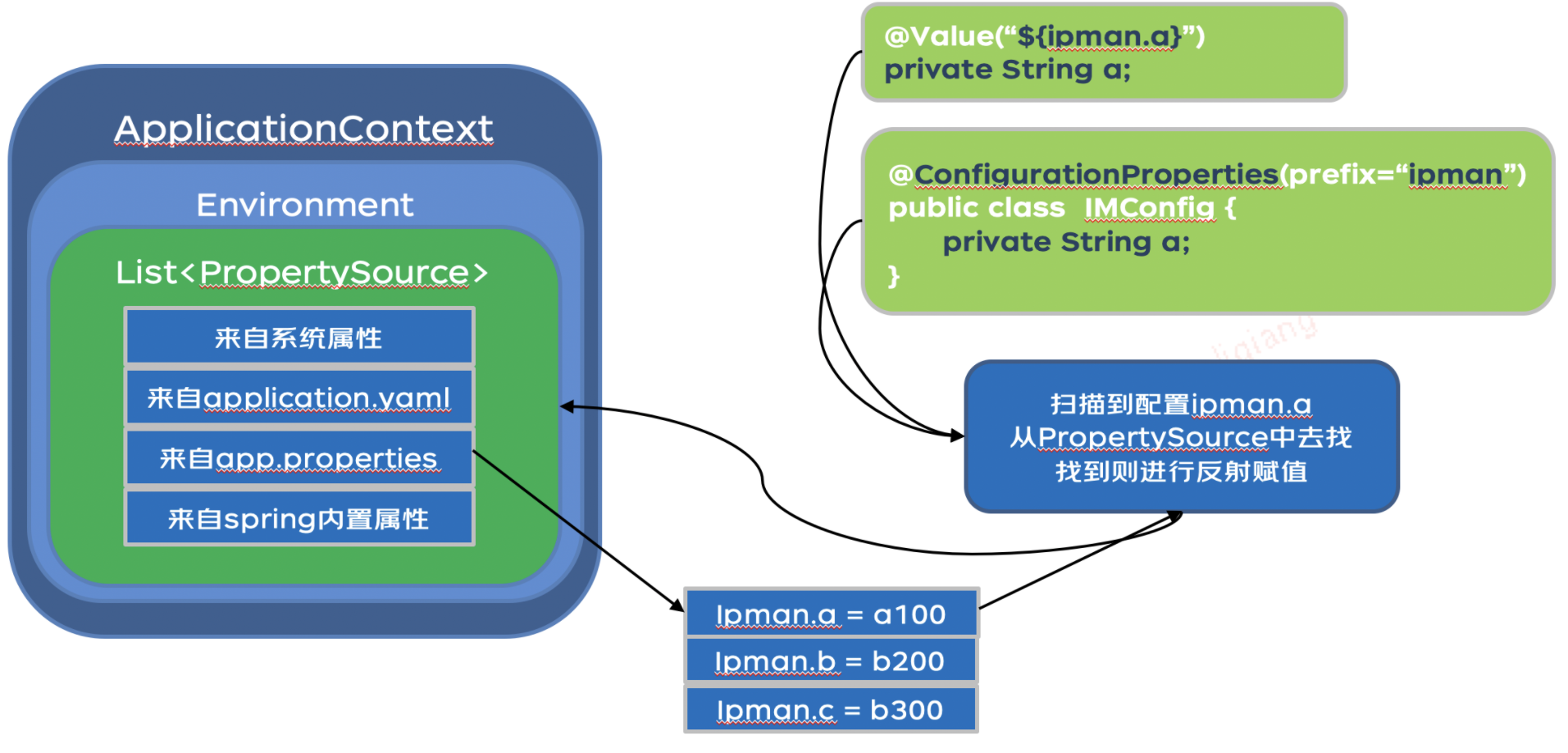
以下只是一个非常简易的配置中心版本,通过下述能大致理解配置中心核心原理,仅是用来学习和探讨。
在分布式系统中,配置管理是一个关键问题。一个高效的配置中心可以帮助我们集中管理配置,动态更新配置,并且与应用程序无缝集成。
本文将基于 Apollo 和 Nacos 的设计思想,从零开始设计并实现一个 Java简易版配置中心,包括 Server 和 Client 两部分。
其中,Server 负责保存所有持久化的配置数据,Client 通过 Server 提供的 API 获取所需的配置集合,并在 Server 数据变化时获取新的配置数据。
此外,还将与 Spring Boot 的集成,处理通过@Value注解和@ConfigurationProperties注解绑定的属性。
配置中心由 Server 和 Client 两部分组成:
- Server:负责存储和管理所有的配置数据,提供 API 供 Client 获取配置,并在配置变化时通知 Client。
- Client:通过调用 Server 提供的 API 获取配置数据,并在配置变化时更新 Spring本地配置。
- 配置存储:Server 端持久化配置数据,提供接口供管理员版本控制、添加、修改和删除配置。
- 配置获取:Client 端在启动时扫描所有配置,从 Server 获取所需的配置数据后初始化 Spring本地配置。
- 配置更新:Client 端长轮询感知 Server 端的配置数据变化,变化时更新 Spring本地配置。
- Server 模块:配置存储、API 服务、配置变更通知。
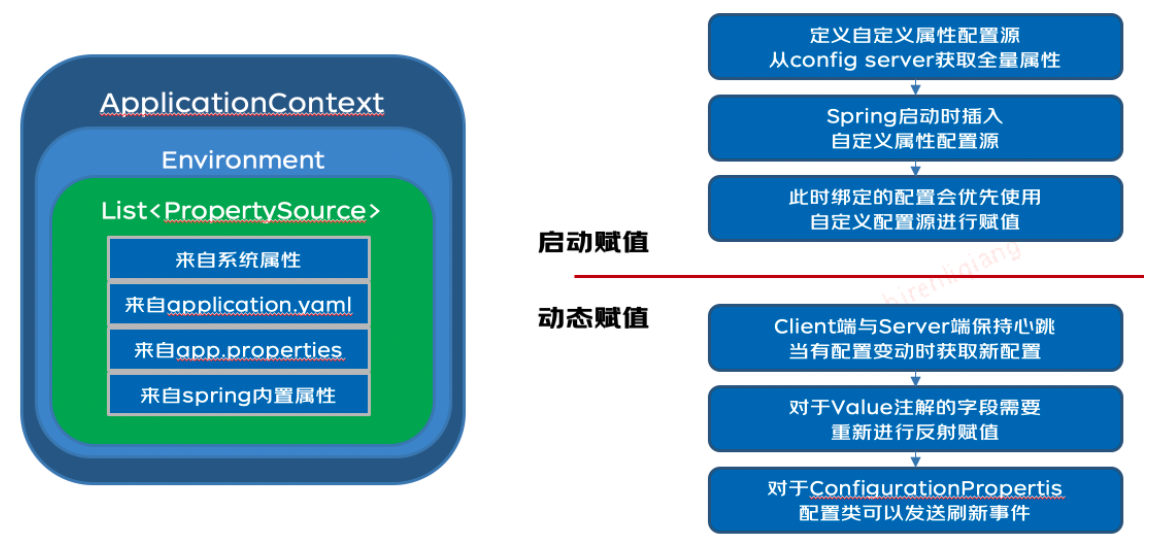
- Client 模块:配置获取、配置变更监听、与 Spring Boot 集成。配置变更分为启动赋值、动态赋值两个部分
- Spring Boot:用于构建 Server 和 Client 应用,通过SpringMVC DeferredResult 实现配置变更通知 Client端。
- Spring Cloud Context:当 Client端感知到配置变更时,像 Spring程序发布 EnvironmentChangeEvent 事件,通过监听这个事件实现 Spring本地配置动态更新。
- MySQL:用于持久化存储配置数据,为了方便演示(本文方便演示,用H2)。
Client 端
-
spring-context :
Spring Framework的一个核心模块,主要用于管理应用程序上下文,提供依赖注入、事件机制、资源管理等基础功能。 -
spring-cloud-context:是
spring-context在分布式场景的一个扩展,支持分布式配置管理、上下文刷新、环境属性和消息总线等高级功能。 -
需要注意的是,按照 Spring 的规范,在容器启动后,无法通过修改配置文件来动态刷新标记了
@ConfigurationProperties注解的类的属性。不过随着spring-cloud的出现,可以通过spring-cloud-context提供的EnvironmentChangeEvent实现配置的动态刷新,从而使应用程序能够在运行时动态修改配置类。 -
okhttp:用于 client端 通过 http 访问 server端的网络工具类。
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>6.1.6</version>
</dependency>
<!-- 用于配置自动更新 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-context</artifactId>
<version>4.1.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.squareup.okhttp3</groupId>
<artifactId>okhttp</artifactId>
<version>4.12.0</version>
</dependency>
Server 端
- spring-web:作为配置中心的
Server端,本文会用MVC特性实现长轮询。 - h2 或 mysql: 任意一个即可,用于持久化配置信息,配置中心一般都会用
mysql进行持久化数据(*H2*内存型,方便演示)。 - mybatis: ORM框架,方便与
h2和mysql数据库 进行CRUD操作。
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.h2database</groupId>
<artifactId>h2</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>3.0.3</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>8.0.32</version>
</dependency>
目前基本上都是至少3个维度管理key-value配置,目标是为了满足管理不同应用、不同环境、不同集群、不同空间的配置,进行合理的分层设计,便于规范的权限、流程治理等特性
- 在
application.yaml中添加以下mysql 驱动相关配置(演示用H2内存数据库即可)
spring:
application:
name: config-server
datasource:
driver-class-name: org.h2.Driver
url: jdbc:h2:mem:h2db
username: root
password: 自定义
sql:
init:
schema-locations: classpath:db.sql
mode: always
h2:
console:
enabled: true
path: /h2
settings:
web-allow-others: true
mybatis:
configuration:
log-impl: org.apache.ibatis.logging.stdout.StdOutImpl
- 创建
Configs配置类、ConfigsMapper接口类,基于 MyBatis 提供针对应用 (app)、命名空间 (ns) 和环境 (env) 的 CRUD 方法。
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
public class Configs {
private String app; // 应用
private String env; // 环境
private String ns; // 命名空间
private String pkey; // 配置键
private String pval; // 配置值
}
@Repository
@Mapper
public interface ConfigsMapper {
@Select("select * from configs where app=#{app} and env=#{env} and ns=#{ns}")
List<Configs> list(String app, String env, String ns);
@Select("select * from configs where app=#{app} and env=#{env} and ns=#{ns} and pkey=#{pkey}")
Configs select(String app, String env, String ns, String pkey);
@Insert("insert into configs(app, env, ns, pkey, pval) values(#{app}, #{env}, #{ns}, #{pkey}, #{pval})")
int insert(Configs configs);
@Update("update configs set pval=#{pval} where app=#{app} and env=#{env} and ns=#{ns} and pkey=#{pkey}")
int update(Configs configs);
}
- 在
classpath目录下(即resources文件夹),添加一个名为db.sql的文件,用于创建和初始化配置表configs的数据。
pkey:参数键 , pval:参数值
create table if not exists `configs` (
`app` varchar(64) not null,
`env` varchar(64) not null,
`ns` varchar(64) not null,
`pkey` varchar(64) not null,
`pval` varchar(128) null
);
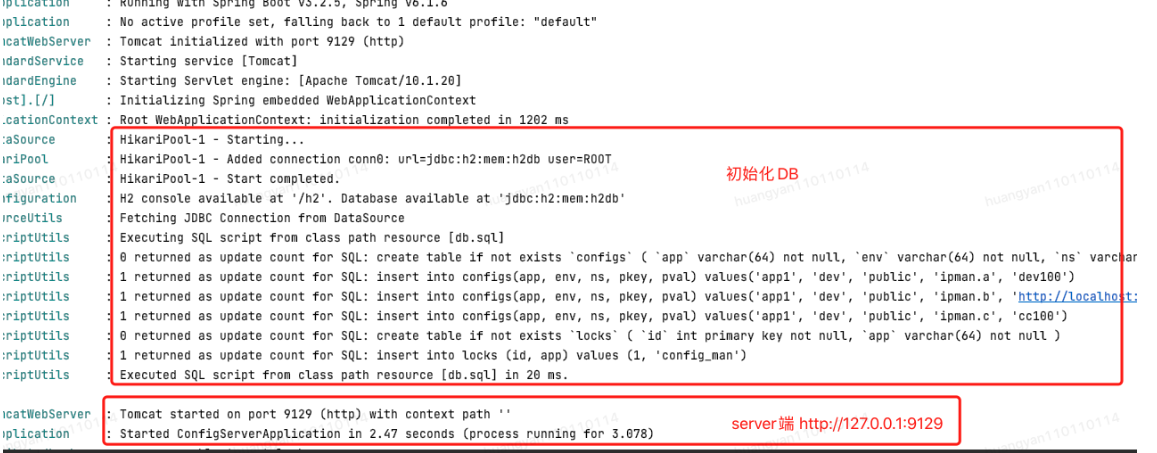
insert into configs(app, env, ns, pkey, pval) values('app1', 'dev', 'public', 'ipman.a', 'dev100');
insert into configs(app, env, ns, pkey, pval) values('app1', 'dev', 'public', 'ipman.b', 'http://localhost:9192');
insert into configs(app, env, ns, pkey, pval) values('app1', 'dev', 'public', 'ipman.c', 'cc100');
以上是数据等准备工作...
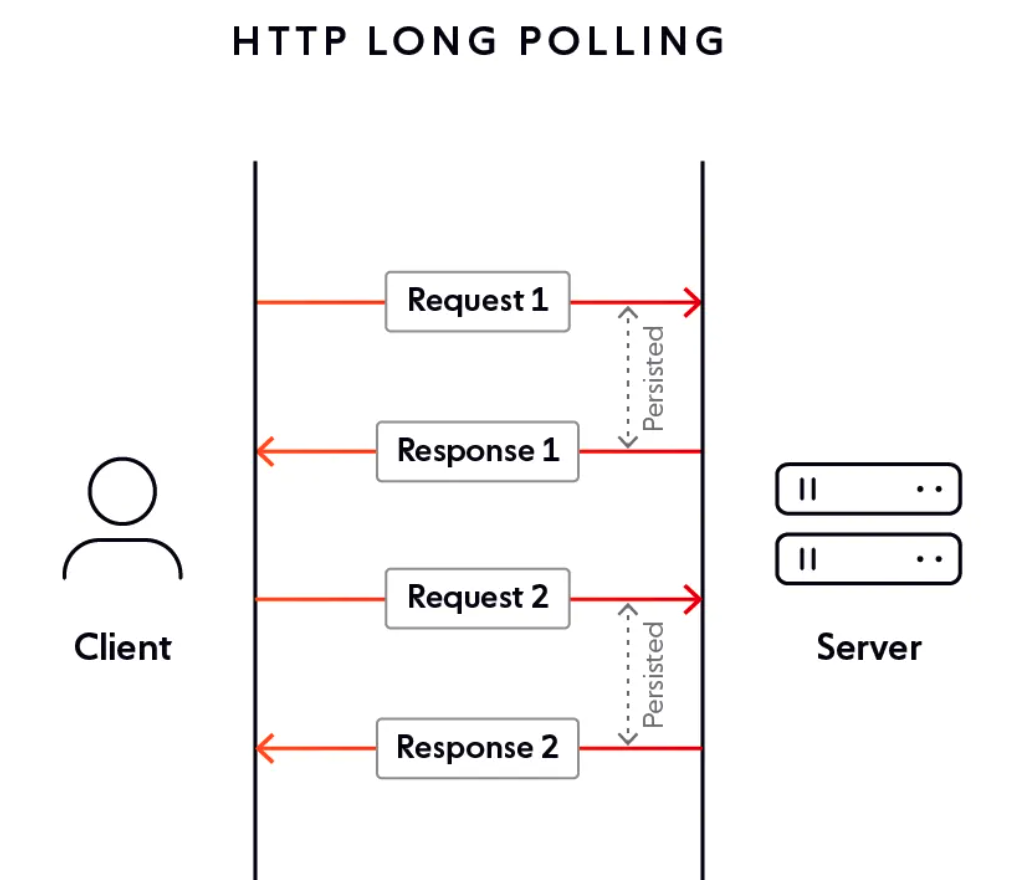
目标是为了客户端和服务端保持了一个长连接,从而能第一时间获得配置更新的推送。参考 Apollo 考虑到会有数万客户端向服务端发起长连,在服务端使用了async servlet (Spring DeferredResult) 来服务Http Long Polling请求。
实现 WebMvcConfigurer 配置,主要是配置异步请求支持,设置任务执行器和超时时间。关于DeferredResult 的代码实现后续会讲。
/**
* WebMvc配置类,用于自定义Spring MVC的配置
*/
@Configuration
public class WebMvcConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {
/**
* 定义并配置一个线程池任务执行器,用于处理异步请求。
*
* @return 配置好的ThreadPoolTaskExecutor实例。
*/
@Bean
public ThreadPoolTaskExecutor mvcTaskExecutor() {
ThreadPoolTaskExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolTaskExecutor();
executor.setCorePoolSize(10); // 核心线程数
executor.setQueueCapacity(100); // 队列容量
executor.setMaxPoolSize(25); // 最大线程数
return executor;
}
/**
* 配置异步请求支持,设置任务执行器和超时时间。
*
* @param configurer 异步支持配置器
*/
@Override
public void configureAsyncSupport(AsyncSupportConfigurer configurer) {
configurer.setTaskExecutor(mvcTaskExecutor());
configurer.setDefaultTimeout(60_000L); // 设置默认超时时间 10s
}
/**
* 全局异常处理器,捕获并处理异步请求超时异常。
*/
@ControllerAdvice
static class GlobalExceptionHandler {
/**
* 处理异步请求超时异常,返回304状态码。
*
* @param e 异常实例
* @param request HTTP请求
*/
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.NOT_MODIFIED) //返回 304 状态码
@ResponseBody
@ExceptionHandler(AsyncRequestTimeoutException.class) //捕获特定异常
public void handleAsyncRequestTimeoutException(AsyncRequestTimeoutException e, HttpServletRequest request) {
System.out.println("handleAsyncRequestTimeoutException");
}
}
}
Map<String, Long> VERSION:用于存储各应用的配置版本号,当配置发生变化时会更新该版本号。
MultiValueMap<String, DeferredResult<Long>> appKeyDeferredResult:当客户端请求服务器获取指定应用的版本号时,该请求会被DeferredResult挂起并保持长连接(这点类似于 Apollo 默认的60秒超时)。如果在这段时间内有客户端关注的配置发生变化,挂起的客户端请求会立即返回。
此外,还包括一些客户端访问服务器的核心接口,例如:
- 查询数据库以获取配置列表
- 更新或插入数据库中的配置
- 获取配置版本号
/**
* 配置服务控制器,提供配置的查询、更新和版本查询功能
*/
@RestController
@Slf4j
public class ConfigController {
@Autowired
ConfigsMapper mapper;
// 用于存储配置的版本信息
Map<String, Long> VERSION = new HashMap<>();
// 用于存储appKey与DeferredResult之间的映射,以支持异步返回配置版本信息
MultiValueMap<String, DeferredResult<Long>> appKeyDeferredResult = new LinkedMultiValueMap<>();
// 生成应用键
static String getAppKey(String app, String env, String ns) {
return app + "-" + env + "-" + ns;
}
/**
* 查询配置列表。
*
* @param app 应用名称
* @param env 环境标识
* @param ns 命名空间
* @return 配置列表
*/
@RequestMapping("/list")
public List<Configs> list(@RequestParam("app") String app,
@RequestParam("env") String env,
@RequestParam("ns") String ns) {
return mapper.list(app, env, ns);
}
/**
* 更新配置。
*
* @param app 应用名称
* @param env 环境标识
* @param ns 命名空间
* @param params 要更新的配置参数映射
* @return 更新后的配置列表
*/
@RequestMapping("/update")
public List<Configs> update(@RequestParam("app") String app,
@RequestParam("env") String env,
@RequestParam("ns") String ns,
@RequestBody Map<String, String> params) {
String appKey = getAppKey(app, env, ns);
log.info("config update. push {} {}", app, params);
log.debug("config update. push in defer debug {} {}", app, params);
// 查询或更新配置, 并更新版本号
params.forEach((k, v) -> insertOrUpdate(new Configs(app, env, ns, k, v)));
VERSION.put(appKey, System.currentTimeMillis());
// 如果有配置更新, 返回获取版本 /version 的请求
List<DeferredResult<Long>> deferredResults = appKeyDeferredResult.get(appKey);
if (deferredResults != null) {
deferredResults.forEach(deferredResult -> {
Long version = VERSION.getOrDefault(appKey, -1L);
deferredResult.setResult(version);
log.debug("config version poll set defer for {} {}", ns, version);
});
}
return mapper.list(app, env, ns);
}
/**
* 插入或更新配置项
* @param configs 查询或更新配置
*/
private void insertOrUpdate(Configs configs) {
Configs conf = mapper.select(configs.getApp(), configs.getEnv(), configs.getNs(), configs.getPkey());
if (conf == null) {
mapper.insert(configs);
} else {
mapper.update(configs);
}
}
/**
* 异步查询配置版本。
*
* @param app 应用名称
* @param env 环境标识
* @param ns 命名空间
* @return DeferredResult,异步返回配置的版本号
*/
@GetMapping("/version")
public DeferredResult<Long> version(@RequestParam("app") String app,
@RequestParam("env") String env,
@RequestParam("ns") String ns) {
String appKey = getAppKey(app, env, ns);
log.info("config version poll {}", appKey);
log.debug("config version poll in defer debug {}", appKey);
// 创建并返回一个异步结果对象,用于后续通知
DeferredResult<Long> deferredResult = new DeferredResult<>();
deferredResult.onCompletion(() -> {
System.out.println("onCompletion");
appKeyDeferredResult.remove(appKey);
});
deferredResult.onTimeout(() -> {
System.out.println("onTimeout");
appKeyDeferredResult.remove(appKey);
});
deferredResult.onError((Throwable t) -> {
System.out.println("onError");
appKeyDeferredResult.remove(appKey);
});
appKeyDeferredResult.add(appKey, deferredResult);
log.debug("return defer for {}", ns);
return deferredResult;
}
}
server端版本号定义9129,用于client端访问
server:
port: 9129
客户端的实现相对复杂得多,需要与服务器保持心跳长连接,以便在配置变更时及时更新本地配置。此外,客户端还需兼容 Spring PropertySource 中任意配置源的变更(如:xx.yaml, xxx.properties)。配置变更的赋值过程主要分为两个部分:容器启动时的赋值、启动后的动态赋值。
需要确保配置中心的配置优先级高于本地默认配置,并且同时支持@Value注解和@ConfigurationProperties注解下的配置变更操作。
整体设计包含几个概念。
集成自定义Spring配置源
- IMPropertySource:将自定义的
IMConfigService配置实现类包装成Spring Framework的键值对配置属性源。这样就支持了在@Value注解和@ConfigurationProperties注解下获取配置的场景了。 - IMConfigService:自定义配置实现类,用于客户端应用获取配置信息,包括获取所有配置、按键获取指定配置、处理配置变化等。
与Server端建立通信
- IMRepository:用于从
Server端获取配置,通过长轮询检测应用配置版本变化,并获取最新配置信息。当检测到配置变化时,通知IMConfigService处理配置变化。 - IMRepositoryChangeListener:定义配置变化时的回调方法,由
IMRepository的配置变更检测触发,IMConfigService负责实现和处理配置变化。 - ConfigMeta:用于配置
Client端访问Server端的接口地址、应用、环境和命名空间等信息。
目标:无缝衔接Spring设置和获取 配置的方式,利用 spring-cloud-context 发布spring 配置变更事件,实现@ConfigurationProperties 注解下的配置动态更新(@Value 注解下,动态修改配置的方式后面会讲)
IMConfigService:配置服务接口,用于管理和提供配置信息。实现IMRepositoryChangeListener接口,以监听和处理配置变更。
/**
* 配置服务接口,用于管理和提供配置信息。
* 实现了IMRepositoryChangeListener接口,用于监听配置的变更。
*/
public interface IMConfigService extends IMRepositoryChangeListener {
/**
* 获取默认配置服务实例。
*
* @param applicationContext 应用上下文,用于获取应用相关资源。
* @param meta 配置元数据,描述配置的来源和其它必要信息。
* @return 返回配置服务实例。
*/
static IMConfigService getDefault(ApplicationContext applicationContext, ConfigMeta meta) {
// 获取默认配置仓库实例, 从仓库中(远程server服务)上加载配置
IMRepository repository = IMRepository.getDefault(meta);
// 从配置中心server,获取配置
Map<String, String> config = repository.getConfig();
// 创建配置服务实例
IMConfigService configService = new IMConfigServiceImpl(applicationContext, config);
// 注册配置变更监听器
repository.addListener(configService);
return configService;
}
/**
* 获取所有配置属性的名称。
*
* @return 返回配置属性名称数组。
*/
String[] getPropertyNames();
/**
* 根据属性名称获取属性值
*
* @param name 属性名称。
* @return 返回属性值,如果不存在,则返回null。
*/
String getProperty(String name);
}
IMPropertySource:继承 EnumerablePropertySource,将 IMConfigServiceImpl定义到Spring 配置的数据源中。
/**
* 该类是EnumerablePropertySource的子类,用于提供配置属性。
* 它将IMConfigService作为属性源,
* - 可以通过getPropertyNames()获取所有属性名,
* - 通过getProperty(String name)获取指定属性的值。
*/
public class IMPropertySource extends EnumerablePropertySource<IMConfigService> {
/**
* 构造函数,初始化属性源。
* 通过SpringPropertySource添加配置中心数据源, 这样Spring就能拿到我们写入的配置了
*
* @param name 属性源的名称。
* @param source 提供配置属性的服务实例。
*/
public IMPropertySource(String name, IMConfigService source) {
super(name, source);
}
@Override
@SuppressWarnings("NullableProblems")
public String[] getPropertyNames() {
return source.getPropertyNames();
}
@Override
public Object getProperty(@Nullable String name) {
return source.getProperty(name);
}
}
IMConfigServiceImpl:客户端本地配置管理
IMConfigServiceImpl使用Map<String, String> config存储客户端本地配置,提供以下核心功能:
- 获取所有配置属性名称
- 根据属性名称获取对应的配置值
- 处理配置变化
启动阶段:
- 配置初始化:
config配置通过IMRepository#getConfig方法从服务器端获取。 - 配置注入:
IMConfigServiceImpl被添加到 Spring 的PropertySource中,使得 Spring 应用可以使用@Value注解和@ConfigurationProperties注解来获取配置。获取时会调用IMConfigServiceImpl#getPropertyNames方法。 - 配置变更处理:
onChange方法监听IMRepository#heartbeat方法。当收到配置变更事件时,通过applicationContext.publishEvent(new EnvironmentChangeEvent(keys))发布 Spring 应用配置变更事件。Spring Cloud Context 接收到该事件后,会扫描并重新初始化@ConfigurationProperties的 bean 以更新配置信息。
注意事项:
- 标记
@Value注解的属性无法通过上述方式修改值,只能通过反射的方式进行修改,具体方法将在后续部分详细说明。
/**
* 配置服务实现类,用于管理和提供配置信息
*/
@Slf4j
public class IMConfigServiceImpl implements IMConfigService {
// 配置信息
Map<String, String> config;
// 应用上下文
ApplicationContext applicationContext;
/**
* 构造函数,初始化配置服务。
*
* @param applicationContext 应用上下文,用于发布事件。
* @param config 初始配置信息。
*/
public IMConfigServiceImpl(ApplicationContext applicationContext, Map<String, String> config) {
this.applicationContext = applicationContext;
this.config = config;
}
/**
* 获取所有配置属性的名称。
*
* @return 配置属性名称数组。
*/
@Override
public String[] getPropertyNames() {
if (this.config == null) {
return new String[]{};
}
return this.config.keySet().toArray(new String[0]);
}
/**
* 根据属性名称获取对应的配置值。
*
* @param name 属性名称。
* @return 对应的配置值,如果不存在则返回null。
*/
@Override
public String getProperty(String name) {
return this.config.getOrDefault(name, null);
}
/**
* 配置发生变化时的处理逻辑。
* 更新配置信息,并发布环境变更事件。
*
* @param changeEvent 配置变更事件,包含新的配置信息。
*/
@Override
public void onChange(ChangeEvent changeEvent) {
// 对比新旧值的变化
Set<String> keys = calcChangeKeys(config, changeEvent.config());
if (keys.isEmpty()) {
log.info("[IM_CONFIG] calcChangeKeys return empty, ignore update.");
}
this.config = changeEvent.config();
if (!config.isEmpty()) {
/// 通过 spring-cloud-context 刷新配置
log.info("[IM_CONFIG] fire an EnvironmentChangeEvent with keys:" + config.keySet());
applicationContext.publishEvent(new EnvironmentChangeEvent(keys));
}
}
/**
* 计算配置变化的键集合。
*
* @param oldConfigs 旧配置信息。
* @param newConfigs 新配置信息。
* @return 发生变化的配置键集合。
*/
private Set<String> calcChangeKeys(Map<String, String> oldConfigs, Map<String, String> newConfigs) {
if (oldConfigs.isEmpty()) return newConfigs.keySet();
if (newConfigs.isEmpty()) return oldConfigs.keySet();
// 比较新旧配置,找出变化的键
Set<String> news = newConfigs.keySet().stream()
.filter(key -> !newConfigs.get(key).equals(oldConfigs.get(key)))
.collect(Collectors.toSet());
oldConfigs.keySet().stream()
.filter(key -> !newConfigs.containsKey(key))
.forEach(news::add);
return news;
}
}
目标:向配置中心 server端获取数据,感知配置变化并发布事件通知 IMConfigServiceImpl 再发布Spring配置变更事件
IMRepositoryChangeListener : 提供配置发生变化时的回调 onChange方法。
@FunctionalInterface
public interface IMRepositoryChangeListener {
/**
* 配置发生变化时的回调方法。
*
* @param changeEvent 包含配置元数据和新配置信息的事件对象。
* - meta: 配置的元数据,描述了配置的相关信息。
* - config: 新的配置信息,以键值对的形式存储。
*/
void onChange(ChangeEvent changeEvent);
/**
* ChangeEvent 类是一个记录类(JDK 16及以上版本特性),用于封装配置变化事件的信息。
* 包含配置的元数据和新配置的数据。
*/
record ChangeEvent(ConfigMeta meta, Map<String, String> config) {}
// 如果jdk版本低于16, 不兼容record, 以下是低版本Java的实现
// @Data
// @AllArgsConstructor
// class ChangeEvent {
// private ConfigMeta meta;
// private Map<String, String> config;
// }
}
IMRepository:定义获取当前所有配置、添加配置变更监听器等核心方法。
public interface IMRepository {
/**
* 获取默认配置仓库实例。
* 通过给定的配置元数据初始化配置仓库。
*
* @param meta 配置元数据,描述配置源的相关信息。
* @return 返回默认配置仓库实例。
*/
static IMRepository getDefault(ConfigMeta meta) {
return new IMRepositoryImpl(meta);
}
/**
* 获取当前所有配置。
* 该方法用于一次性获取配置源中的所有配置项。
*
* @return 返回包含所有配置项的Map,配置项的键为配置名,值为配置值。
*/
Map<String, String> getConfig();
/**
* 添加配置变更监听器。
* 通过添加监听器,可以监听配置项的变更事件。
*
* @param listener 配置变更监听器实例。
*/
void addListener(IMRepositoryChangeListener listener);
}
IMRepositoryImpl:实现了IMRepository接口的配置仓库类,用于管理和更新配置数据。最核心的方法是 heartbeat 用于通过Server端获取配置的版本号,用于检测配置版本是否需要更新。
- 注意:以下关于 HttpUtils 的方法代码省略
/**
* 实现了IMRepository接口的配置仓库类,用于管理和更新配置数据。
*/
public class IMRepositoryImpl implements IMRepository {
// 当前配置实例的元数据信息, 列: 应用,环境,命名空间,配置服务信息
ConfigMeta meta;
// 存储配置的版本信息
Map<String, Long> versionMap = new HashMap<>();
// 存储配置数据
Map<String, Map<String, String>> configMap = new HashMap<>();
// 定时任务执行器
// 配置变更监听器列表
List<IMRepositoryChangeListener> listeners = new ArrayList<>();
/**
* 构造函数,初始化配置仓库
*
* @param meta 配置元数据,用于指定配置服务的地址和密钥等信息。
*/
public IMRepositoryImpl(ConfigMeta meta) {
this.meta = meta;
// 异步长轮训心跳检测任务
new Thread(this::heartbeat).start();
}
/**
* 添加配置变更监听器。
*
* @param listener 配置变更监听器实例。
*/
public void addListener(IMRepositoryChangeListener listener) {
listeners.add(listener);
}
/**
* 获取所有配置, 第一次初始化时, 通过Config-Server获取
*
* @return 返回当前配置的数据映射表。
*/
@Override
public Map<String, String> getConfig() {
String key = meta.genKey();
if (configMap.containsKey(key)) {
return configMap.get(key);
}
return findAll();
}
/**
* 获取所有配置, 通过Config-Server获取
*
* @return 返回从配置服务器获取到的配置数据映射表。
*/
private @NotNull Map<String, String> findAll() {
String listPath = meta.listPath();
System.out.println("[IM_CONFIG] list all configs from ipman config server.");
List<Configs> configs = HttpUtils.httpGet(listPath, new TypeReference<List<Configs>>() {
});
Map<String, String> resultMap = new HashMap<>();
configs.forEach(c -> resultMap.put(c.getPkey(), c.getPval()));
return resultMap;
}
/**
* 心跳检测任务, 通过Config-Server获取配置的版本号,用于检测配置版本是否有更新。
*/
private void heartbeat() {
while (true) {
try {
// 通过请求Config-Server获取配置版本号
String versionPath = meta.versionPath();
HttpUtils.OkHttpInvoker okHttpInvoker = new HttpUtils.OkHttpInvoker();
okHttpInvoker.init(20_000, 128, 300);
Long version = JSON.parseObject(okHttpInvoker.get(versionPath), new TypeReference<Long>() {
});
// 检查是否有配置更新
String key = meta.genKey();
Long oldVersion = versionMap.getOrDefault(key, -1L);
if (version > oldVersion) {
System.out.println("[IM_CONFIG] current=" + version + ", old=" + oldVersion);
System.out.println("[IM_CONFIG] need update new configs.");
versionMap.put(key, version);
Map<String, String> newConfigs = findAll();
configMap.put(key, newConfigs);
// 通知所有监听器配置发生了变更
System.out.println("[IM_CONFIG] fire an EnvironmentChangeEvent with keys:" + newConfigs.keySet());
listeners.forEach(listener ->
listener.onChange(new IMRepositoryChangeListener.ChangeEvent(meta, newConfigs)));
}
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("[IM_CONFIG] loop request new configs.");
}
}
}
}
目标:将自定义PropertySource添加到 Spring容器中运行
PropertySourcesProcessor 是一个配置类
- 获取已有的配置列表: 获取当前
ConfigurableEnvironment中的配置列表。 - 初始化配置元数据: 设置
ConfigMeta,包括服务器请求地址、应用名称、环境、命名空间等信息。 - 初始化配置服务: 先初始化
IMRepositoryImpl从服务器获取配置,然后初始化IMConfigServiceImpl实现配置获取和配置变更等基础功能。 - 包装配置服务: 将
IMConfigServiceImpl包装成IMPropertySource,使其成为 Spring 的配置数据源。 - 组合属性源: 将
IMPropertySource添加到CompositePropertySource中,形成一个复合的属性源。 - 设置优先级: 将自定义的属性源添加到
ConfigurableEnvironment的配置列表中,并设置为最高优先级。
/**
* 该类是一个配置类,用于在Spring应用启动时,通过http请求从ipman-config-server获取配置,并将配置添加到Spring环境变量中。
*/
@Data
public class PropertySourcesProcessor implements BeanFactoryPostProcessor, ApplicationContextAware, EnvironmentAware, PriorityOrdered {
private final static String IPMAN_PROPERTY_SOURCES = "IMPropertySources";
private final static String IPMAN_PROPERTY_SOURCE = "IMPropertySource";
Environment environment;
ApplicationContext applicationContext;
/**
* 处理 BeanFactory,在 Spring 应用启动过程中注入自定义属性源。
*
* @param beanFactory ConfigurableListableBeanFactory,
* Spring BeanFactory 的一个接口,提供访问和操作 Spring 容器中所有 Bean 的能力。
* @throws BeansException 如果处理过程中发生错误。
*/
@Override
public void postProcessBeanFactory(@NonNull ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
// 检查是否已存在 ipman 的属性源,若存在则不重复添加
ConfigurableEnvironment ENV = (ConfigurableEnvironment) environment;
if (ENV.getPropertySources().contains(IPMAN_PROPERTY_SOURCES)) {
return;
}
// 设置config-server远程服务的调用信息
String app = ENV.getProperty("ipman.app", "app1");
String env = ENV.getProperty("ipman.env", "dev");
String ns = ENV.getProperty("ipman.ns", "public");
String configServer = ENV.getProperty("ipman.configServer", "http://localhost:9129");
// 使用获取到的配置创建配置服务和属性源
ConfigMeta configMeta = new ConfigMeta(app, env, ns, configServer);
// 创建配置中心实现类, 省去技术细节, 理解了下:
// 1.启动时候 ConfigService 从 Repository拿配置, 同时 Repository 关联了 ConfigService 这个对象,.
// 2.当 Repository 巡检发现配置变了, 在去改 ConfigService 里的 config.
// 3.改完后, 最终再用EnvironmentChangeEvent 去刷新
IMConfigService configService = IMConfigService.getDefault(applicationContext, configMeta);
// 创建SpringPropertySource, 此时Spring就能识别我们自定义的配置了
IMPropertySource propertySource = new IMPropertySource(IPMAN_PROPERTY_SOURCE, configService);
// 创建组合属性源并将 ipman 的属性源添加到其中
CompositePropertySource composite = new CompositePropertySource(IPMAN_PROPERTY_SOURCES);
composite.addPropertySource(propertySource);
// 将组合属性源添加到环境变量中,并确保其被最先访问
ENV.getPropertySources().addFirst(composite);
}
/**
* 获取Bean处理器的优先级,实现 PriorityOrdered 接口。
*
* @return int 返回处理器的优先级,值越小优先级越高。
*/
@Override
public int getOrder() {
return Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE;
}
/**
* 设置 Spring 环境配置
*
* @param environment Environment,Spring 环境接口,提供环境变量的访问。
*/
@Override
public void setEnvironment(@NonNull Environment environment) {
this.environment = environment;
}
/**
* 设置应用上下文
*
* @param applicationContext Spring应用的上下文环境。
*/
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(@NonNull ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
this.applicationContext = applicationContext;
}
}
在 Spring 中,@Value注解支持多种形式的占位符配置。以下是一些常见的形式及其解析方式:
- 简单占位符:
@Value("${some.key}")
private String someKey;
解析后得到的键:"some.key"
- 嵌套占位符:
@Value("${${some.key}}")
private String nestedKey;
解析后得到的键:"some.key"
- 带默认值的占位符:
@Value("${some.key:${some.other.key:100}}")
private String someKeyWithDefault;
解析后得到的键:"some.key", "some.other.key"
- 嵌套占位符带默认值:
@Value("${${some.key:other.key}}")
private String nestedKeyWithDefault;
解析后得到的键:"some.key"
- 多重嵌套占位符:
@Value("${${some.key}:${another.key}}")
private String multiNestedKey;
解析后得到的键:"some.key", "another.key"
- 结合 SpEL 表达式:
@Value("#{new java.text.SimpleDateFormat('${some.key}').parse('${another.key}')}")
private Date parsedDate;
解析后得到的键:"some.key", "another.key"
总结起来,@Value注解支持以下几种占位符配置形式:
- 简单占位符
${some.key} - 带默认值的占位符
${some.key:${some.other.key:100}} - 嵌套占位符
${${some.key}} - 嵌套占位符带默认值
${${some.key:other.key}} - 多重嵌套占位符
${${some.key}:${another.key}} - 结合 SpEL 表达式
#{new java.text.SimpleDateFormat('${some.key}').parse('${another.key}')}
下面提供了某配置中心,开源版本中@Value配置的解析工具, 通过 #extractPlaceholderKeys 可以解析 @Value 注解 ${} 中的配置key
public class PlaceholderHelper {
private static final String PLACEHOLDER_PREFIX = "${";
private static final String PLACEHOLDER_SUFFIX = "}";
private static final String VALUE_SEPARATOR = ":";
private static final String SIMPLE_PLACEHOLDER_PREFIX = "{";
private static final String EXPRESSION_PREFIX = "#{";
private static final String EXPRESSION_SUFFIX = "}";
private PlaceholderHelper() {
}
private static final PlaceholderHelper INSTANCE = new PlaceholderHelper();
public static PlaceholderHelper getInstance() {
return INSTANCE;
}
/**
* Resolve placeholder property values, e.g.
* <br />
* <br />
* "${somePropertyValue}" -> "the actual property value"
*/
public Object resolvePropertyValue(ConfigurableBeanFactory beanFactory, String beanName, String placeholder) {
// resolve string value
String strVal = beanFactory.resolveEmbeddedValue(placeholder);
BeanDefinition bd = (beanFactory.containsBean(beanName) ? beanFactory
.getMergedBeanDefinition(beanName) : null);
// resolve expressions like "#{systemProperties.myProp}"
return evaluateBeanDefinitionString(beanFactory, strVal, bd);
}
private Object evaluateBeanDefinitionString(ConfigurableBeanFactory beanFactory, String value,
BeanDefinition beanDefinition) {
if (beanFactory.getBeanExpressionResolver() == null) {
return value;
}
Scope scope = (beanDefinition != null ? beanFactory
.getRegisteredScope(Objects.requireNonNull(beanDefinition.getScope())) : null);
return beanFactory.getBeanExpressionResolver()
.evaluate(value, new BeanExpressionContext(beanFactory, scope));
}
/**
* Extract keys from placeholder, e.g.
* <ul>
* <li>${some.key} => "some.key"</li>
* <li>${some.key:${some.other.key:100}} => "some.key", "some.other.key"</li>
* <li>${${some.key}} => "some.key"</li>
* <li>${${some.key:other.key}} => "some.key"</li>
* <li>${${some.key}:${another.key}} => "some.key", "another.key"</li>
* <li>#{new java.text.SimpleDateFormat('${some.key}').parse('${another.key}')} => "some.key", "another.key"</li>
* </ul>
*/
public Set<String> extractPlaceholderKeys(String propertyString) {
Set<String> placeholderKeys = new LinkedHashSet<>();
if (!isNormalizedPlaceholder(propertyString) && !isExpressionWithPlaceholder(propertyString)) {
return placeholderKeys;
}
Stack<String> stack = new Stack<>();
stack.push(propertyString);
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
String strVal = stack.pop();
int startIndex = strVal.indexOf(PLACEHOLDER_PREFIX);
if (startIndex == -1) {
placeholderKeys.add(strVal);
continue;
}
int endIndex = findPlaceholderEndIndex(strVal, startIndex);
if (endIndex == -1) {
// invalid placeholder?
continue;
}
String placeholderCandidate = strVal.substring(startIndex + PLACEHOLDER_PREFIX.length(), endIndex);
// ${some.key:other.key}
if (placeholderCandidate.startsWith(PLACEHOLDER_PREFIX)) {
stack.push(placeholderCandidate);
} else {
// some.key:${some.other.key:100}
int separatorIndex = placeholderCandidate.indexOf(VALUE_SEPARATOR);
if (separatorIndex == -1) {
stack.push(placeholderCandidate);
} else {
stack.push(placeholderCandidate.substring(0, separatorIndex));
String defaultValuePart =
normalizeToPlaceholder(placeholderCandidate.substring(separatorIndex + VALUE_SEPARATOR.length()));
if (StringUtils.hasText(defaultValuePart)) {
stack.push(defaultValuePart);
}
}
}
// has remaining part, e.g. ${a}.${b}
if (endIndex + PLACEHOLDER_SUFFIX.length() < strVal.length() - 1) {
String remainingPart = normalizeToPlaceholder(strVal.substring(endIndex + PLACEHOLDER_SUFFIX.length()));
if (!StringUtils.hasText(remainingPart)) {
stack.push(remainingPart);
}
}
}
return placeholderKeys;
}
private boolean isNormalizedPlaceholder(String propertyString) {
return propertyString.startsWith(PLACEHOLDER_PREFIX) && propertyString.endsWith(PLACEHOLDER_SUFFIX);
}
private boolean isExpressionWithPlaceholder(String propertyString) {
return propertyString.startsWith(EXPRESSION_PREFIX) && propertyString.endsWith(EXPRESSION_SUFFIX)
&& propertyString.contains(PLACEHOLDER_PREFIX);
}
private String normalizeToPlaceholder(String strVal) {
int startIndex = strVal.indexOf(PLACEHOLDER_PREFIX);
if (startIndex == -1) {
return null;
}
int endIndex = strVal.lastIndexOf(PLACEHOLDER_SUFFIX);
if (endIndex == -1) {
return null;
}
return strVal.substring(startIndex, endIndex + PLACEHOLDER_SUFFIX.length());
}
private int findPlaceholderEndIndex(CharSequence buf, int startIndex) {
int index = startIndex + PLACEHOLDER_PREFIX.length();
int withinNestedPlaceholder = 0;
while (index < buf.length()) {
if (StringUtils.substringMatch(buf, index, PLACEHOLDER_SUFFIX)) {
if (withinNestedPlaceholder > 0) {
withinNestedPlaceholder--;
index = index + PLACEHOLDER_SUFFIX.length();
} else {
return index;
}
} else if (StringUtils.substringMatch(buf, index, SIMPLE_PLACEHOLDER_PREFIX)) {
withinNestedPlaceholder++;
index = index + SIMPLE_PLACEHOLDER_PREFIX.length();
} else {
index++;
}
}
return -1;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String strVal = "${some.key:other.key}";
System.out.println(new PlaceholderHelper().extractPlaceholderKeys(strVal));
strVal = "${some.key:${some.other.key:100}}";
System.out.println(new PlaceholderHelper().extractPlaceholderKeys(strVal));
strVal = "${${some.key}}";
System.out.println(new PlaceholderHelper().extractPlaceholderKeys(strVal));
strVal = "${${some.key:other.key}}";
System.out.println(new PlaceholderHelper().extractPlaceholderKeys(strVal));
strVal = "${${some.key}:${another.key}}";
System.out.println(new PlaceholderHelper().extractPlaceholderKeys(strVal));
}
}
动态处理被 @Value 注解的配置目标
目标:由于EnvironmentChangeEvent应用事件只能动态修改@ConfigurationProperties相关的类属性,因此标记了@Value注解的类成员变量无法通过这种方式进行动态修改。为了解决这个问题,需要采用以下方式进行处理:
SpringValue:用于声明@Value注解的配置信息。
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
public class SpringValue {
private Object bean; // 配置关联的关联的 Bean 对象
private String beanName; // 配置关联的关联的 Bean 对象名称
private String key; // @Value配置的key
private String placeholder; // @Value配置的占位符
private Field field; // @Value配置的 Bean 成员
}
FieldUtils: 用于扫描Bean中是否有特定Value注解的 Filed成员
/**
* 提供用于检索类中具有特定注解或满足某些条件的字段的工具方法
*/
public interface FieldUtils {
/**
* 查找类中所有被指定注解标注的字段
*
* @param aClass 要搜索的类。
* @param annotationClass 指定的注解类型。
* @return 所有被指定注解标注的字段列表。
*/
static List<Field> findAnnotatedField(Class<?> aClass, Class<? extends Annotation> annotationClass) {
return findField(aClass, f -> f.isAnnotationPresent(annotationClass));
}
/**
* 根据给定的函数条件查找类中所有满足条件的字段
*
* @param aClass 要搜索的类。
* @param function 用于判断字段是否满足条件的函数。
* @return 所有满足条件的字段列表。
*/
static List<Field> findField(Class<?> aClass, Function<Field, Boolean> function) {
List<Field> result = new ArrayList<>();
while (aClass != null) {
Field[] fields = aClass.getDeclaredFields();
for (Field f : fields) {
if (function.apply(f)) {
result.add(f);
}
}
// spring中有些类会被CGLIB代理,所以需要通过父类获取Field
aClass = aClass.getSuperclass();
}
return result;
}
}
SpringValueProcessor:动态更新 @Value 注解的成员变量
当IMConfigServiceImpl触发配置变更后,会发布EnvironmentChangeEvent应用事件。此时,需要监听这个事件,并对标记了@Value注解的成员变量进行动态赋值。
- 实现
BeanPostProcessor后置处理器:
- 扫描类中是否存在
@Value注解的成员变量。 - 如果存在,继续处理。
- 记录注解信息:
- 获取成员变量实例,提取
${}占位符信息(例如,@Value("${some.key}")中的some.key)。 - 获取
Field实例、Bean 实例和 key 名称。 - 将这些信息记录到
VALUE_HOLDER集合中,以便后续使用。
- 监听
EnvironmentChangeEvent配置变更事件:
- 当监听到
EnvironmentChangeEvent事件时,从VALUE_HOLDER中获取与 key 相关的所有Field实例。 - 通过反射解析并设置新的值。
/**
* process spring value
* 1. 扫描所有 spring value,保存起来
* 2. 在配置变更时, 更新所有 spring value
*
* @Author IpMan
* @Date 2024/5/12 12:04
*/
@Slf4j
public class SpringValueProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor, BeanFactoryAware, ApplicationListener<EnvironmentChangeEvent> {
// 占位符操作工具,如: ${key:default}, 拿到 key
static final PlaceholderHelper placeholderHelper = PlaceholderHelper.getInstance();
// 保存所有使用@SpringValue注解的字段及其相关信息
static final MultiValueMap<String, SpringValue> VALUE_HOLDER = new LinkedMultiValueMap<>();
private BeanFactory beanFactory;
/**
* 设置BeanFactory,使处理器能够访问Spring BeanFactory。
*
* @param beanFactory Spring的BeanFactory。
* @throws BeansException 如果设置过程中发生错误。
*/
@Override
public void setBeanFactory(@NotNull BeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
this.beanFactory = beanFactory;
}
/**
* 在Bean初始化之前处理Bean,扫描并保存所有使用@SpringValue注解的字段。
*
* @param bean 当前处理的Bean实例。
* @param beanName 当前处理的Bean名称。
* @return 处理后的Bean实例。
* @throws BeansException 如果处理过程中发生错误。
*/
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(@NotNull Object bean, @NotNull String beanName) throws BeansException {
List<Field> fields = FieldUtils.findAnnotatedField(bean.getClass(), Value.class);
fields.forEach(field -> {
log.info("[IM_CONFIG] >> find spring value:{}", field);
Value value = field.getAnnotation(Value.class);
placeholderHelper.extractPlaceholderKeys(value.value()).forEach(key -> {
log.info("[IM_CONFIG] >> find spring value:{} for field:{}", key, field);
SpringValue springValue = new SpringValue(bean, beanName, key, value.value(), field);
VALUE_HOLDER.add(key, springValue);
}
);
}
);
return bean;
}
/**
* 当@Value配置, 发生改变时,更新所有相关字段的值。
*
* @param event 包含环境变量变更信息的事件。
*/
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(@NotNull EnvironmentChangeEvent event) {
// 更新所有与变更的键相关的@SpringValue字段的值
log.info("[IM_CONFIG] >> update spring value for keys: {}", event.getKeys());
event.getKeys().forEach(key -> {
log.info("[IM_CONFIG] >> update spring value: {}", key);
List<SpringValue> springValues = VALUE_HOLDER.get(key);
if (springValues == null || springValues.isEmpty()) {
return;
}
// 更新每个相关@Value字段的值
springValues.forEach(springValue -> {
log.info("[IM_CONFIG] >> update spring value:{} for key:{}", springValue, key);
try {
// 解析并设置新值
Object value = placeholderHelper.resolvePropertyValue((ConfigurableBeanFactory) beanFactory,
springValue.getBeanName(), springValue.getPlaceholder());
log.info("[IM_CONFIG] >> update spring value:{} for holder:{}", value, springValue.getPlaceholder());
springValue.getField().setAccessible(true);
springValue.getField().set(springValue.getBean(), value);
} catch (IllegalAccessException ex) {
log.error("[IM_CONFIG] >> update spring value error", ex);
}
});
});
}
}
目标:上述代码讲解了如何实现 Spring 配置数据源的集成、客户端和服务器端的长轮询机制、配置获取、变更通知,以及@Value 注解的处理方式。接下来,从使用的角度出发,我们需要思考如何有效利用这个注册中心的功能。
IMConfigRegistry:将客户端功能注入到 Spring 容器
IMConfigRegistry是一个实现ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar接口的类,用于在 Spring 容器中注册BeanDefinition。其核心功能如下:
注册 BeanDefinition:registerBeanDefinitions方法会在导入注解元数据时被调用。
判断 PropertySourcesProcessor 是否已注册:
- 如果已注册,输出 "PropertySourcesProcessor already registered" 并返回。
- 如果未注册,输出 "register PropertySourcesProcessor",并创建
PropertySourcesProcessor的BeanDefinition,然后将其注册到 Spring 容器中。
通过这种方式,IMConfigRegistry确保了客户端的所有功能都能正确注入到 Spring 容器中,从而使得应用可以有效利用注册中心的功能。
public class IMConfigRegistry implements ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar {
@Override
public void registerBeanDefinitions(@NonNull AnnotationMetadata importingClassMetadata,
@NonNull BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
// 注册 @ConfigurationProperties() 配置方式的注册中心处理器
registerClass(registry, PropertySourcesProcessor.class);
// 注册 @Value() 配置方式的注册中心处理器
registerClass(registry, SpringValueProcessor.class);
}
/**
* 向给定的 BeanDefinitionRegistry 注册一个类。
* 如果该类已经注册,则不进行重复注册。
*
* @param registry BeanDefinitionRegistry 实例,用于注册 Bean。
* @param aClass 需要注册的类。
*/
private static void registerClass(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry, Class<?> aClass) {
System.out.println("registry " + aClass.getName());
// 判断PropertySourcesProcessor 是否已经注册Bean
Optional<String> first = Arrays.stream(registry.getBeanDefinitionNames())
.filter(x -> aClass.getName().equals(x))
.findFirst();
if (first.isPresent()) {
System.out.println(aClass.getName() + " already registered");
return;
}
// 注册PropertySourcesProcessor
AbstractBeanDefinition beanDefinition =
BeanDefinitionBuilder.genericBeanDefinition(aClass).getBeanDefinition();
registry.registerBeanDefinition(aClass.getName(), beanDefinition);
System.out.println("registered " + aClass.getName());
}
}
EnableIpManConfig: 注解用于提供开启配置中心的客户端功能。通过使用@EnableIpManConfig注解,可以自动激活配置中心的客户端功能。该注解通过@Import导入IMConfigRegistry.class,实现客户端 Bean 的自动注册。
@Documented
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Inherited
@Import({IMConfigRegistry.class})
public @interface EnableIpManConfig {
}
讲到这,Like版本就基本完工了...
准备测试用的配置(yaml和properties都行)
ipman:
a: "a-00"
b: "b-00"
c: "c-00"
准备测试用的一个标记 @ConfigurationProperties 注解的配置类
@Data
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "ipman")
public class DemoConfig {
private String a;
private String b;
private String c;
}
启动时开启 @EnableIpManConfig 配置中心Client端
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableConfigurationProperties({DemoConfig.class})
@EnableIpManConfig // 激活配置中心
@RestController
public class ConfigDemoApplication {
@Value("${ipman.a:213213}")
private String a;
@Value("${ipman.b}")
private String b;
@Value("${ipman.c}")
private String c;
@Autowired
private DemoConfig demoConfig;
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(ConfigDemoApplication.class, args);
}
@Autowired
Environment environment;
@GetMapping("/")
public String demo() {
return "ipman.a = " + a + ", \n" +
"ipman.b = " + b + ", \n" +
"ipman.c = " + c + ", \n" +
"ipman.demo.a = " + demoConfig.getA() + ", \n" +
"ipman.demo.b = " + demoConfig.getB() + ", \n" +
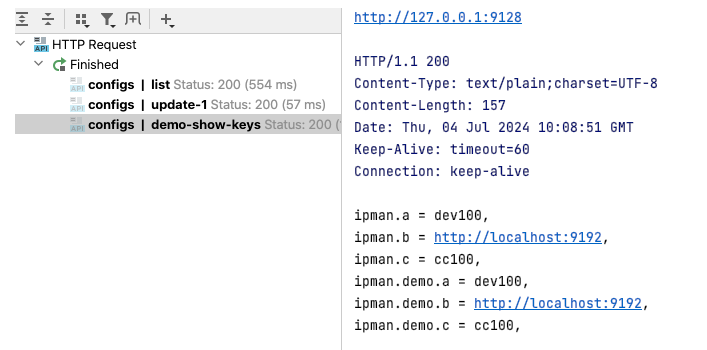
"ipman.demo.c = " + demoConfig.getC() + ", \n";
}
@Bean
ApplicationRunner applicationRunner() {
System.out.println("===> " + Arrays.toString(environment.getActiveProfiles()));
return args -> {
System.out.println(a);
System.out.println(demoConfig.getA());
};
}
}
这个结果与Server端初始化的H2数据库数据是一致的
为了验证配置的动态变更,可以模拟调用服务器端发布最新配置。随后,经过短暂的停顿后,再对比客户端是否成功更新了该配置。
@SpringBootTest(classes = {ConfigDemoApplication.class})
@Slf4j
class ConfigDemoApplicationTests {
static ApplicationContext context1;
@Autowired
private DemoConfig demoConfig;
static MockMvc mockMvc;
@BeforeAll
static void init() {
System.out.println(" ================================ ");
System.out.println(" ============ 9129 ============= ");
System.out.println(" ================================ ");
System.out.println(" ================================ ");
context1 = SpringApplication.run(ConfigServerApplication.class,
"--logging.level.root=info",
"--logging.level.org.springframework.jdbc=debug",
"--logging.level.cn.ipman.config=debug",
"--mybatis.configuration.log-impl=org.apache.ibatis.logging.stdout.StdOutImpl",
"--server.port=9129",
"--spring.application.name=config-server",
"--spring.datasource.driver-class-name=org.h2.Driver",
"--spring.datasource.url=jdbc:h2:mem:h2db",
"--spring.datasource.username=root",
"--spring.datasource.password=123456",
"--spring.sql.init.schema-locations=classpath:db.sql",
"--spring.sql.init.mode=always",
"--spring.h2.console.enabled=true",
"--spring.h2.console.path=/h2",
"--spring.h2.console.settings.web-allow-others=true"
);
mockMvc = MockMvcBuilders.webAppContextSetup((WebApplicationContext) context1).build();
}
@Test
void contextLoads() throws Exception {
System.out.println("config demo running ... ");
Map<String, String> configs = new HashMap<>();
configs.put("ipman.a", "demo1");
configs.put("ipman.b", "demo2");
configs.put("ipman.c", "demo3");
// 模拟调用 config-server 修改配置
MvcResult mvcResult = mockMvc.perform(
MockMvcRequestBuilders.post("/update?app=app1&env=dev&ns=public")
.content(JSON.toJSONString(configs))
.contentType("application/json")).andDo(print())
.andExpect(MockMvcResultMatchers.status().isOk())
.andReturn();
List<Configs> newConfigs = JSON.parseObject(
mvcResult.getResponse().getContentAsString(),
new TypeReference<List<Configs>>() {
}
);
System.out.println("config update to " + newConfigs);
// 验证 config-client 是否将配置也成功更新
Thread.sleep(5_000 * 2);
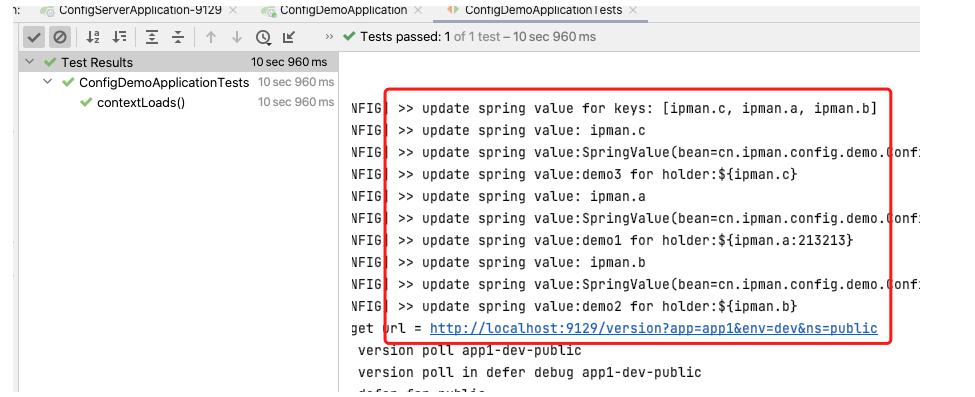
Assertions.assertEquals(configs.get("ipman.a"), demoConfig.getA());
Assertions.assertEquals(configs.get("ipman.b"), demoConfig.getB());
Assertions.assertEquals(configs.get("ipman.c"), demoConfig.getC());
}
@AfterAll
static void destroy() {
System.out.println(" =========== close spring context ======= ");
SpringApplication.exit(context1, () -> 1);
}
}
测试结果,成功实现了动态发布与配置变更
以上只是一个非常简易的配置中心版本,通过以上讲述能大致理解配置中心核心原理,仅是用来学习和探讨。