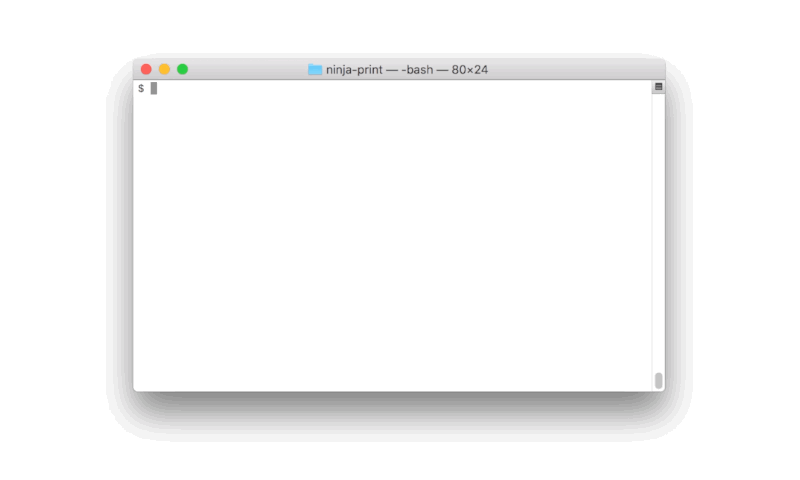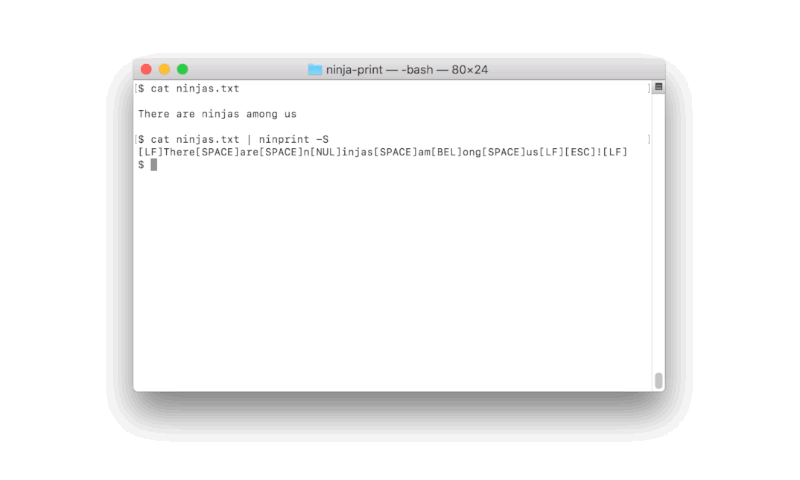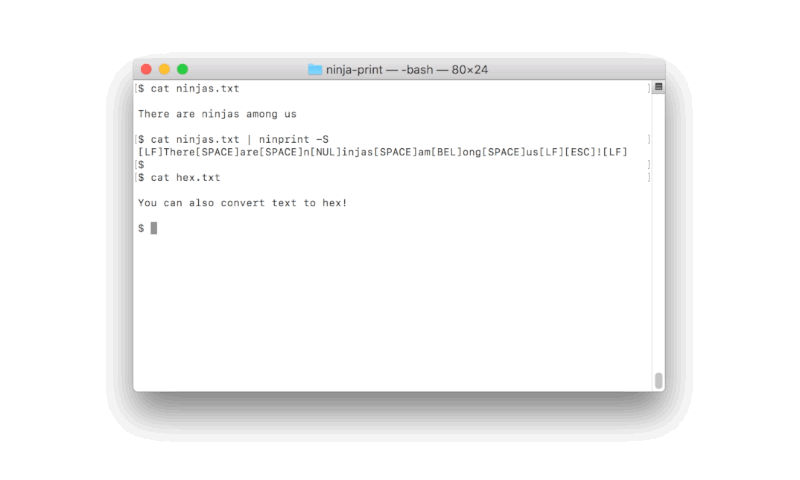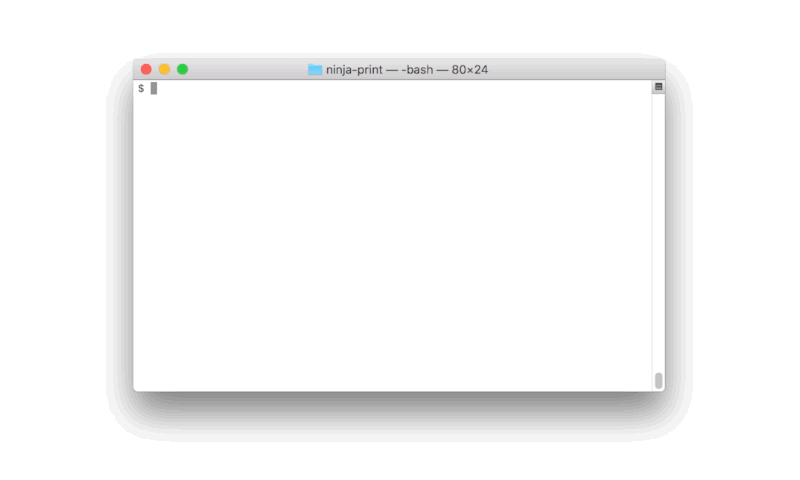
ninprint is a utility for printing human-readable special characters.
Are you ever working with binary or string data that contains special characters (NUL, CR, LF, etc)? Unfortunately standard print commands (echo, printf, console.log, etc) will not display special characters, making it difficult to determine exactly where they exist in a string. ninprint makes your life easy by printing out a human-readable form of each character.
ninprint requires NodeJS and NPM/Yarn.
npm install -g ninprintyarn global add ninprintYou can pipe output from other processes into ninprint:
$ printf "From pipe: \0\r\n" | ninprint
F r o m [SPACE] p i p e : [SPACE] [NUL] [CR] [LF]Pipe in files:
$ printf "From file: \b\f\t" > test.bin
$ ninprint < test.bin
F r o m [SPACE] f i l e : [SPACE] [BS] [FF] [TAB]Pass a string as an argument:
$ ninprint "Test"
T e s tBash requires $'abc' syntax for escape characters:
$ ninprint $'Test\r\n'
T e s t [CR] [LF]Note: ninprint $'Test\0\r\n' will terminate after Test because of the \0 null character.
-
-f, --format [type]:Set the output format. Format types are:
-
default:Print zero-width special characters and spaces using their abbreviated form. Print all other characters as is.
$ printf "Test \0\r\n" | ninprint -f default T e s t [SPACE] [NUL] [CR] [LF]
-
escape:Print common C-style escape sequences. Print all other characters as
default.Supported escape sequence characters are:
Character Escape [NUL]\0[BEL]\a[BS]\b[TAB]\t[LF]\n[VT]\v[FF]\f[CR]\r[ESC]\e$ printf "Test \0\r\n" | ninprint -f escape T e s t [SPACE] \0 \r \n
-
octal-escape:Print all characters using their octal escape sequence.
$ printf "Test \0\r\n" | ninprint -f octal-escape \124 \145 \163 \164 \40 \0 \15 \12
-
hex-escape:Print all characters using their hexadecimal escape sequence.
$ printf "Test \0\r\n" | ninprint -f hex-escape \x54 \x65 \x73 \x74 \x20 \x0 \xD \xA
-
hex:Print all characters in hexadecimal.
$ printf "Test \0\r\n" | ninprint -f hex 54 65 73 74 20 00 0D 0A
-
octal:Print all characters in octal.
$ printf "Test \0\r\n" | ninprint -f octal 124 145 163 164 040 000 015 012
-
binary:Print all characters in binary.
$ printf "Test \0\r\n" | ninprint -f binary 01010100 01100101 01110011 01110100 00100000 00000000 00001101 00001010
-
-
-s, --separator [value]:Set the string that separates output values. Default is ' ' (space)
$ printf "Test \0\r\n" | ninprint -s ... T...e...s...t...[SPACE]...[NUL]...[CR]...[LF]
$ printf "Test \0\r\n" | ninprint -s $'\n' T e s t [SPACE] [NUL] [CR] [LF]
-
-S:Don't separate output values (equivalent to -s '')
$ printf "Test \0\r\n" | ninprint -S Test[SPACE][NUL][CR][LF]
$ printf "Test \0\r\n" | ninprint -f escape -S Test[SPACE]\0\r\n
$ printf "Test \0\r\n" | ninprint -f hex -S 5465737420000D0A
You can also use ninprint as a Node/Webpack module.
npm install ninprintyarn add ninprintYou can print directly to the console:
const { print } = require("ninprint");
print("Hello world.");
// Output:
// H e l l o [SPACE] w o r l d .
print("Line feed:\n");
// Output:
// L i n e [SPACE] f e e d : [LF]You can use convert to return a string:
const { convert } = require("ninprint");
const test1 = convert("Carriage return:\r");
console.log(test1);
// Output:
// C a r r i a g e [SPACE] r e t u r n : [CR]
const test2 = convert("Null character:\0");
console.log(test2);
// Output:
// N u l l [SPACE] c h a r a c t e r : [NUL]You can also pass a Buffer to print/convert:
const { print, convert } = require("ninprint");
print(new Buffer([0x00, 0x01, 0x02, 0x03, 0x04, 0x05]));
// Output:
// [NUL] [SOH] [STX] [ETX] [EOT] [ENQ]
const test3 = convert(new Buffer([0x06, 0x07, 0x08, 0x09, 0x0A, 0x0B]));
console.log(test3);
// Output:
// [ACK] [BEL] [BS] [TAB] [LF] [VT]print and convert both take an options object as a second parameter.
const { print, convert, Format } = require("ninprint");
print("Test\0\r\n", {
format: Format.DEFAULT,
separator: " "
});
const test1 = convert("Test\0\r\n", {
format: Format.ESCAPE,
separator: ""
});Possible options are:
-
format:The output format. Possible format types are:
Format.DEFAULTFormat.ESCAPEFormat.OCTAL_ESCAPEFormat.HEX_ESCAPEFormat.HEXFormat.OCTALFormat.BINARY
Where:
{ Format } = require("ninprint")See
formatin the CLI options for explanations of each format type. -
separator:The string that separates output values. Default is " " (space)
See
separatorin the CLI options for examples.