_reads,disk_writes,network_tx,network_rx,avg_q_len | ||
| 1676052364.968383,f775ddd0c164,4700,mlc,6824,8,3093000000,1399000000,2.21,0.00,0.00,1.00,1.00,0.45,10622.72,0.00,0.00,0.00,0.00,0.00,1.00 | ||
| 1676052364.968449,f775ddd0c164,4700,mlc,6824,10,3093000000,1371000000,2.26,0.00,0.00,1.00,1.00,0.43,11610.88,0.00,0.00,0.00,0.00,0.00,1.00 | ||
| 1676052364.968496,f775ddd0c164,4700,mlc,6824,9,3093000000,1375000000,2.25,0.00,0.00,1.00,1.00,0.45,11610.88,0.00,0.00,0.00,0.00,0.00,1.00 | ||
| 1676052364.968533,f775ddd0c164,4700,mlc,6824,7,3093000000,1341000000,2.31,0.00,0.00,1.00,1.00,0.46,11363.84,0.00,0.00,0.00,0.00,0.00,1.00 | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| ### NN\_detect | ||
| ``` | ||
| usage: NN_detect.py [-h] [-p PID] [-c CID] [--outfile OUTFILE] [-s SYSTEM_WIDE_SIGNATURES_PATH | -r REF_SIGNATURE] [-d DISTANCE_RATIO] | ||
| Detect Noisy Neighbors for a given PID (process-level) or container ID (container-level). | ||
| options: | ||
| -h, --help show this help message and exit | ||
| -p PID, --pid PID PID (process-level) | ||
| -c CID, --cid CID Container ID (container-level) | ||
| --outfile OUTFILE Output file to save live-updated performance data | ||
| -s SYSTEM_WIDE_SIGNATURES_PATH, --system_wide_signatures_path SYSTEM_WIDE_SIGNATURES_PATH | ||
| path to signatures_*.csv CSV file with referernce signatures per container ID, as generated by dockermon. | ||
| -r REF_SIGNATURE, --ref_signature REF_SIGNATURE | ||
| The tool will use this signature as a baseline. Use the output of either procmon or dockermon to collect the signature. The first element in the signature is `cycles`. All live updated signatures will be compared | ||
| to this reference signature. Use a standalone signature (when the process is the only process executing in the system), or any signature collected over a performance-acceptable duration. | ||
| -d DISTANCE_RATIO, --distance_ratio DISTANCE_RATIO | ||
| Acceptable ratio of change in signature from reference, default is 0.1. If the distance is higher than this value, the monitored workload will flagged as a noisy neighbor victim. | ||
| ``` | ||
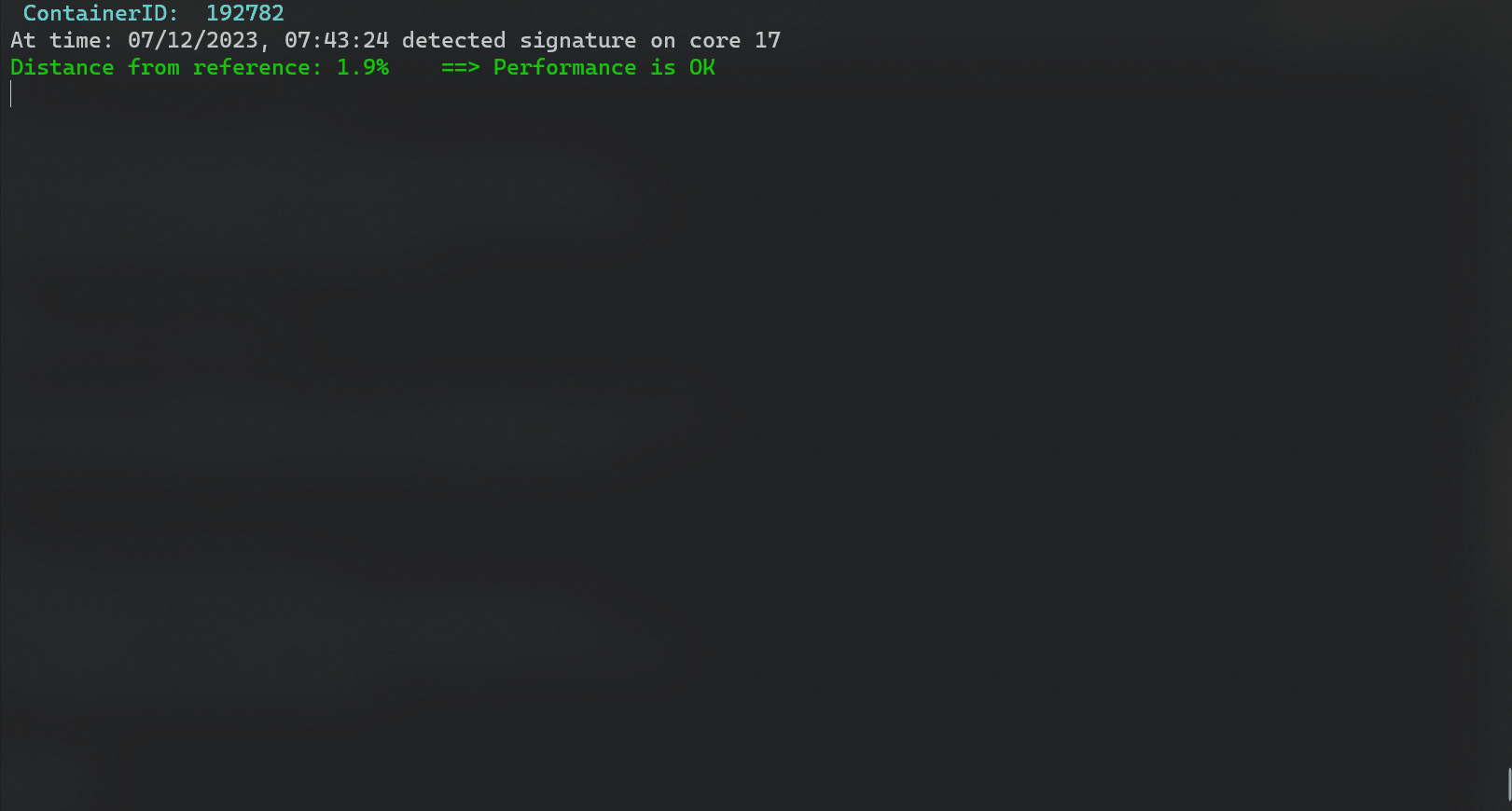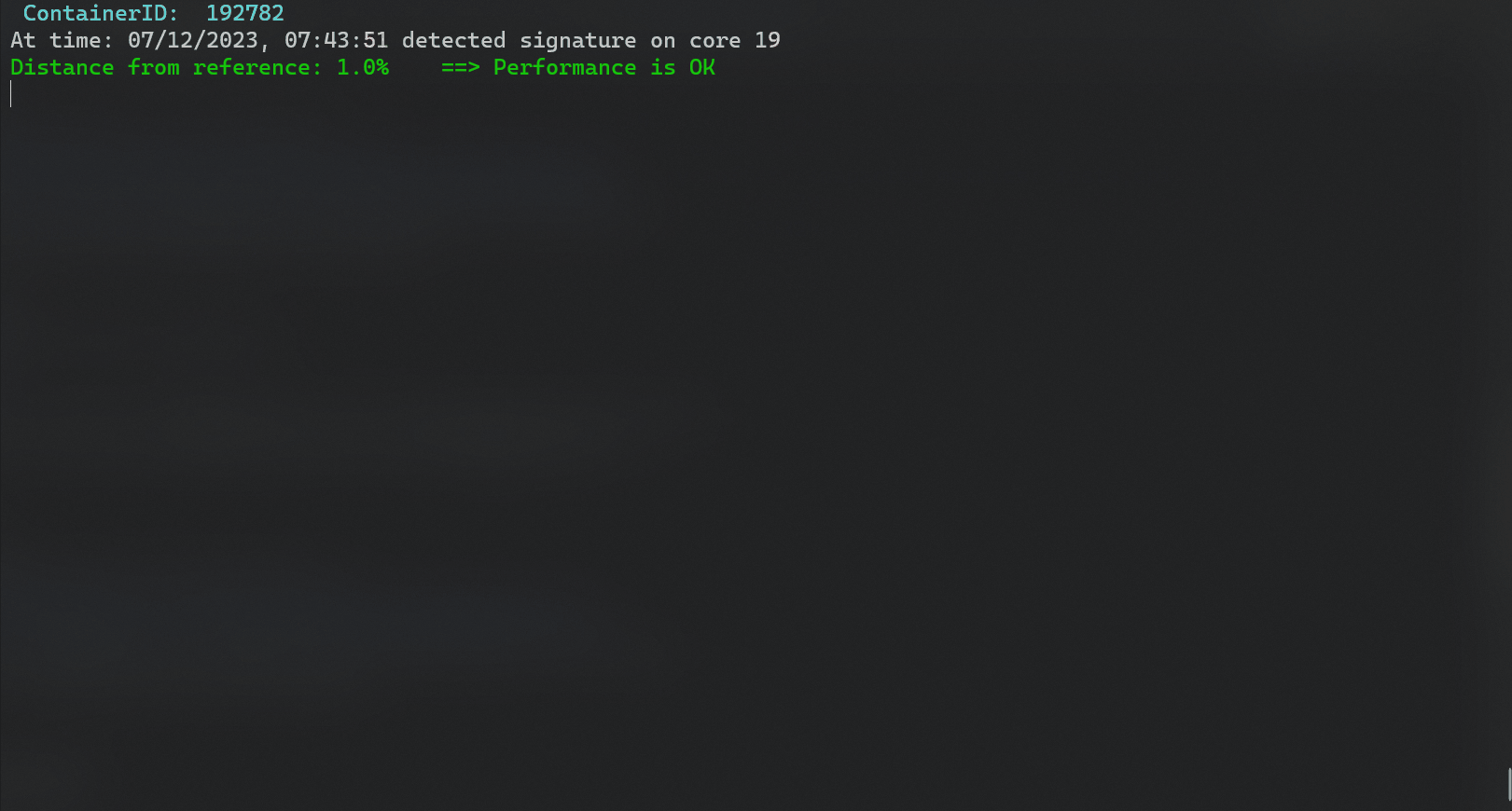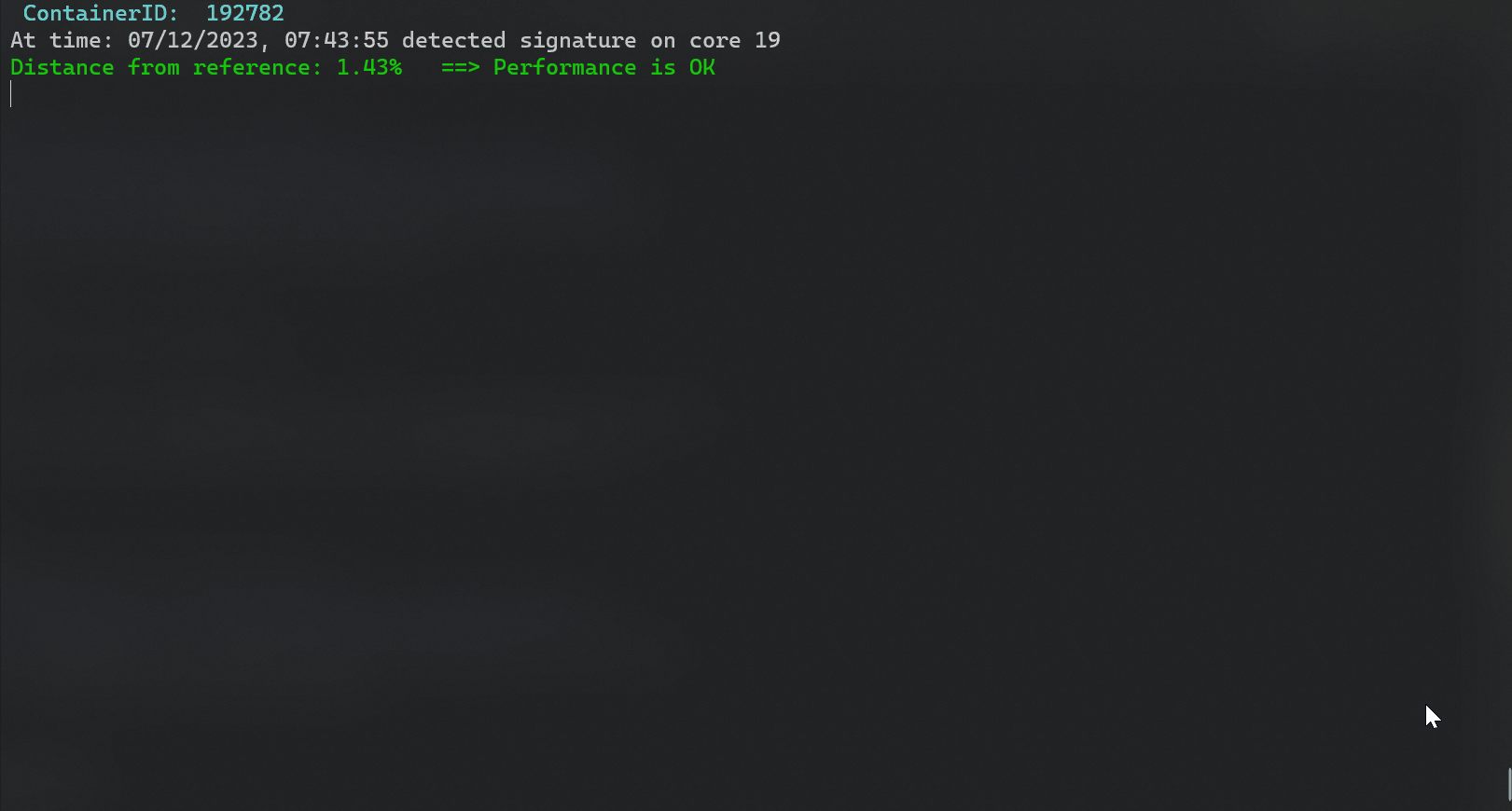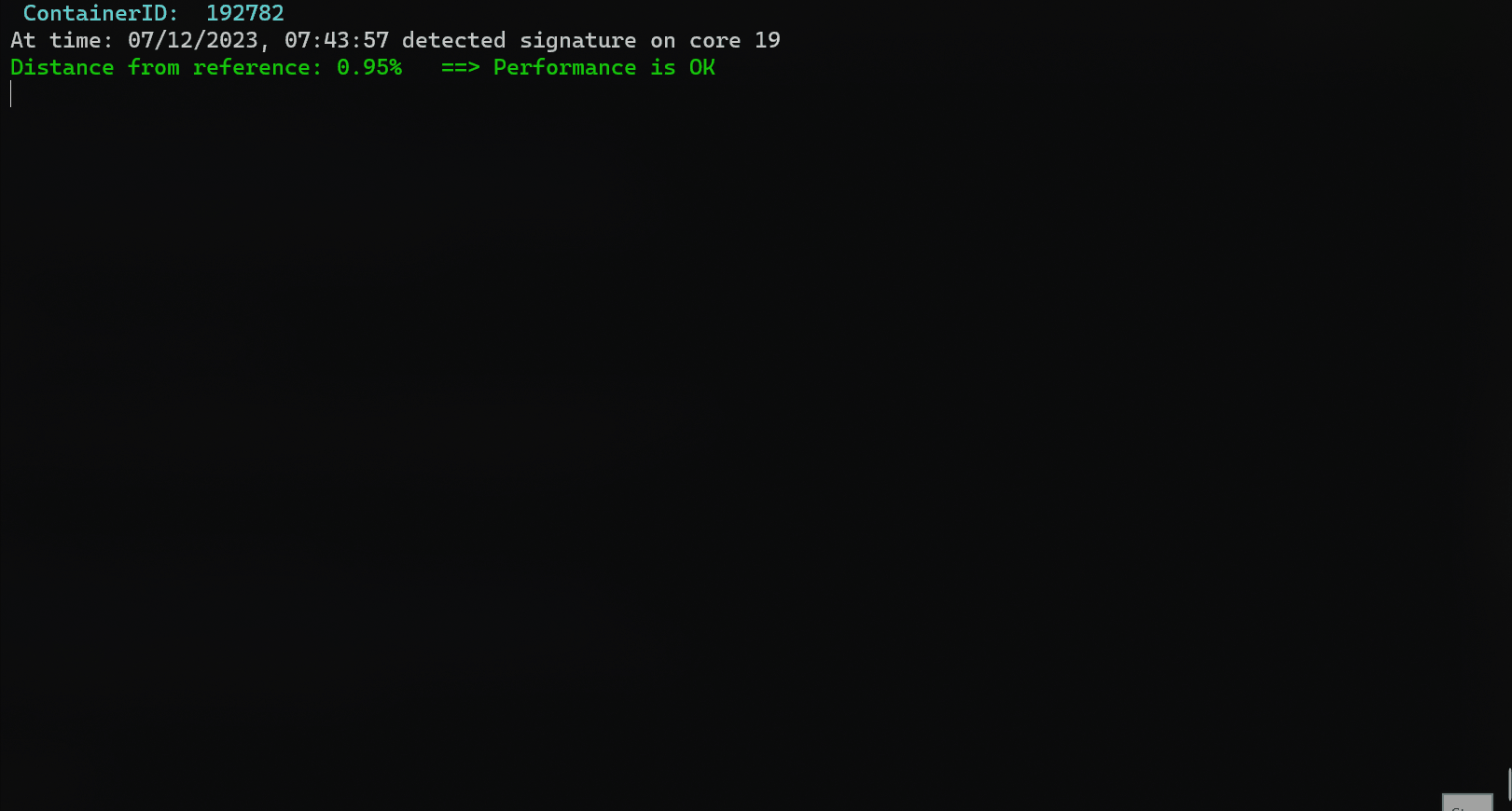
| ### Example output | ||
| ``` | ||
| ----------------------------------------------------------------- | ||
| Header: Timestamp,containerID,core,cycles,insts,cpi,l1i_mpi,l1d_hit_ratio,l1d_miss_ratio,l2_miss_ratio,l3_miss_ratio,local_bw,remote_bw,disk_reads,disk_writes,network_tx,network_rx,avg_q_len | ||
| Reference Signature: [3097000000.0, 1305000000.0, 2.37, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 1.0, 0.41, 10925.44, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0] | ||
| Detected Signature on core 7 : [3093000000.0, 1361000000.0, 2.27, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 1.0, 0.47, 11791.36, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 2.0] | ||
| Distance from reference: 6.0% ==> Performance is OK | ||
| Detected Signature on core 8 : [3092000000.0, 1408000000.0, 2.2, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 1.0, 0.43, 11289.6, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 2.0] | ||
| Distance from reference: 7.89% ==> Performance is OK | ||
| Detected Signature on core 10 : [3091000000.0, 1391000000.0, 2.22, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 1.0, 0.44, 11791.36, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0] | ||
| Distance from reference: 6.59% ==> Performance is OK | ||
| Detected Signature on core 9 : [3092000000.0, 1403000000.0, 2.2, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 1.0, 0.42, 12042.24, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 2.0] | ||
| Distance from reference: 7.51% ==> Performance is OK | ||
| ``` | ||
| ======= | ||
| ## Units: | ||
| | Metric | Unit | | ||
| | -----------------| -------------| | ||
| | cycles | RAW | | ||
| | insts | RAW | | ||
| | cpi | RAW | | ||
| | l1i_mpi | Percentage | | ||
| | l1d_hit_ratio | Percentage | | ||
| | l1d_miss_ratio | Percentage | | ||
| | l2_miss_ratio | Percentage | | ||
| | l3_miss_ratio | Percentage | | ||
| | local_bw | MB/sec | | ||
| | remote_bw | MB/sec | | ||
| | disk_reads | MB/sec | | ||
| | disk_writes | MB/sec | | ||
| | network_tx | MB/sec | | ||
| | network_rx | MB/sec | | ||
| | scheduled_count | RAW | | ||
| | avg_q_len | RAW | | ||
| | avg_q_latency | milliseconds | | ||
|  | ||
|
|
||
| ## Notes: | ||
| ** Interference Detector was developed using the following as references: | ||
| 1. github.com/iovisor/bcc/tools/llcstat.py (Apache 2.0) | ||
| 2. github.com/iovisor/bcc/tools/tcptop.py (Apache 2.0) | ||
| 3. github.com/iovisor/bcc/blob/master/examples/tracing/disksnoop.py (Apache 2.0) | ||
| 4. github.com/iovisor/bcc/blob/master/tools/runqlen.py (Apache 2.0) | ||
| 5. github.com/iovisor/bcc/blob/master/tools/runqlat.py (Apache 2.0) | ||
|
|
||
| ** Interference Detector currently supports "Skylake", "Cascade Lake", "Ice Lake", and "Sapphire Rapids" platforms only. It also supports AWS metal instances where PMUs are available (e.g., r5.metal, m5.metal, m6i.metal, etc.). For AWS Single socket instances (r.g., c5.12xlarge, c6i.16xlarge), offcore counters are not available. Hence offcore metrics (e.g., local_bw, remote_bw) will be zeroed out. | ||
|
|
||
| 5. github.com/iovisor/bcc/blob/master/tools/runqlat.py (Apache 2.0) |
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
Oops, something went wrong.