_/_/_/ _/_/_/ _/
_/ _/ _/ _/ _/
_/_/_/ _/_/_/ _/_/_/_/_/
_/ _/ _/
_/ _/ _/
PowerShell PowerUp is a Server Management Framework.
- This PowerShell project is compatible with PowerShell v2 and higher.
- PowerShell PowerUp extends your existing command line with tons of new cmdlets and modules.
- It's 100% customizable and works without dependencies.
Holy fucking creeper shit, this is the best PowerShell Server Management Framework I've used!
-- You in a few seconds
Download the latest release:
and unzip it in the directory of your choice OR use git to clone the whole repository:
git clone git://github.com/janikvonrotz/PowerShell-PowerUp.git
Now add a profile configuration file to the config folder:
COPY \templates\Profile\Example.profile.config.xml TO \config\...
And
RENAME Example.profile.config.xml TO [Something].profile.config.xml
Now take your time to edit your new PowerShell PowerUp profile config file. Checkout the documentation below for more information.
EDIT [Something].profile.config.xml
SAVE [Something].profile.config.xml
Open your Powershell commandline and enter:
PS C:\PowerShell-PowerUp> Set-ExecutionPolicy remotesigned
Or depending on your windows security restrictions:
PS C:\PowerShell-PowerUp> Set-ExecutionPolicy unrestricted
At last execute the install script from the PowerShell commad line:
PS C:\PowerShell-PowerUp> .\Microsoft.PowerShell_profile.install.ps1
PowerShell PowerUp Package Manager
By default the install script installs these features:
The PowerShell ISE uses a different profile script. With this feature enabled the installation script creates a second profile script for the PowerShell ISE with the same features as the normal profile script.
To use PowerShell function like a library in other programming languages just install this feature and add your functions scripts to the functions folder $PSfunctions.Path.
This features logs the PowerShell prompt output for every session into the log folder $PSlogs.Path.
The path to the session log file is stored in $PSlogs.SessionFile.
Based on the PowerShell PowerUp config files definitions you can add these features:
Would you like to use git from your PowerShell command line or another executable. The first and last thing you'll need is a system variable entry of the executable path.
Installation
To enable this feature add this code to the profile installaton config file:
<SystemVariable Value="%ProgramFiles(x86)%\Git\bin" Name="Path" Target="Machine"></SystemVariable>
Or
<SystemVariable Value="$home" Name="Path" Target="Machine"></SystemVariable>
Or
<SystemVariable Value="\apps\Git\cmd" Name="Path" Target="Machine"></SystemVariable>
Adds a section to the profile script to customize your PowerShell Profile script.
Installation
To enable this feature update the status attribute to Enabled
<Feature Name="Custom PowerShell Profile script" Status="Enabled"></Feature>
Adds a section to the profile script to customize your PowerShell Profile ISE script. Requires the feature:
- Add ISE Profile Script
Installation
To enable this feature update the status attribute to Enabled
<Feature Name="Custom PowerShell Profile ISE script" Status="Enabled"></Feature>
Installation
To enable this feature update the status attribute to Enabled
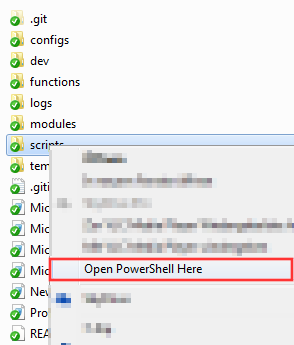
<Feature Name="Enable Open Powershell here" Status="Enabled"></Feature>
Every time you start a new prompt a nice quote will be shown.
Installation
To enable this feature update the status attribute to Enabled
<Feature Name="Get Quote Of The Day" Status="Enabled"></Feature>
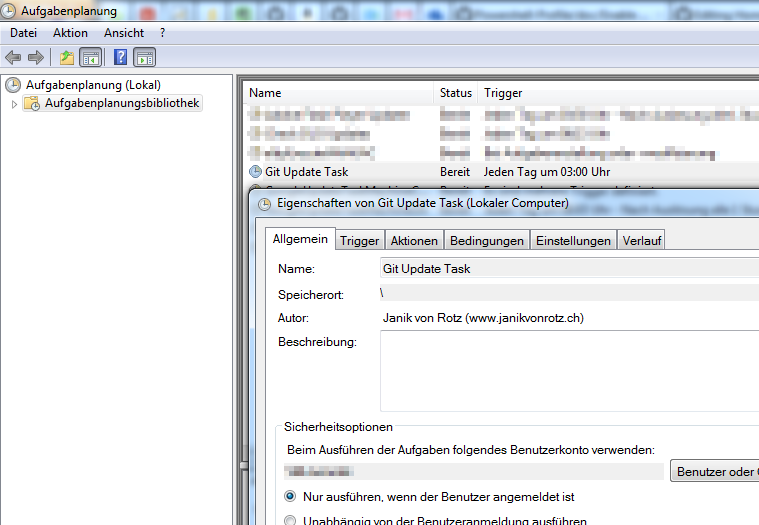
This feature will add a sheduled windows task and if required the latest git client. In a daily schedule the repository will be updated from the github repository.
Also possible from the command line Update-PowerShellProfile.
Installation
To enable this feature update the status attribute to Enabled
<Feature Name="Git Update" Status="Enabled"></Feature>
Clean up the log folder by a daily task or everytime a PowerShell prompt opens.
Also possible from the command line Delete-ObsoleteLogFiles.
Installation
To enable this feature update the status attribute to Enabled
<Feature Name="Log File Retention" Days="x" MaxFilesToKeep="x" Run="asDailyJob,withProfileScript" Status="Enabled"></Feature>
Options
Every option can be combined or stand alone.
- Days: Older log files than x Days will be deleted.
- MaxFilesToKeep: Older log files than x Days will be deleted.
- Run: Add
asDailyJobto run the clean up as windows job and/or addwithProfileScriptto run the clean up every time a PowerShell prompt starts.
In case you don't know there's a possibility to manage your windows server with PowerShell. Checkout the Multi Remote Management feature for more inforamtion. Anyway to enable for other clients to connection you host with PowerShell Remoting you'll have to add this feature.
Installation
To enable this feature update the status attribute to Enabled
<Feature Name="Powershell Remoting" Status="Enabled"></Feature>
You'll get a bunch of new functions to manage your service installation. Some of this are from the backers of PowerShell PowerUp and others are included from other projects.
PowerShell PowerUp can mange these services:
- Multi Remote Management
- Package Manager
- PowerShell PowerUp
- Scripts and Shortcuts
- SharePoint
- SQL Sever
- TrueCrypt
- Windows Event Log
- Windows features/components
- Windows Scheduled Task
These functions are part of Jeffrey Paarhuis project: Client-side SharePoint PowerShell. I've imported the functions of this project and updated the naming concept and metadata.
In order to use these commands you have to install the Managed .NET Client-Side Object Model (CSOM) of SharePoint 2013. Run the command Install-PPApp "SharePoint Server 2013 Client Components SDK" to install this app.
These functions are part of Aaron Jensen project: Carbon.
Carbon is a DevOps PowerShell module for automating the configuration of Windows 2008, Windows 2008 R2, and 7 computers. Carbon can configure and manage:
- Local users and groups
- IIS websites, virtual directories, and applications
- Certificates
- .NET connection strings and app settings
- Junctions
- File system permissions
- Hosts file
- INI files
- Performance counters
- Services
- Shares
- Windows features/components
This index has been made with this script: https://gist.github.com/10965567
A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z
Get-ActiveDirectoryUserGroups
Sync-ADGroupMember
Get-ADPrincipalGroupMembershipRescurse
Backup-AllSPLists
Backup-AllSPSites
Backup-AllSPWebs
Backup-AllSQLDBs
Get-AvailableDriveLetter
-
Get-ChildItemRecurse
Get-CleanSPUrl
Mount-Dir
Add-DomainUserToLocalGroup
Remove-EnvironmentVariableValue
Set-EnvironmentVariableValue
Get-File
Get-FileEncoding
Format-FileSize
Report-FileSystemPermissions
Connect-FTP
SPO-Functions
-
Get-HostFileEntries
Add-HostFileEntry
Remove-HostFileEntry
Connect-HTTP
Disable-InternetExplorerEnhancedSecurityConfiguration
Enable-InternetExplorerEnhancedSecurityConfiguration
-
-
-
Get-Path
Get-PathAndFilename
Install-PowerShellPowerUp
Update-PowerShellPowerUp
Get-PPApp
Install-PPApp
Get-PPConfiguration
Copy-PPConfigurationFile
Write-PPErrorEventLog
Send-PPErrorReport
Update-PPEventLog
Write-PPEventLog
Get-PPScript
Start-PPScript
Add-PPScriptShortcut
Remove-PPScriptShortcut
Export-PPSPWeb
Import-PPSPWeb
Export-PSCredential
Import-PSCredential
Connect-PSS
Connect-RDP
Get-RemoteConnection
Update-ScheduledTask
Connect-SCP
Set-SPADGroupPermission
Disable-SPBlobCache
Enable-SPBlobCache
Export-SPList
Get-SPList
Import-SPList
Move-SPList
Get-SPListFiles
Get-SPListItems
Export-SPLists
Get-SPLists
Get-SPManagedMetadataServiceTerms
Connect-SPO
Get-SPObjectPermissions
Add-SPOCalculatedFieldtoList
Submit-SPOCheckIn
Submit-SPOCheckOut
Add-SPOChoiceFieldtoList
Add-SPOChoicesToField
Add-SPOCurrencyFieldtoList
Set-SPOCustomMasterPage
Add-SPODateTimeFieldtoList
Add-SPODocumentLibrary
Set-SPODocumentPermissions
Switch-SPOEnableDisableSolution
Enable-SPOFeature
Add-SPOField
Test-SPOField
Find-SPOFieldName
Add-SPOFieldsToList
Copy-SPOFile
Save-SPOFile
Convert-SPOFileVariablesToValues
Add-SPOFolder
Copy-SPOFolder
Add-SPOGroup
Get-SPOGroup
Add-SPOList
Add-SPOListItems
Set-SPOListPermissions
Set-SPOMasterPage
Add-SPONoteFieldtoList
Add-SPONumberFieldtoList
Join-SPOParts
Add-SPOPictureLibrary
Get-SPOPrincipal
Add-SPOPrincipalToGroup
Get-SPORole
Open-SPORootsite
Open-SPOSite
Add-SPOSolution
Install-SPOSolution
Uninstall-SPOSolution
Get-SPOSolutionId
Convert-SPOStringVariablesToValues
Add-SPOSubsite
Open-SPOSubsite
Add-SPOTextFieldtoList
Add-SPOUserFieldtoList
Add-SPOWebpart
Set-SPOWebPermissions
Request-SPOYesOrNo
Get-SPUrl
Move-SPWeb
Get-SPWebs
Run-SQLServerAgentJob
Load-SQLServerManagementObjects
Connect-SSH
Convert-StringToScriptBlock
New-TreeObjectArray
Get-TreeObjectArrayAsList
Dismount-TrueCryptContainer
Mount-TrueCryptContainer
Get-TrueCyptContainer
-
-
-
-
By adding scripts and configuration files to the config folder you can make use of this features:
Use your PowerShell installation as an remote management software.
Supported protocols:
- rdp = Remote Deskopt Protocol (Microsoft Remote Desktop Connections)
- rps = Remote Powershell Session (PowerShell Remoting)
- http = Hypertext Transfer Protocol (default browser)
- https = Secure Hypertext Transfer Protocol (default browser)
- ssh = Secure Shell (Putty)
- scp = Secure Copy (WinSCP)
- ftp = File Transfer Protocol (WinSCP)
- sftp = Secutre File Transfer Protocol (WinSCP)
- vmware = custom WMware protocols (VMware PowerCLI)
Installation
Add remote configuration file to the config folder $PSconfigs.Path:
Run Copy-Item $(Get-Childitem -Filter $PSconfigs.Remote.Filter $PStemplates.Path -Recurse).Fullname $PSconfigs.Path
Rename EXAMPLE.remote.config.xml to [SOMETHING].remote.config.xml
Edit [SOMETHING].remote.config.xml
Options
- Key: A short and unique name to identify the remote device
- Name: IP or Hostname
- User (optional): [Domain]\[Username] or [Username]@[Domain]
- Description (optional): Add comments or a short description for the device
- Protocol (optional): Use this modification if the default port doesn't match.
- Name: Protocolname
- Port: Set new port number
- SnapIns (optional): will be loaded when connecting with rps
- PrivatKey (optional): Path to your private key file (PowerShell variables allowed)
Commands
Get-RemoteConnectionalias: grcConnect-PSSalias: crpsConnect-RDPalias: crdpConnect-Httpalias: chttpConnect-SSHalias: csshConnect-SCPalias: cscpConnect-FTPalias: cftpConnect-VSpherealias: cvsConnect-VMalias: cvm
Connect-Http alias: chttp
To force a connection with https instead with the default http, add this code to the selected servers in the remote configuration file:
<Protocol Name="https" Port=""></Protocol>
If the server isn't configured in the configuration file, add the parameter [-Secure]:
Connect-HTTPSession 192.168.90.2 -Secure
Package Manger allows you to integrate custom application installers in order to distribute them on you server.
Compared to other package managers this one doesn't depend on a online web service. The install definitions are stored in the lib hub.
Commands
Add task config files from the template folder to the config folder and run the update command. The defined task will be automatically added to the windows task scheduler.
Commands
- Report to the windows event log.
- Create and update a custom event log.
Installation
Copy and alter an eventlog config file from the template folder to the config folder. The update command will create or update your custom eventlog based on the configuration files in the config folder.
Commands
The installation and the installed profile script using the project folders and the related PowerShell global variables from the Microsoft.PowerShell_profile.config.ps1 file.
You can merge multiple configuration types in one configuration file as long they're not part of standalone configuration files or distribute the the configurations into multiple files in multiple directoryies.
To load configurations you have several possibilities:
Load the configuration files with predefined filters:
Get-ChildItem -Path $PSconfigs.Path -Filter $PSconfigs.Mail.Filter -Recurse | %{[xml]$(get-content $_.FullName)}
Load the configuration type from several configuration files
Get-ChildItem -Path $PSconfigs.Path -Filter $PSconfigs.File.Filter -Recurse | %{[xml]$(get-content $_.FullName)} | %{$_.Content.Feature}
Load the app configurations from the lib folder:
Get-ChildItem -Path $PSlib.Path -Filter $PSconfigs.App.Filter -Recurse | %{[xml]$(get-content $_.FullName)}
Or use the Get-PPConfiguration function
The configuration files for the different configuration types are stored in the template folder. Each folder represent a configuration file type.
File
This is the root configuration file type.
Filename: $PSconfigs.File.Filter
XMLNameSpace1: Content
App
This configuration type is stored in the lib folder.
Filename: $PSconfigs.App.Filter
Datafile: $PSconfigs.App.Datafile
XMLNameSpace1: Content.App
XMLNameSpace2: Content.PackageManager
EventLog
Filename: $PSconfigs.EventLog.Filter
XMLNameSpace1: Content.Eventlog
Mail
Filename: $PSconfigs.Mail.Filter
XMLNameSpace1: Content.Mail
Profile
Filename: $PSconfigs.Profile.Filter
XMLNameSpace1: Content.Feature
XMLNameSpace2: Content.SystemVariable
Script
Filename: $PSconfigs.Script.Filter
XMLNameSpace1: Content.Script
Server
Filename: $PSconfigs.Server.Filter
XMLNameSpace1: Content.Server
TrueCryptContainer
Filename: $PSconfigs.TrueCryptContainer.Filter
XMLNameSpace1: Content.TrueCryptContainer
User
Filename: $PSconfigs.User.Filter
XMLNameSpace1: Content.User
These files aren't merge able with other configuratio files, also they were created by an function or a third party pogramm.
Credential
Filename: $PSconfigs.credential.Filter
Use the Export-PSCredential command to create this configuration file.
Task
Filename: $PSconfigs.Task.Filter
Use the export function from the windows job console or copy a template from the template folder.
The PowerShell Profile task configuration files are extended with an additional description field to store the job name of the task.
These fils are used to save configurations for PowerShell PowerUp modules
Package Manager
Filename: $PSconfigs.App.DataFile
These files are temporary data files used by the PowerShell PowerUp modules.
Script Shortcut
Filename: $PSconfigs.ScriptShortcut.DataFile
TrueCryptContainer
Filename: $PSconfigs.TrueCryptContainer.DataFile
The heart of PowerShell PowerUp are the following folders, based on these folders you'll find a global variable containing the path to the folder and further useful stuff.
-
Variable:
$PSapps- Application variables used by PowerShell PowerUp
-
Variable:
$PSconfigsand folder: configs- Add the PowerShell PowerUp config files to this folder.
- There aren't any definitions for the folder structure.
-
Variable:
$PSfunctionsand folder: functions- Add the PowerShell function scripts to this folder
- There aren't any definitions for the folder structure.
-
Variable:
$PSlogsand folder: logs- If transcription is enabled, logs will be stored in this folder.
-
Variable:
$PSbinand folder: bin- This folder will be added to the system path environment variable.
- This folder contains links to binaries mostly used by the package installer.
-
Variable:
$PSliband folder: lib- This folder contains dlls and modules used by PowerShell PowerUp.
- This is the repository for the PowerShell PowerUp Package Manager.
-
Variable:
$PSscriptsand folder: scripts- Store your scripts here.
-
templates
$PStemplates- This folder contains the templates for the PowerShell PowerUp config files.