-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 288
How to add λ PostgreSQL Notification using k8s
Cesar Celis Hernandez edited this page Mar 26, 2022
·
3 revisions
- Reand & understand page: postgresql-kubernetes or any similar page
- Read and understand: How-to-add-a-notification
- Read and understand: minio-bucket-notification-guide
To save events of our MinIO System in a DataBase
$ psql -h 127.0.0.1 -U postgres -d minio_events
minio_events=# select * from bucketevents;
key | value
--------------------+----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
images/myphoto.jpg | {"Records": [{"s3": {"bucket": {"arn": "arn:aws:s3:::images", "name": "images", "ownerIdentity": {"principalId": "minio"}}, "object": {"key": "myphoto.jpg", "eTag": "1d97bf45ecb37f7a7b699418070df08f", "size": 56060, "sequencer": "147CE57C70B31931"}, "configurationId": "Config", "s3SchemaVersion": "1.0"}, "awsRegion": "", "eventName": "s3:ObjectCreated:Put", "eventTime": "2016-10-12T21:18:20Z", "eventSource": "aws:s3", "eventVersion": "2.0", "userIdentity": {"principalId": "minio"}, "responseElements": {}, "requestParameters": {"sourceIPAddress": "[::1]:39706"}}]}
(1 row)- Find any previous cluster:
kind get clusters - Delete previous clusters if any:
kind delete clusters kind - Start by creating the cluster, operator and tenant using our yamls:
kind create cluster --config ~/operator/testing/kind-config.yaml
kubectl apply -k ~/operator/resources
kubectl apply -k ~/operator/examples/kustomization/tenant-lite
- Wait until the cluster is ready with the operator and tenants:
Creating cluster "kind" ...
✓ Ensuring node image (kindest/node:v1.21.1) 🖼
✓ Preparing nodes 📦 📦 📦 📦 📦
✓ Writing configuration 📜
✓ Starting control-plane 🕹️
✓ Installing CNI 🔌
✓ Installing StorageClass 💾
✓ Joining worker nodes 🚜
Set kubectl context to "kind-kind"
You can now use your cluster with:
kubectl cluster-info --context kind-kind
Thanks for using kind! 😊
namespace/minio-operator created
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/tenants.minio.min.io created
serviceaccount/console-sa created
serviceaccount/minio-operator created
clusterrole.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/console-sa-role created
clusterrole.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/minio-operator-role created
clusterrolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/console-sa-binding created
clusterrolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/minio-operator-binding created
configmap/console-env created
service/console created
service/operator created
deployment.apps/console created
deployment.apps/minio-operator created
namespace/tenant-lite created
secret/storage-configuration created
secret/storage-creds-secret created
secret/storage-user created
tenant.minio.min.io/storage-lite created- Use the Bitnami Helm chart for PostgreSQL installation or any other similar method (you can skip the step if you already have it):
helm repo add bitnami https://charts.bitnami.com/bitnami- Make sure to update the repo:
helm repo update- You should see this output below:
helm repo update
Hang tight while we grab the latest from your chart repositories...
...Successfully got an update from the "minio" chart repository
...Successfully got an update from the "ingress-nginx" chart repository
...Successfully got an update from the "minio-operator" chart repository
...Successfully got an update from the "grafana" chart repository
...Successfully got an update from the "prometheus-community" chart repository
...Successfully got an update from the "bitnami" chart repository
Update Complete. ⎈Happy Helming!⎈- Create and Apply Persistent Storage Volume
-
The data in your Postgres database need to persist across pod restarts.
-
File name: postgres-pv.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolume
metadata:
name: postgresql-pv
labels:
type: local
spec:
storageClassName: manual
capacity:
storage: 10Gi
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
hostPath:
path: "/mnt/data"- Then apply the configuration with kubectl:
kubectl apply -f ~/postgres-pv.yaml- Create and Apply Persistent Volume Claim
-
Create a Persistent Volume Claim (PVC) to request the storage allocated in the previous step.
-
File name: postgres-pvc.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
metadata:
name: postgresql-pv-claim
spec:
storageClassName: manual
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
resources:
requests:
storage: 10Gi- Apply the configuration with kubectl:
kubectl apply -f ~/postgres-pvc.yaml- You should see the claim is
Bound:
$ kubectl get pvc
NAME STATUS VOLUME CAPACITY ACCESS MODES STORAGECLASS AGE
postgresql-pv-claim Bound postgresql-pv 10Gi RWO manual 9s- Install Helm Chart, make sure to use same
namespaceasMinIOpod, so that they can communicate with each other for the notification.
helm install --namespace tenant-lite psql-test bitnami/postgresql --set persistence.existingClaim=postgresql-pv-claim --set volumePermissions.enable=true- As a result you should see this output below:
helm install --namespace tenant-lite psql-test bitnami/postgresql --set persistence.existingClaim=postgresql-pv-claim --set volumePermissions.enable=true
NAME: psql-test
LAST DEPLOYED: Fri Mar 25 19:01:29 2022
NAMESPACE: tenant-lite
STATUS: deployed
REVISION: 1
TEST SUITE: None
NOTES:
CHART NAME: postgresql
CHART VERSION: 11.1.9
APP VERSION: 14.2.0
** Please be patient while the chart is being deployed **
PostgreSQL can be accessed via port 5432 on the following DNS names from within your cluster:
psql-test-postgresql.tenant-lite.svc.cluster.local - Read/Write connection
To get the password for "postgres" run:
export POSTGRES_PASSWORD=$(kubectl get secret --namespace tenant-lite psql-test-postgresql -o jsonpath="{.data.postgres-password}" | base64 --decode)
To connect to your database run the following command:
kubectl run psql-test-postgresql-client --rm --tty -i --restart='Never' --namespace tenant-lite --image docker.io/bitnami/postgresql:14.2.0-debian-10-r35 --env="PGPASSWORD=$POSTGRES_PASSWORD" \
--command -- psql --host psql-test-postgresql -U postgres -d postgres -p 5432
> NOTE: If you access the container using bash, make sure that you execute "/opt/bitnami/scripts/entrypoint.sh /bin/bash" in order to avoid the error "psql: local user with ID 1001} does not exist"
To connect to your database from outside the cluster execute the following commands:
kubectl port-forward --namespace tenant-lite svc/psql-test-postgresql 5432:5432 &
PGPASSWORD="$POSTGRES_PASSWORD" psql --host 127.0.0.1 -U postgres -d postgres -p 5432- Connect to the DataBase by providing the password via environmental variable and create the table as shown below:
export POSTGRES_PASSWORD=$(kubectl get secret --namespace tenant-lite psql-test-postgresql -o jsonpath="{.data.postgres-password}" | base64 --decode)kubectl run psql-test-postgresql-client --rm --tty -i --restart='Never' --namespace tenant-lite --image docker.io/bitnami/postgresql:14.2.0-debian-10-r35 --env="PGPASSWORD=$POSTGRES_PASSWORD" \
--command -- psql --host psql-test-postgresql -U postgres -d postgres -p 5432CREATE TABLE events (
key serial PRIMARY KEY,
value varchar(30),
event_time timestamp DEFAULT now(),
event_data text
);You should see:
postgres=# CREATE TABLE events (
postgres(# key serial PRIMARY KEY,
postgres(# value varchar(30),
postgres(# event_time timestamp DEFAULT now(),
postgres(# event_data text
postgres(# );
CREATE TABLE- Now you can create the notification either via UI or
mccommands:
-
9443is to access via UI:
kubectl port-forward storage-lite-pool-0-0 9443 --namespace tenant-lite-
9000is to access viamc
kubectl port-forward storage-lite-pool-0-0 9000 --namespace tenant-lite- Te get the
PostgreSQLpassword:
# To get DB password previously set in an environment variable
echo $POSTGRES_PASSWORD- To set the alias via
mcfrom your host afterport-forwardhas been issued:
mc alias set myminio/ https://localhost:9000 minio minio123 --insecure- Connection String:
user=postgres password=ARITtEQLD2 host=psql-test-postgresql dbname=postgres port=5432 sslmode=disable
- Table:
events
- Queue Dir:
blank or empty
- Queue Limit:
10000
- Comment:
any comment is fine
- Save the notification and restart
MinIOeither via UI, or viamc
- To apply the configuration, remember to update the password:
mc admin config set myminio notify_postgres:1 connection_string="user=postgres password=tW207PzjmB host=psql-test-postgresql dbname=postgres port=5432 sslmode=disable" table="events" format="namespace" --insecure- To restart
MinIOServer viamccommand, remember same can be achieved viaConsoleUI:
mc admin service restart myminio --insecure- You should see:
$ mc admin config set myminio notify_postgres:1 connection_string="user=postgres password=tW207PzjmB host=psql-test-postgresql dbname=postgres port=5432 sslmode=disable" table="events" format="namespace" --insecure
Successfully applied new settings.
Please restart your server 'mc admin service restart myminio'.
$ mc admin service restart myminio --insecure
Restart command successfully sent to `myminio`. Type Ctrl-C to quit or wait to follow the status of the restart process.
...
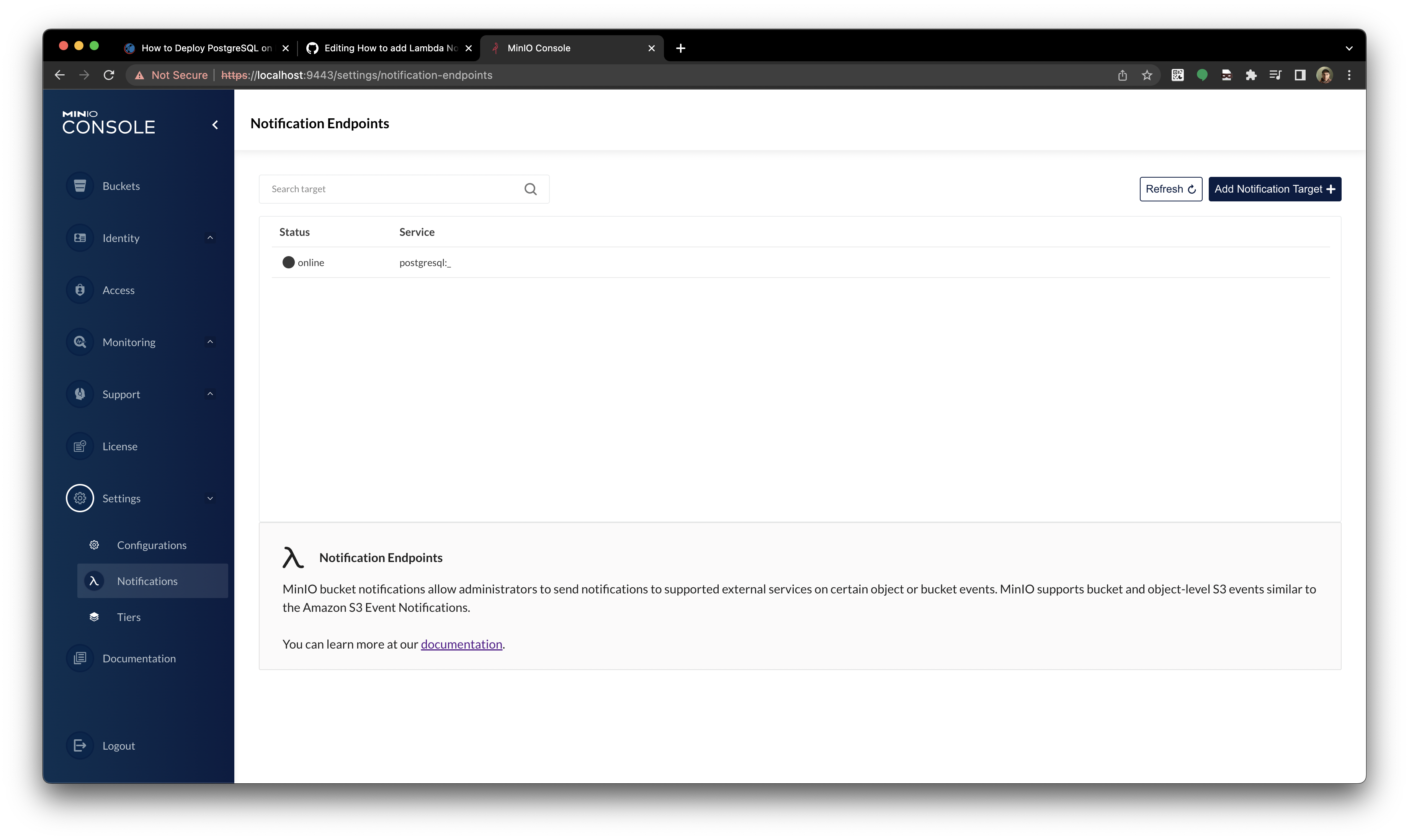
Restarted `myminio` successfully in 2 seconds- Then port-forward again and visit the page, notification was created!:
kubectl port-forward storage-lite-pool-0-0 9443 --namespace tenant-lite