-
Goterators is util library that support aggregate & transforms functions list in Go.
-
Iterate:
-
Condition:
-
Aggregate:
-
Support generic functions that fit with all your types.
-
The API and functions are inspired by Rust and Javascript.
- Go 1.18
This assumes you already have a working Go environment.
Use Go get to pull goterators for using
go get -u github.com/ledongthuc/goterators
Import the package goterators into your project before using.
import "github.com/ledongthuc/goterators"
- For-each function does the same
forin Go. Just another option to loop through items in a list.
goterators.ForEach(list1, func(item int) {
// handle each item in the list
})
goterators.ForEach(list2, func(item string) {
// handle each item in the list
})
goterators.ForEach(list3, func(item MyStruct) {
// handle each item in the list
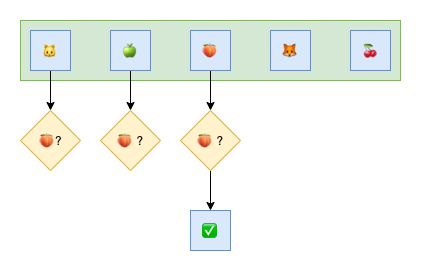
})- Find function returns the first element and its index in the list that meets the functional condition. If no element meet the condition function, return the error "Not Found".
matchedInt, index, err := goterators.Find(list, func(item int) bool {
return item == 1
})
matchedString, index, err := goterators.Find(list, func(item string) bool {
return item == "searching text"
})
matchedStruct, index, err := goterators.Find(list, func(item MyStruct) bool {
return item == searchingStruct
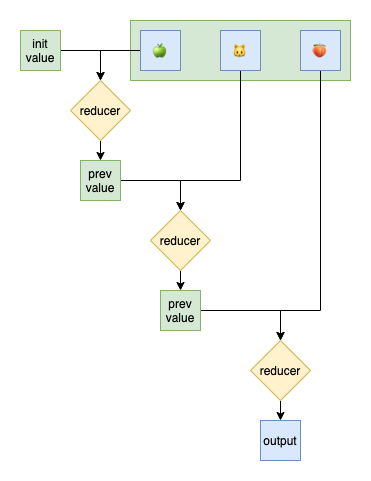
})- Similar to Fold Left, Reduce function runs the reducer function on each element of the array. In order, the reduce function passes in the return value from the calculation on the preceding element. The final result of running the reducer across all elements of the array is the return value of the final reducer on the last element.
- Reduce function has 3 parameters:
- list: source list we want to process.
- initial value: the previous value that's used in the reducer call of the first element. At this time, previous = initial value, current = first element of the list.
- reducer function: the function will run on all elements of the source list.
- Can use Reduce() or ReduceLeft() or FoldLeft()
// Sum
total := goterators.Reduce(list, 0, func(previous int, current int, index int, list []int) int {
return previous + current
})
// Mapping ints to floats
items := goterators.Reduce(testSource, []float64{}, func(previous []float64, current int, index int, list []int) []float64 {
return append(previous, float64(current))
})- Similar to Fold Right, Reduce right function run the reducer function on each element of the array, from last to the first element. In order, the reduce function passes in the return value from the calculation on the preceding element. The final result of running the reducer across all elements of the array is the return value of the final reducer on the first element.
- Reduce function has 3 parameters:
- list: source list we want to process.
- initial value: the previous value that's used in the reducer call of the last element. At this time, previous = initial value, current = last element of list.
- reducer function: the function will run on all elements of the source list.
- Can use ReduceRight() or FoldRight()
// Reverse
reversedList := goterators.Reduce(list, []string{}, func(previous []string, current string, index int, list []string) []string {
return append(list, current)
})- Filter function return items that pass the filter function.
filteredItems := goterators.Filter(list, func(item int) bool {
return item % 2 == 0
})
filteredItems := goterators.Filter(list, func(item string) bool {
return item.Contains("ValidWord")
})
filteredItems := goterators.Filter(list, func(item MyStruct) bool {
return item.Valid()
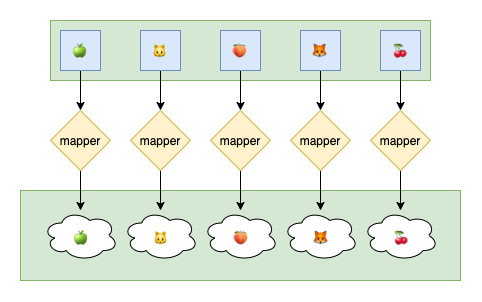
})- Map function converts items in the list to the output list.
mappedItems := goterators.Map(testSource, func(item int64) float64 {
return float64(item)
})
prices := goterators.Map(testSource, func(item Order) Price {
return item.GetPrice()
})- Every function checks all elements in the list with condition function. If it's yes return true; otherwise, return false.
valid := goterators.Every(list, func(item int) bool { item % 2 == 0 })
valid := goterators.Every(list, func(item string) bool { len(item) < 20 }) - Some function check at least one element in the list meet the condition; return true, or return false if all elements don't meet the condition.
valid := goterators.Some(list, func(item int) bool { item % 2 == 0 })
valid := goterators.Some(list, func(item string) bool { len(item) < 20 }) - Group groups elements into the nested level. Use a build-group function to define group type.
groups := goterators.Group(list, func(item Product) groupKey {
return item.ComposeGroupKey()
}) // Group contains [ [ Product1, Product2, Product3 ], [ Product4, Product5 ] ]
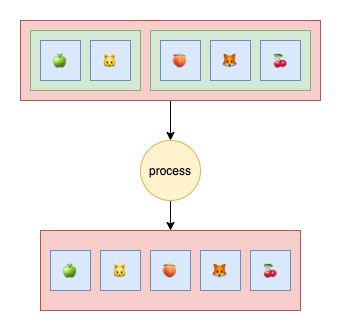
- Flat returns a new array with all sub-array elements concatenated with 1 level depth.
output := goterators.Flat([][]int{{1,2}, {3}}) // output = {1,2,3}- Exist function checks the existence of an element in the list.
matchedInt, err := goterators.Exist(list, 1)
matchedString, err := goterators.Exist(list, "searching string")
matchedStruct, err := goterators.Exist(list, SearchingStruct)- Include check if source list contains all items from the sub-list item.
list := []int{1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20}
subList := []int{8, 15, 19}
result := goterators.Include(list, subList)
fmt.Println("Include: ", result)- IncludeSome check if source list contains any items from the sub-list item.
list := []int{1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20}
subList := []int{8, 15, 19}
result := goterators.IncludeSome(list, subList)
fmt.Println("IncludeSome: ", result)- Count returns number of checking item exists in source list
testSource := []int{1, 1, 1, 2, 2, 3, 3, 3, 3, 4}
fmt.Println("Count: ", goterators.Count(testSource, 3))- CountList returns sub-list counter of input sub-list that want to count from source list.
testSource := []int{1, 1, 1, 2, 2, 3, 3, 3, 3, 4}
fmt.Println("CountList: ", goterators.CountList(testSource, []int{1, 1, 2, 3, 5}))- Mode return a value that appears most often in the source list.
testSource := []int{1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20}
mostOftenValue, counter := goterators.Mode(testSource)
fmt.Println("Mode: ", mostOftenValue, counter)- Sum plus all item from source list
testSource := []int{1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20}
fmt.Println("Sum: ", goterators.Sum(testSource))- Average sum of all the source list divided by the total number of source list
- We can use Average() or Mean()
testSource := []int{1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20}
fmt.Println("Average: ", goterators.Average(testSource))
fmt.Println("Mean: ", goterators.Mean(testSource))- Max find largest value from source list
testSource := []int{20, 17, 9, 21, 18, 3, 11, 5}
result, err := goterators.Max(testSource)
fmt.Println("Max: ", result)- Min find smallest value from source list
testSource := []int{20, 17, 9, 21, 18, 3, 11, 5}
result, _ := goterators.Min(testSource)
fmt.Println("Min: ", result)- Median return a value in the middle of an ordered source list. If number of item in source is even, return right item. Make sure source list are sorted
testSource := []int{1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20}
median, index, _ := goterators.Median(testSource)
fmt.Println("Median: ", median, ", with index: ", index)- Range return max - min
testSource := []int{20, 17, 9, 21, 18, 3, 11, 5}
fmt.Println("Range: ", goterators.Range(testSource))- MidRange return (max + min) / 2
testSource := []int{20, 17, 9, 21, 18, 3, 11, 5}
fmt.Println("Range: ", goterators.Range(testSource))MIT
All your contributions to project and make it better, they are welcome. Feel free to reach me https://thuc.space or create an issue to start it.
- Viet Nam We Build group https://webuild.community for discussion