Velox is an R package for performing fast extraction and manipulation operations on geographic raster data. velox is fast because all raster computations are performed in C++ (using the excellent Rcpp API), and all data is held in memory. velox is intended to be used together with the raster package, to which it provides a straightforward interface.
Currently, the following operations are implemented in velox:
- Focal value calculation (i.e. moving window filters)
- Raster value extraction given polygons
- Rasterization of polygons
- Raster aggregation
- Cropping
- Image patch flattening (similar to Matlab's im2col) and reconstruction
The development of velox was funded in part by the Swiss National Science Foundation under COST action IS1107, SERI project C12.0087.
Velox should work on all major operating systems (Linux, Mac OS, Windows).
For its read and write methods, velox requires the rgdal package, which relies on the external GDAL (>= 1.6.3) and PROJ.4 (>= 4.4.9) libraries. On Debian/Ubuntu (>= 12.04), GDAL and PROJ.4 can be installed by entering
sudo apt-get install libgdal-dev libproj-devin a terminal. Further, velox depends on the rgeos package, which in turn requires the external GEOS library (>= 3.2.0). To install GEOS on Debian/Ubuntu (>= 12.04), enter
sudo apt-get install libgeos-devin a terminal.
Once the system dependencies are available, you can either install velox from CRAN
install.packages("velox")or you can install the development version using the install_github function from the devtools package:
library(devtools)
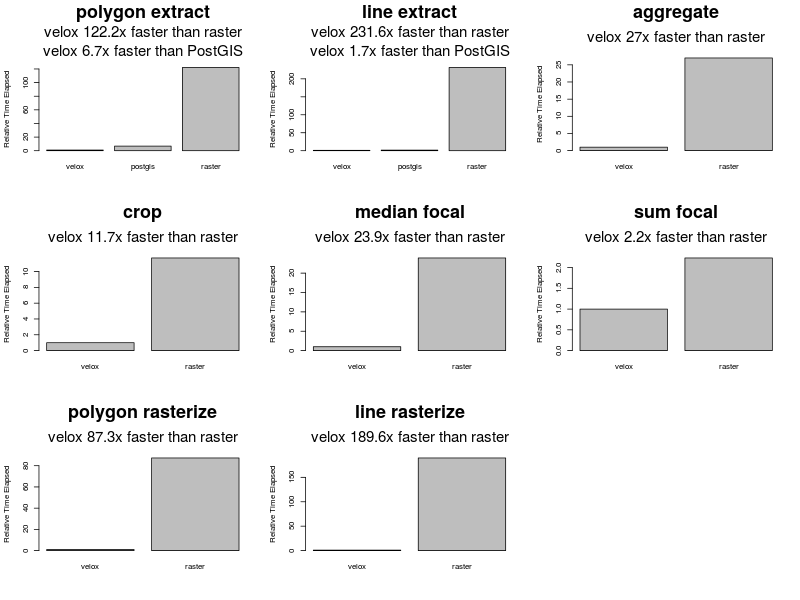
install_github("hunzikp/velox")The following performance tests were peformed on a i7-6920HQ CPU @ 2.90GHz, using raster 2.5-8, PostgreSQL 9.5 and PostGIS 2.2.
See here for the underlying R script.
VeloxRaster objects are created with the velox function:
library(velox)
library(raster)
## From GDAL readable raster file
vx1 <- velox("myraster.tif")
## From RasterLayer object
rl <- raster("myraster.tif")
vx2 <- velox(rl)
## From RasterStack object
rs <- stack("myraster.tif")
vx3 <- velox(rs)
## From matrix
mat <- matrix(1:100, 10, 10)
vx4 <- velox(mat, extent=c(0,1,0,1), res=c(0.1,0.1), crs="+proj=longlat +datum=WGS84 +no_defs")
## From list of matrices
mat.ls <- list(matrix(1:100, 10, 10), matrix(100:1, 10, 10))
vx5 <- velox(mat.ls, extent=c(0,1,0,1), res=c(0.1,0.1), crs="+proj=longlat +datum=WGS84 +no_defs")
## From list of VeloxRasters
vx.ls <- list(vx4, vx5)
vx6 <- velox(vx.ls)VeloxRaster objects are ReferenceClass objects and thus mutable:
## Crop VeloxRaster
mat <- matrix(1:100, 10, 10)
vx <- velox(mat, extent=c(0,1,0,1), res=c(0.1,0.1), crs="+proj=longlat +datum=WGS84 +no_defs")
cropext <- c(0.3,0.7,0.3,0.7)
vx$crop(cropext)
> vx$extent
[1] 0.3 0.7 0.3 0.7We can also aggregate a VeloxRaster...
## Aggregate VeloxRaster
mat <- matrix(1:100, 10, 10)
vx <- velox(mat, extent=c(0,1,0,1), res=c(0.1,0.1), crs="+proj=longlat +datum=WGS84 +no_defs")
vx$aggregate(factor=c(2,2), aggtype="sum")... or calculate focal values (i.e. apply a moving window filter):
## Apply filter to VeloxRaster
mat <- matrix(1:100, 10, 10)
vx <- velox(mat, extent=c(0,1,0,1), res=c(0.1,0.1), crs="+proj=longlat +datum=WGS84 +no_defs")
vx$medianFocal(wrow=3, wcol=3, bands=1)## Make VeloxRaster
mat <- matrix(1:100, 10, 10)
extent <- c(0,1,0,1)
vx <- velox(mat, extent=extent, res=c(0.1,0.1), crs="+proj=longlat +datum=WGS84 +no_defs")
## Make SpatialPolygonsDataFrame
library(sp)
library(rgeos)
set.seed(0)
coords <- cbind(runif(10, extent[1], extent[2]), runif(10, extent[3], extent[4]))
sp <- SpatialPoints(coords)
spol <- gBuffer(sp, width=0.2, byid=TRUE)
spdf <- SpatialPolygonsDataFrame(spol, data.frame(id=1:length(spol)), FALSE)
## Extract values and calculate mean
ex.mat <- vx$extract(spdf, fun=mean)## Make VeloxRaster
mat <- matrix(0, 10, 10)
extent <- c(0,1,0,1)
vx <- velox(mat, extent=extent, res=c(0.1,0.1), crs="+proj=longlat +datum=WGS84 +no_defs")
## Make SpatialPolygonsDataFrame
library(sp)
library(rgeos)
set.seed(0)
coords <- cbind(runif(10, extent[1], extent[2]), runif(10, extent[3], extent[4]))
sp <- SpatialPoints(coords)
spol <- gBuffer(sp, width=0.05, byid=TRUE)
spdf <- SpatialPolygonsDataFrame(spol, data.frame(id=1:length(spol)), FALSE)
## Rasterize polygons using "id" column
vx$rasterize(spdf, field="id", band=1)## Make VeloxRaster with two bands
mat1 <- matrix(1, 10, 10)
mat2 <- matrix(2, 10, 10)
extent <- c(0,1,0,1)
vx <- velox(list(mat1, mat2), extent=extent, res=c(0.1,0.1), crs="+proj=longlat +datum=WGS84 +no_defs")
## Cast band 1 as RasterLayer
rl <- vx$as.RasterLayer(band=1)
## Cast both bands as RasterStack
rs <- vx$as.RasterStack()
## Back to VeloxRaster
vx2 <- velox(rs)Because most of velox's functionality comes in the form of VeloxRaster methods, accessing the help pages is performed as follows:
## See all methods of VeloxRaster
?VeloxRaster
## See help for method 'extract'
?VeloxRaster_extract
## See help for method 'crop'
?VeloxRaster_crop
## etc...