English | 简体中文
ymdb is a simple distributed key-value storage system.
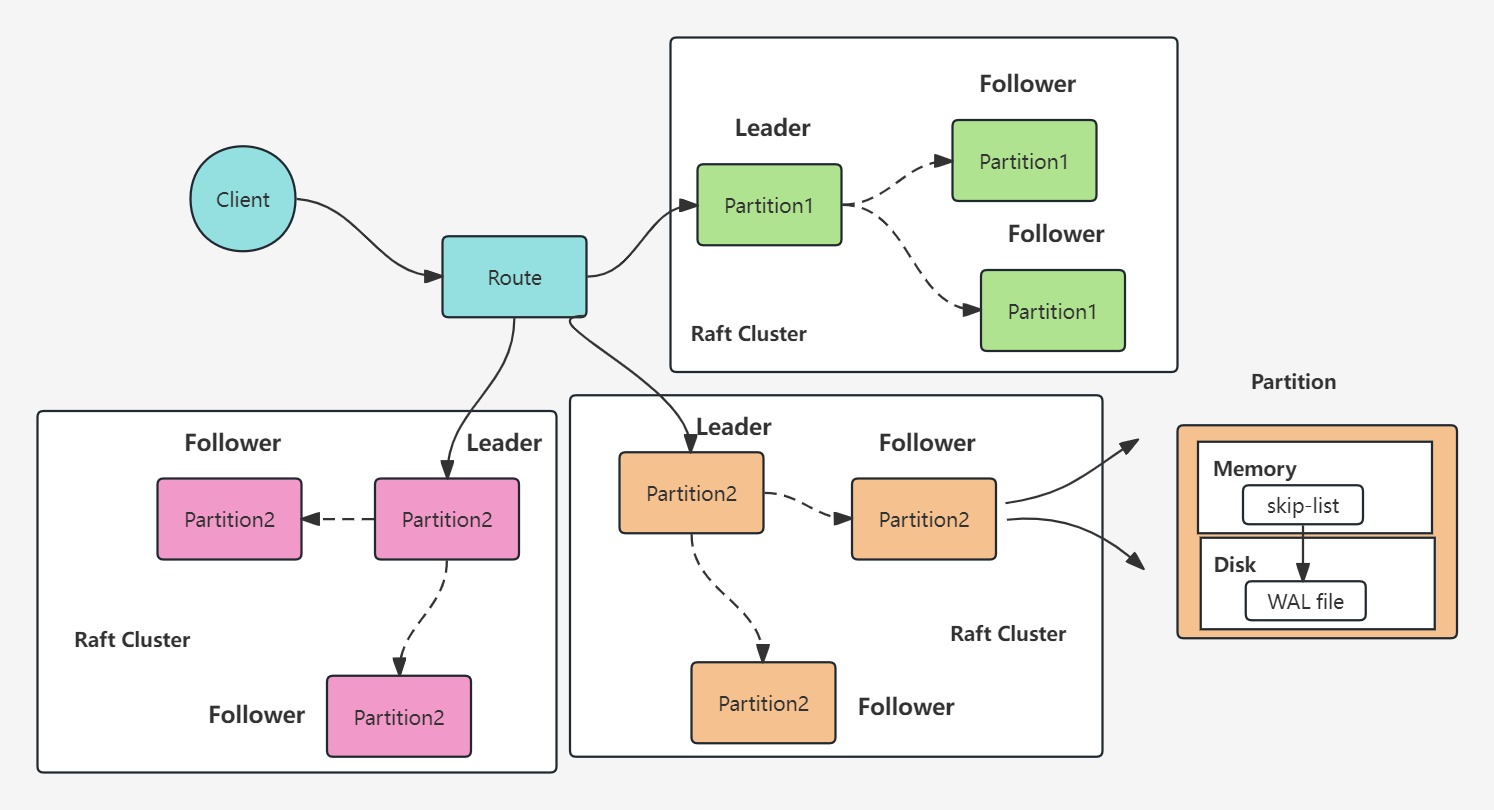
ymdb maintains a skip-list in memory to speed up key retrieval and stores values in WAL files on disk.
You can run ymdb on a cluster, distributed ymdb uses the raft protocol for distributed consensus and a consistent hashing algorithm for data partitioning and load balancing.
ymdb also supports crash consistency.
Before running ymdb, you need to prepare some directories:
- wal file directory: you can set wal file directory in
./config/ymDB.yamlor set wal file directory by flags when executemain(eg../main --store_file_path ./wal/store --restore_file_path ./wal/restore). - raft data directory: you can set raft data directory by flags when execute
main(eg../main --raft_data_dir ./ymdb-cluster)
For a more detailed directory organization and setup, see the example under example folder.
An example of ymdb running on a cluster is provided under the example folder:
Start an ymdb cluster by executing the following script under the ymdb project folder:
./example/run_ymdb_cluster.shNow you have ymdb running on a nine-node cluster with three partitions.
You can then run a cluster client and interact with the ymdb cluster by executing the following script:
./example/run_cluster_client.shFirstly, use the following command to pull the Docker image of the ymdb server:
docker pull yoonamessi/ymdb:0.1Then, use the following command to run a Docker container:
docker run -v ${your_host_store_path}:${path_in_ymDB.yaml} -v ${your_host_restore_path}:${path_in_ymDB.yaml} -p ${host_port}:${port_in_ymDB.yaml} -d ymdb:0.1This is an example:
docker run -v /root/ymdbdata/walDir/store:/root/ymdb/walDir/store -v /root/ymdbdata/walDir/restore:/root/ymdb/walDir/restore -p 8099:8099 -d ymdb:0.1Run the following command to start a ymdb client(Note that the port connected by the client must match the port exposed by the container to the host):
go run ymDB-cli.goThen you can manipulate ymdb through the database client.
Using put [key] [value] to store a KV pair to the database.
Using get [key] to get the value of the key.
Using delete [key] to delete a KV pair.
The benchmark result is a bit weird because put doesn't have to wait for ymdb to return, get needs to get the query result, and there's also the overhead involved in the communication.
goos: windows
goarch: amd64
pkg: github.com/lim-yoona/ymdb/benchmark
cpu: 12th Gen Intel(R) Core(TM) i7-12650H
BenchmarkPutGet
BenchmarkPutGet/put
BenchmarkPutGet/put-16 339727 2994 ns/op 2392 B/op 40 allocs/op
BenchmarkPutGet/get
BenchmarkPutGet/get-16 915457 2891 ns/op 2186 B/op 37 allocs/op
PASS