TL;DR
find a Debian or Ubuntu box with root on a clean public IP and run:
apt-get update\
&& apt-get -y install vim dnsutils curl sudo\
&& curl -sSL https://get.docker.com/ | sh\
&& mkdir -p ~/netflix-proxy\
&& cd ~/netflix-proxy\
&& curl -L https://github.com/ab77/netflix-proxy/archive/latest.tar.gz\
| tar xz --strip-components=1\
&& ./build.sh
See the Wiki page(s) for some common troubleshooting ideas.
netflix-proxy is a smart DNS proxy to stream Netflix, Hulu[n2], HBO Now and others out of region. It is deployed using Docker containers and uses dnsmasq and sniproxy[n1] to provide SmartDNS services. It can also be used to bypass[n17] The Great Firewall and works for some blocked sites, such as PornHub. And if you happen to live in Germany and want to watch YouTube like the rest of the world does, just add googlevideo.com to dnsmasq.conf file and run docker restart dnsmasq.
 Update March/2017: Raspberry Pi un-blocking solution http://unzoner.com/ is live and works on all devices. You'll need to supply your own Raspberry Pi or compatible device. Subscribe to the mailing list and be notified of new features, updates, etc.
Update March/2017: Raspberry Pi un-blocking solution http://unzoner.com/ is live and works on all devices. You'll need to supply your own Raspberry Pi or compatible device. Subscribe to the mailing list and be notified of new features, updates, etc.
If you have access to a high-speed residential Internet connection and would like to have your ISP fees paid in exchange for hosting a small piece of kit, please email [email protected] your interest.
The following are supported out of the box, however adding additional services is trivial and is done by updating dnsmasq.conf file and running docker restart dnsmasq:
- Netflix
- Hulu[n2]
- HBO Now
- Amazon Instant Video
- Crackle
- Pandora
- Vudu
- blinkbox
- BBC iPlayer[n5]
- NBC Sports and potentially many more
This project is free, covered by the MIT License. It is provided without any warranty and can be used for any purpose, including private and commercial. However, if you are planning to use it for commercial purposes (i.e make money off it), please do not expect free support, as it would be unfair. A commercial support model can always be negotiated, if required. Please contact me if this is something that interests you.
The following paragraphs show how to get this solution up and running with a few different Cloud providers I've tried so far. If you prefer a video tutorial, here is one prapared by one of the users. Note, OpenVZ won't work[n15], make sure to get a proper virtual machine using KVM or Xen.
(Netflix is blocked[n16]) The following is based on a standard Ubuntu Docker image provided by DigitalOcean, but should in theory work on any Linux distribution with Docker pre-installed.
- Head over to Digital Ocean to get $10 USD credit
- Create a Droplet in a geographic location of interest using the latest Docker image (find in under
One-click Appstab). - SSH to your server and run:
mkdir -p ~/netflix-proxy\
&& cd ~/netflix-proxy\
&& curl -L https://github.com/ab77/netflix-proxy/archive/latest.tar.gz\
| tar xz --strip-components=1\
&& ./build.sh
- Make sure to record the URL and credentials for the
netflix-proxyadmin site. - Set your DNS server to the IP given at the end of the script, then go to this site to make sure the same IP is displayed.
- Finally, enjoy
Netflixand others out of region. - Enjoy or raise a new issue if something doesn't work quite right (also
#netflix-proxyon freenode).
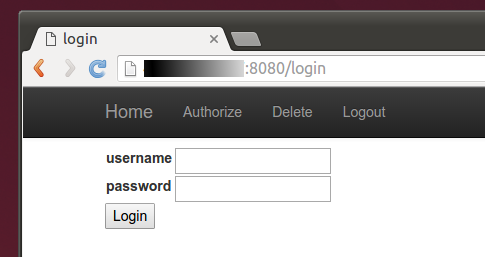
If you want to share your system with friends and family, you can authorise their home IP address(s) using the netflix-proxy admin site, located at http://<ipaddr>:8080/, where ipaddr is the public IP address of your VPS. Login using admin account with the password you recorded during the build. If you've forgotten your admin credentials, reset.
The admin account does not restrict the entry or removal of IPs. If you want to restrict the entry of IPs to the current client IP using an automatically populated drop-down, create a standard user account using the account-creator.sh script located in the auth directory, which will prompt you for the input and create the user account.
You can also use the netflix-proxy admin site to update your IP address, should your ISP assign you a new one (e.g. via DHCP). If your IP address does change, all HTTP/HTTPS requests will automatically be redirected to the admin site on port 8080. All DNS requests will be redirected to dnsmasq instance running on port 5353. You will most likely need to purge your browser and system DNS caches after this. On Windows, run ipconfig /flushdns. On OS X, run:
sudo killall -HUP mDNSResponder\
&& sudo dscacheutil -flushcache`
Then restart the browser (e.g chrome://restart) and/or reboot the relevant devices. This mechanism should work on browsers, but will most likely cause errors on other devices, such as Apple TVs and smart TVs. If you Internet stops working all of a sudden, try loading a browser and going to netflix.com.
- to automatically authorise client IP using a script (where
ipaddris the public IP address of your VPS), substitute admin credentials and run:
curl -L http://<ipaddr>:8080/autoadd?username=<admin-username>&password=<admin-password>
- to manually authorise a specific IP, substitute admin credentials and run:
curl -L http://<ipaddr>:8080/autoadd?ip=<your-public-ipaddr>&username=<admin-username>&password=<admin-password>
WARNING: do not do enable this unless you know what you are doing.
To enable automatic authorization of every IP that hits your proxy, set AUTO_AUTH = True in auth/settings.py and run service netflix-proxy-admin restart. This setting will effectively authorize any IP hitting your proxy IP with a web browser for the first time, including bots, hackers, spammers, etc. Upon successful authorization, the browser will be redirected to Google.
The DNS service is configured with recursion turned on by default, so after a successful authorization, anyone can use your VPS in DNS amplification attacks, which will probably put you in breach of contract with the VPS provider. You have been WARNED.
The build script automatically configures the system with DNS recursion turned on. This has security implications, since it potentially opens your DNS server to a DNS amplification attack, a kind of a DDoS attack. This should not be a concern however, as long as the iptables firewall rules configured automatically by the build script for you remain in place. However if you ever decide to turn the firewall off, please be aware of this.
The following command line options can be optionaly passed to build.sh for additional control:
Usage: ./build.sh [-b 0|1] [-c <ip>]
-b grab docker images from repository (0) or build locally (1) (default: 0)
-c specify client-ip instead of being taken from ssh_connection
In order to update your existing database schema, please run the provided update.sh script. Alternatively you can run the schema updates manually (e.g. if you skipped a version).
The build script has been designed to work on Ubuntu and Debian. It will most likely fail on all other distributions. Some pre-requisites require the locale to be set correctly and some provider OS images need extra help. If you get locale issues reported by Python and/or pip during the build, try running the following first:
export LANGUAGE=en_US.UTF-8\
&& export LANG=en_US.UTF-8\
&& export LC_ALL=en_US.UTF-8\
&& export LC_CTYPE="en_US.UTF-8"\
&& locale-gen en_US.UTF-8\
&& sudo apt-get -y install language-pack-en-base\
&& sudo dpkg-reconfigure locales
(Netflix is blocked[n16]) The following is based on a Debian image provided by Vultr, but should in theory work on any Debian distribution.
- For a limited time, head over to Vultr to create and account and get $20 USD credit.
- Create a compute instance in a geographic location of interest using Debian or Ubuntu image.
- SSH to your server and run:
apt-get update\
&& apt-get -y install vim dnsutils curl sudo\
&& curl -sSL https://get.docker.com/ | sh\
&& mkdir -p ~/netflix-proxy\
&& cd ~/netflix-proxy\
&& curl -L https://github.com/ab77/netflix-proxy/archive/latest.tar.gz\
| tar xz --strip-components=1\
&& ./build.sh
- Make sure to record the credentials for the
netflix-proxyadmin site. - Set your DNS server to the IP given at the end of the script, then go to this site to make sure the same IP is displayed.
- Finally, enjoy
Netflixand others out of region. - Enjoy or raise a new issue if something doesn't work quite right (also
#netflix-proxyon freenode).
(Netflix is blocked[n16]) The following is based on a standard Ubuntu image provided by Kamatera.
- Head over to Kamatera to start your 30 Day Free Trial.
- Create a new server in a geographic location of interest using Ubuntu or Debian image.
- SSH to your server and run:
apt-get update\
&& apt-get -y install vim dnsutils curl sudo\
&& curl -sSL https://get.docker.com/ | sh\
&& mkdir -p ~/netflix-proxy\
&& cd ~/netflix-proxy\
&& curl -L https://github.com/ab77/netflix-proxy/archive/latest.tar.gz\
| tar xz --strip-components=1\
&& ./build.sh
- Make sure to record the URL and credentials for the
netflix-proxyadmin site. - Set your DNS server to the IP given at the end of the script, then go to this site to make sure the same IP is displayed.
- Finally, enjoy
Netflixand others out of region. - Enjoy or raise a new issue if something doesn't work quite right (also
#netflix-proxyon freenode).
(Netflix is blocked[n16]) The following is based on a Debian or Ubuntu images provided by RamNode.
- Head over to RamNode to create an account and buy a KVM VPS in a geographic location of interest (OpenVZ won't work).
- Log into the
VPS Control Paneland (re)install the OS using Ubuntu or Debian image. - SSH to your server and run:
apt-get update\
&& apt-get -y install vim dnsutils curl sudo\
&& curl -sSL https://get.docker.com/ | sh\
&& mkdir -p ~/netflix-proxy\
&& cd ~/netflix-proxy\
&& curl -L https://github.com/ab77/netflix-proxy/archive/latest.tar.gz\
| tar xz --strip-components=1\
&& ./build.sh
- Make sure to record the credentials for the
netflix-proxyadmin site. - Set your DNS server to the IP given at the end of the script, then go to this site to make sure the same IP is displayed.
- Finally, enjoy
Netflixand others out of region. - Enjoy or raise a new issue if something doesn't work quite right (also
#netflix-proxyon freenode).
(Netflix is blocked[n16]) The following is based on a standard Ubuntu image provided by Linode, but should work on any Linux distribution without Docker installed.
- Head over to Linode and sign-up for an account.
- Create a new
Linodein a geographic location of interest and deploy an Ubuntu image into it. - SSH to your server and run:
apt-get update\
&& apt-get -y install vim dnsutils curl sudo\
&& curl -sSL https://get.docker.com/ | sh\
&& mkdir -p ~/netflix-proxy\
&& cd ~/netflix-proxy\
&& curl -L https://github.com/ab77/netflix-proxy/archive/latest.tar.gz\
| tar xz --strip-components=1\
&& ./build.sh
- Make sure to record the credentials for the
netflix-proxyadmin site. - Set your DNS server to the IP given at the end of the script, then go to this site to make sure the same IP is displayed.
- Finally, enjoy
Netflixand others out of region. - Enjoy or raise a new issue if something doesn't work quite right (also
#netflix-proxyon freenode).
(untested) The following is based on a standard Ubuntu image provided by DreamHost, but should work on any Linux distribution without Docker installed and running under non-root user (e.g. Amazon Web Services[n13]).
- Head over to DreamHost and sign-up for an account.
- Find the
DreamComputeorPublic Cloud Computingsection and launch an Ubuntu instance in a geographic location of interest. - Make sure to add an additional firewall rule to allow DNS:
Ingress - IPv4 - UDP - 53 - 0.0.0.0/0 (CIDR) - Also add a
Floating IPto your instance. - SSH to your server and run:
sudo apt-get update\
&& sudo apt-get -y install vim dnsutils curl\
&& curl -sSL https://get.docker.com/ | sh\
&& sudo usermod -aG docker $(whoami | awk '{print $1}')\
&& mkdir -p ~/netflix-proxy\
&& cd ~/netflix-proxy\
&& curl -L https://github.com/ab77/netflix-proxy/archive/latest.tar.gz\
| tar xz --strip-components=1\
&& ./build.sh
- Make sure to record the credentials for the
netflix-proxyadmin site. - Set your DNS server to the IP given at the end of the script, then go to this site to make sure the same IP is displayed.
- Finally, enjoy
Netflixand others out of region. - Enjoy or raise a new issue if something doesn't work quite right (also
#netflix-proxyon freenode).
The following is based on Ubuntu image provided by Gandi using root login with SSH key only (no password). For default non-root admin login, adjust step 6 to use sudo where nesessary.
- Head over to Gandi to create a virtual server in a geographic location of interest.
- SSH to your server and run:
apt-get update\
&& apt-get -y install vim dnsutils curl sudo\
&& curl -sSL https://get.docker.com/ | sh\
&& mkdir -p ~/netflix-proxy\
&& cd ~/netflix-proxy\
&& curl -L https://github.com/ab77/netflix-proxy/archive/latest.tar.gz\
| tar xz --strip-components=1\
&& ./build.sh
- Make sure to record the credentials for the
netflix-proxyadmin site. - Set your DNS server to the IP given at the end of the script, then go to this site to make sure the same IP is displayed.
- Finally, enjoy
Netflixand others out of region. - Enjoy or raise a new issue if something doesn't work quite right (also
#netflix-proxyon freenode).
The following has not been tested and is based on a standard Ubuntu image provided by Microsoft Azure using cloud-harness automation tool I wrote a while back and assumes an empty Microsoft Azure subscription. Also, because Azure block ICMP thorough the load-balancer and don't offer native IPv6 support, IPv6 isn't going to work.
- Head over to Microsoft Azure and sign-up for an account.
- Get Python.
- On your workstation, run
git clone https://github.com/ab77/cloud-harness.git ~/cloud-harness. - Follow
cloud-harnessInstallation and Configuration section to set it up. - Create a storage account.
- Create a new hosted service.
- Add a hosted service certificate for SSH public key authentication
- Create a reserved ip address.
- Create a virtual network.
- Create a Ubuntu virtual machine as follows:
./cloud-harness.py azure --action create_virtual_machine_deployment \
--service <your hosted service name> \
--deployment <your hosted service name> \
--name <your virtual machine name> \
--label 'Netflix proxy' \
--account <your storage account name> \
--blob b39f27a8b8c64d52b05eac6a62ebad85__Ubuntu-14_04-LTS-amd64-server-20140414-en-us-30GB \
--os Linux \
--network VNet1 \
--subnet Subnet-1 \
--ipaddr <your reserved ipaddr name> \
--size Medium \
--ssh_auth \
--disable_pwd_auth \
--verbose
- Use the Azure Management Portal to add
DNS (UDP),HTTP (TCP)andHTTPS (TCP)endpoints and secure them to your home/work/whatever IPs using the AzureACLfeature. - SSH to your VM as
azureuserusing custom public TCP port (not22) and use any non-root user Ubuntu instructions to build/installnetflix-proxy.
This project is linked with Travis CI to deploy and test the project automatically. The Python script testbuild.py is used to deploy and test netflix-proxy. This script deploys a test Droplet and then runs a serious of tests to verify (a) that all Docker containers start; (b) the built.sh script outputs the correct message at the end; (c) all the relevant services survive a reboot; and (d) proxy is able to comunicate with Netflix over SSL.
The testbuild.py script can also be used to programatically deploy Droplets from the command line:
usage: testbuild.py digitalocean [-h] --api_token API_TOKEN
[--client_ip CLIENT_IP]
[--fingerprint FINGERPRINT [FINGERPRINT ...]]
[--region REGION] [--branch BRANCH]
[--create] [--destroy] [--list_regions]
[--name NAME]
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
--api_token API_TOKEN
DigitalOcean API v2 secret token
--client_ip CLIENT_IP
client IP to secure Droplet
--fingerprint FINGERPRINT [FINGERPRINT ...]
SSH key fingerprint
--region REGION region to deploy into; use --list_regions for a list
--branch BRANCH netflix-proxy branch to deploy (default: master)
--create Create droplet
--destroy Destroy droplet
--list_regions list all available regions
--name NAME Droplet name
Note, you will need a working Python 2.7 environment and the modules listed in tests/requirements.txt (run pip install -r tests/requirements.txt).
Video playback tests are currently disabled due to provider blocking.
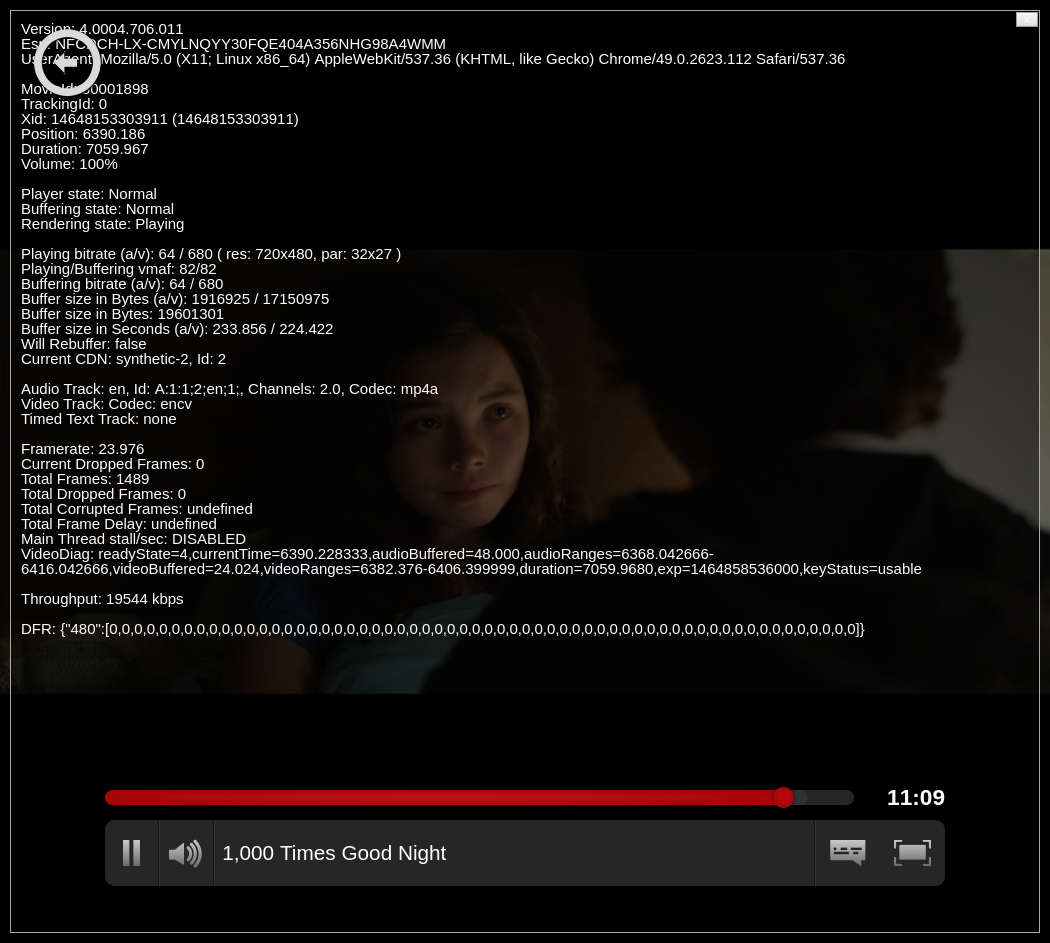
After a successful build deployment, testvideo.py is executed to test Netflix video playback. This is done by playing back 60 seconds of a title known to only be available in the US region (e.g. 1,000 Times Good Night).
usage: testvideo.py netflix [-h] --email EMAIL --password PASSWORD
[--seconds SECONDS] [--titleid TITLEID]
[--tries TRIES]
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
--email EMAIL Netflix username
--password PASSWORD Netflix password
--seconds SECONDS playback time per title in seconds (default: 60)
--titleid TITLEID Netflix title_id to play (default: 80001898)
--tries TRIES Playback restart attempts (default: 4)
A screenshot is saved at the end of the test and uploaded to the gh-pages branch.
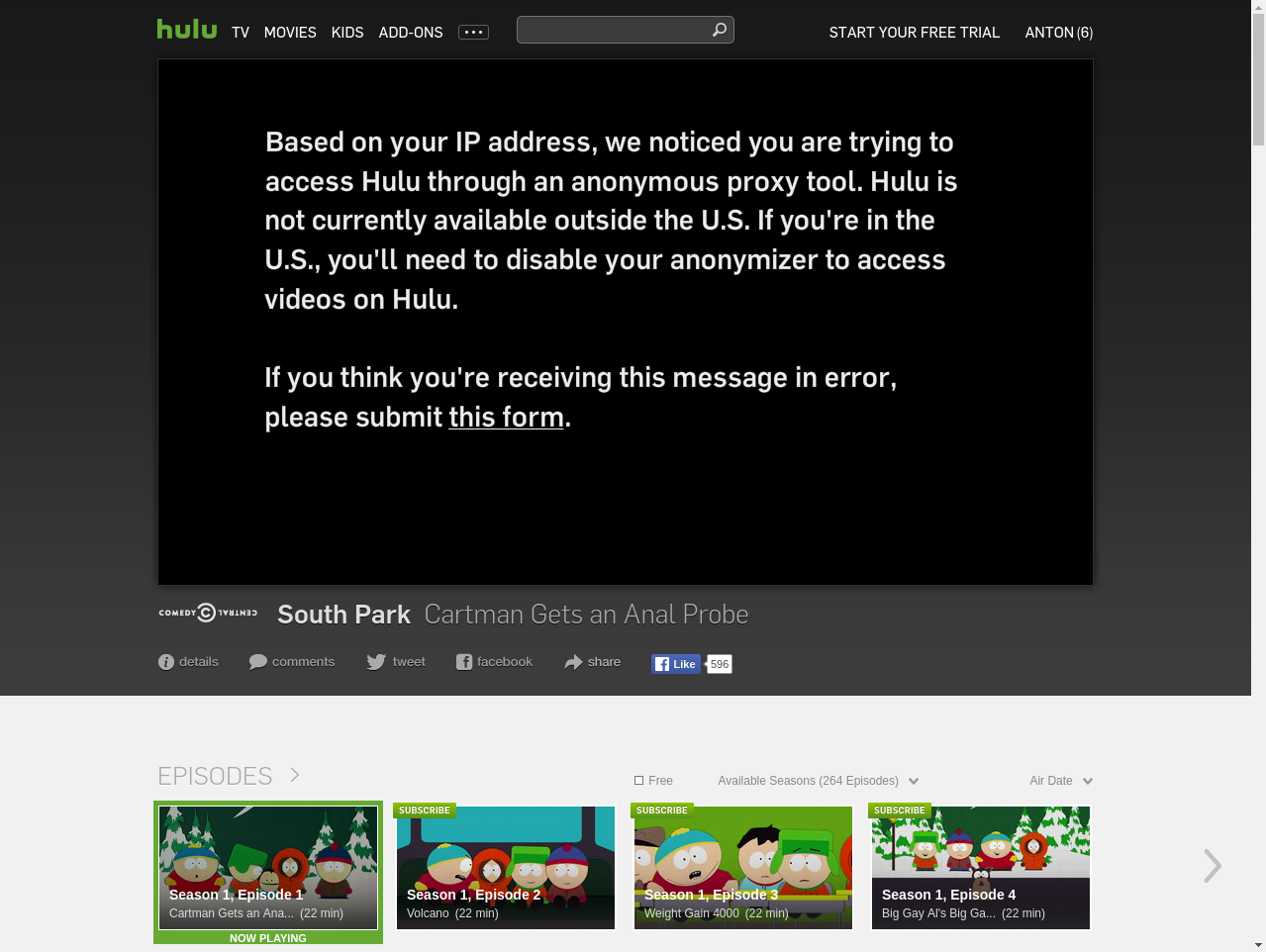
Similarly, testvideo.py is executed to test Hulu video playback using one of the free titles (e.g. South Park S01E01: Cartman Gets an Anal Probe). The build is configured not to fail in the event of Hulu test failing. This is because Hulu is almost cetrtainly blocked from Digital Ocean.
This solution uses IPv6 downstream from the proxy to unblock IPv6 enabled providers, such as Netflix. No IPv6 support on the client is required for this to work, only the VPS must have public IPv6 connectivity. You may also need to turn off IPv6 on your local network (and/or relevant devices).[n6]
+----------+ +-----------+ +-----------------+
| | | | | |
| client | +--------------> | proxy | +-------------> | Netflix, etc. |
| | (ipv4) | | (ipv6) | |
+----------+ +-----------+ +-----------------+
If you have any idea, feel free to fork it and submit your changes back to me.
If you find this useful, please feel free to make a small donation with PayPal or Bitcoin.
| Paypal | Bitcoin |
|---|---|
 |
 1GUrKgkaCkdsrCzb4pq3bJwkmjTVv9X7eG 1GUrKgkaCkdsrCzb4pq3bJwkmjTVv9X7eG |
- SNIProxy by Dustin Lundquist
[email protected]; this solution will only on devices supporting Server Name Indication (SNI)[n7] and only if they use DNS to resolve names. Huluis heavily geo-restricted from most non-residential IP ranges and doesn't support IPv6.- You can now specify your home/office/etc. IP manually using
-c <ip>option tobuild.sh. - See, serverfault post.
- See, this and this. The following four hosts all need to resolve to different public IPs.
- If you have a working IPv6 stack, then your device may be preferring it over IPv4, see this issue.
- See, article.
- See, post.
- See, Using NDP proxying. Both the caching resolver and Docker dual-stack support are disabled by default due to differences in IPv6 configurations provided by various hosting providers (i.e. RamNode).
- See, post.
- See, https://www.facebook.com/GetflixAU/posts/650132888457824, Netflix Geoblocking - Part 2 and read How Netflix is blocking VPNs and Wiki.
- Bypass Netflix Geoblocks with IPv6.
- See, IPv6 on Amazon AWS EC2.
- If Netflix still thinks you are in a wrong country, try a different tunnel server (e.g. in a US location).
- See, article.
- Netflix have most definitely blocked this service provider network ranges, so following the process is unlikely to yield an unblocking solution. If you own a compatible device, you could try
black.boxunzoner. - GFW is probably re-writing DNS responses for certain very sensitive domains (i.e. facebook.com), so unfortunately a simple proxy solution like this won't work. VPN technology is required to bypass, try
black.boxunzoner.
-- v3.0
© 2016 ab1