KSwift it's gradle plugin for generation Swift-friendly API for Kotlin/Native framework.
KSwift give you API for adding your own generator based on KLib metadata information.
- API for extend logic for own cases - just implement your own
ProcessorFeature - Reading of all exported klibs - you can generate swift additions to the api of external libraries
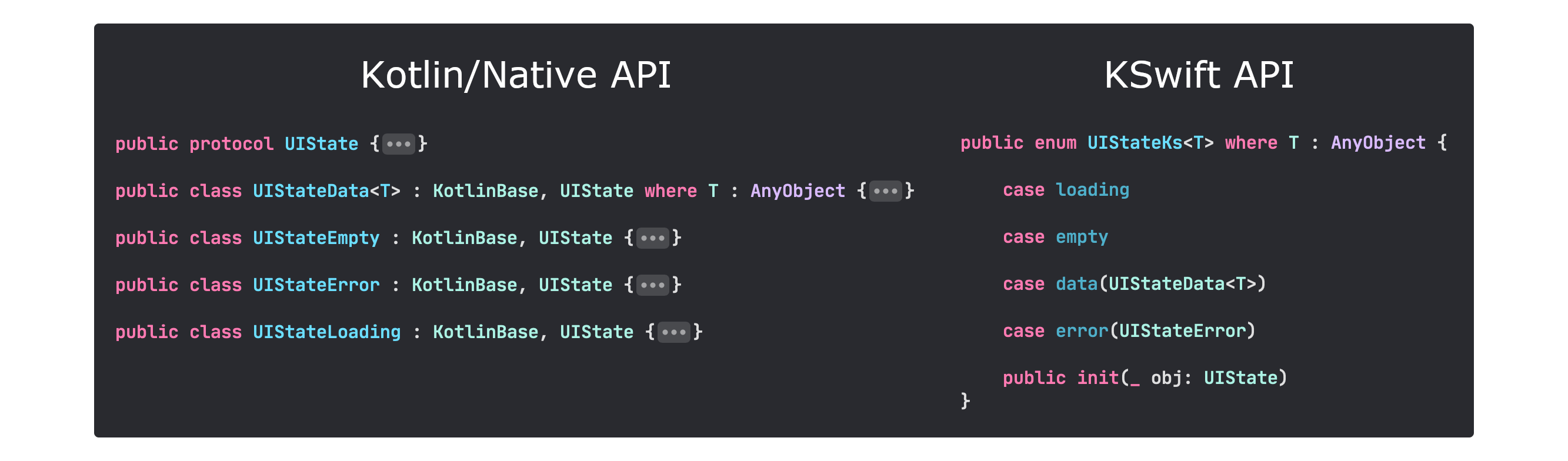
- Kotlin sealed class/interface to Swift enum
- Kotlin extensions for platform classes to correct extensions instead of additional class with static methods
- Flexible filtration - select what you want to generate and what not
- Gradle version 6.0+
- Kotlin 1.5.20
root build.gradle
buildscript {
repositories {
mavenCentral()
google()
gradlePluginPortal()
maven("https://jitpack.io")
}
dependencies {
classpath("dev.icerock.moko:kswift-gradle-plugin:0.3.0")
}
}project where framework compiles build.gradle
plugins {
id("dev.icerock.moko.kswift")
}settings.gradle
pluginManagement {
repositories {
google()
gradlePluginPortal()
mavenCentral()
maven("https://jitpack.io")
}
}project where framework compiles build.gradle
plugins {
id("dev.icerock.moko.kswift") version "0.3.0"
}root build.gradle
allprojects {
repositories {
mavenCentral()
}
}project build.gradle
dependencies {
commonMainApi("dev.icerock.moko:kswift-runtime:0.3.0") // if you want use annotations
}Enable feature in project build.gradle:
kotlin:
kswift {
install(dev.icerock.moko.kswift.plugin.feature.SealedToSwiftEnumFeature)
}groovy:
kswift {
install(dev.icerock.moko.kswift.plugin.feature.SealedToSwiftEnumFeature.factory)
}That's all - after this setup all sealed classes and sealed interfaces will be parsed by plugin and plugin will generate Swift enums for this classes.
For example if you have in your kotlin code:
sealed interface UIState<out T> {
object Loading : UIState<Nothing>
object Empty : UIState<Nothing>
data class Data<T>(val value: T) : UIState<T>
data class Error(val throwable: Throwable) : UIState<Nothing>
}Then plugin will generate source code:
/**
* selector: ClassContext/moko-kswift.sample:mpp-library-pods/com/icerockdev/library/UIState */
public enum UIStateKs<T : AnyObject> {
case loading
case empty
case data(UIStateData<T>)
case error(UIStateError)
public init(_ obj: UIState) {
if obj is shared.UIStateLoading {
self = .loading
} else if obj is shared.UIStateEmpty {
self = .empty
} else if let obj = obj as? shared.UIStateData<T> {
self = .data(obj)
} else if let obj = obj as? shared.UIStateError {
self = .error(obj)
} else {
fatalError("UIStateKs not syncronized with UIState class")
}
}
}For each generated entry in comment generated selector - value of this selector can be used for
filter. By default all entries generated. But if generated code invalid (please report issue in this
case) you can disable generation of this particular entry:
kotlin:
kswift {
install(dev.icerock.moko.kswift.plugin.feature.SealedToSwiftEnumFeature) {
filter = excludeFilter("ClassContext/moko-kswift.sample:mpp-library-pods/com/icerockdev/library/UIState")
}
}groovy:
kswift {
install(dev.icerock.moko.kswift.plugin.feature.SealedToSwiftEnumFeature.factory) {
it.filter = it.excludeFilter("ClassContext/moko-kswift.sample:mpp-library-pods/com/icerockdev/library/UIState")
}
}As alternative you can use includeFilter to explicit setup each required for generation entries:
kotlin:
kswift {
install(dev.icerock.moko.kswift.plugin.feature.SealedToSwiftEnumFeature) {
filter = includeFilter("ClassContext/moko-kswift.sample:mpp-library-pods/com/icerockdev/library/UIState")
}
}groovy:
kswift {
install(dev.icerock.moko.kswift.plugin.feature.SealedToSwiftEnumFeature.factory) {
it.filter = it.includeFilter("ClassContext/moko-kswift.sample:mpp-library-pods/com/icerockdev/library/UIState")
}
}Enable feature in project build.gradle:
kotlin:
kswift {
install(dev.icerock.moko.kswift.plugin.feature.PlatformExtensionFunctionsFeature)
}groovy:
kswift {
install(dev.icerock.moko.kswift.plugin.feature.PlatformExtensionFunctionsFeature.factory)
}That's all - after this setup all extension functions for classes from platform.* package will be
correct swift code.
For example if you have in your kotlin code:
class CFlow<T>(private val stateFlow: StateFlow<T>) : StateFlow<T> by stateFlow
fun UILabel.bindText(coroutineScope: CoroutineScope, flow: CFlow<String>) {
val label = this
coroutineScope.launch {
label.text = flow.value
flow.collect { label.text = it }
}
}Then plugin will generate source code:
public extension UIKit.UILabel {
/**
* selector: PackageFunctionContext/moko-kswift.sample:mpp-library/com.icerockdev.library/Class(name=platform/UIKit/UILabel)/bindText/coroutineScope:Class(name=kotlinx/coroutines/CoroutineScope),flow:Class(name=com/icerockdev/library/CFlow)<Class(name=kotlin/String)> */
public func bindText(coroutineScope: CoroutineScope, flow: CFlow<NSString>) {
return UILabelExtKt.bindText(self, coroutineScope: coroutineScope, flow: flow)
}
}Selector from comment can be used for filters as in first example.
First create buildSrc, if you don't. build.gradle will contains:
plugins {
id("org.jetbrains.kotlin.jvm") version "1.5.21"
}
repositories {
mavenCentral()
google()
gradlePluginPortal()
maven("https://jitpack.io")
}
dependencies {
implementation("com.android.tools.build:gradle:7.0.0")
implementation("org.jetbrains.kotlin:kotlin-gradle-plugin:1.5.21")
implementation("dev.icerock.moko:kswift-gradle-plugin:0.2.0")
}Then in buildSrc/src/main/kotlin create MyKSwiftGenerator:
import dev.icerock.moko.kswift.plugin.context.ClassContext
import dev.icerock.moko.kswift.plugin.feature.ProcessorContext
import dev.icerock.moko.kswift.plugin.feature.ProcessorFeature
import io.outfoxx.swiftpoet.DeclaredTypeName
import io.outfoxx.swiftpoet.ExtensionSpec
import io.outfoxx.swiftpoet.FileSpec
class MyKSwiftGenerator(
override val featureContext: KClass<ClassContext>,
override val filter: Filter<ClassContext>
) : ProcessorFeature<ClassContext>() {
override fun doProcess(featureContext: ClassContext, processorContext: ProcessorContext) {
val fileSpec: FileSpec.Builder = processorContext.fileSpecBuilder
val frameworkName: String = processorContext.framework.baseName
val classSimpleName = featureContext.clazz.name.substringAfterLast('/')
fileSpec.addExtension(
ExtensionSpec
.builder(
DeclaredTypeName.typeName("$frameworkName.$classSimpleName")
)
.build()
)
}
class Config : BaseConfig<ClassContext> {
override var filter: Filter<ClassContext> = Filter.Exclude(emptySet())
}
companion object : Factory<ClassContext, MyKSwiftGenerator, Config> {
override fun create(block: Config.() -> Unit): MyKSwiftGenerator {
val config = Config().apply(block)
return MyKSwiftGenerator(featureContext, config.filter)
}
override val featureContext: KClass<ClassContext> = ClassContext::class
@JvmStatic
override val factory = Companion
}
}in this example will be generated swift extension for each class in kotlin module. You can select
required Context to got required info from klib metadata.
last step - enable feature in gradle:
kotlin:
kswift {
install(MyKSwiftGenerator)
}groovy:
kswift {
install(MyKSwiftGenerator.factory)
}kotlin:
kswift {
iosDeploymentTarget.set("11.0")
}groovy:
kswift {
iosDeploymentTarget = "11.0"
}Swift source code generates in same directory where compiles Kotlin/Native framework. In common case
it directory
build/bin/{iosArm64 || iosX64}/{debugFramework || releaseFramework}/{frameworkName}Swift.
Kotlin/Native cocoapods plugin (and also mobile-multiplatform cocoapods plugin by IceRock) will move
this sources into fixed directory - build/cocoapods/framework/{frameworkName}Swift.
kswift {
excludeLibrary("{libraryName}")
}kswift {
includeLibrary("{libraryName1}")
includeLibrary("{libraryName2}")
}More examples can be found in the sample directory.
Clone project and just open it. Gradle plugin attached to sample by gradle composite build, so you will see changes at each gradle build.
# clone repo
git clone [email protected]:icerockdev/moko-kswift.git
cd moko-kswift
# generate podspec files for cocopods intergration. with integration will be generated swift files for cocoapod
./gradlew kSwiftmpp_library_podsPodspec
./gradlew kSwiftMultiPlatformLibraryPodspec
# go to ios dir
cd sample/ios-app
# install pods
pod install
# now we can open xcworkspace and build ios project
open ios-app.xcworkspace
# or run xcodebuild
xcodebuild -scheme ios-app -workspace ios-app.xcworkspace test -destination "platform=iOS Simulator,name=iPhone 12 mini"
xcodebuild -scheme pods-test -workspace ios-app.xcworkspace test -destination "platform=iOS Simulator,name=iPhone 12 mini"All development (both new features and bug fixes) is performed in develop branch. This
way master sources always contain sources of the most recently released version. Please send PRs
with bug fixes to develop branch. Fixes to documentation in markdown files are an exception to
this rule. They are updated directly in master.
The develop branch is pushed to master during release.
More detailed guide for contributers see in contributing guide.
Copyright 2021 IceRock MAG Inc
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
You may obtain a copy of the License at
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
limitations under the License.