I work on open source full time, which means I 100% rely on donations to make a living. If you find this project helpful, or use it in for commercial purposes, please consider donating to support my work on Patreon or Github Sponsors.
Requirements:
- python >3.10
- Nvidia GPU with enough ram to do what you need
- python venv
- git
Linux:
git clone https://github.com/ostris/ai-toolkit.git
cd ai-toolkit
git submodule update --init --recursive
python3 -m venv venv
source venv/bin/activate
# .\venv\Scripts\activate on windows
# install torch first
pip3 install torch
pip3 install -r requirements.txtWindows:
git clone https://github.com/ostris/ai-toolkit.git
cd ai-toolkit
git submodule update --init --recursive
python -m venv venv
.\venv\Scripts\activate
pip install torch==2.5.1 torchvision==0.20.1 --index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cu124
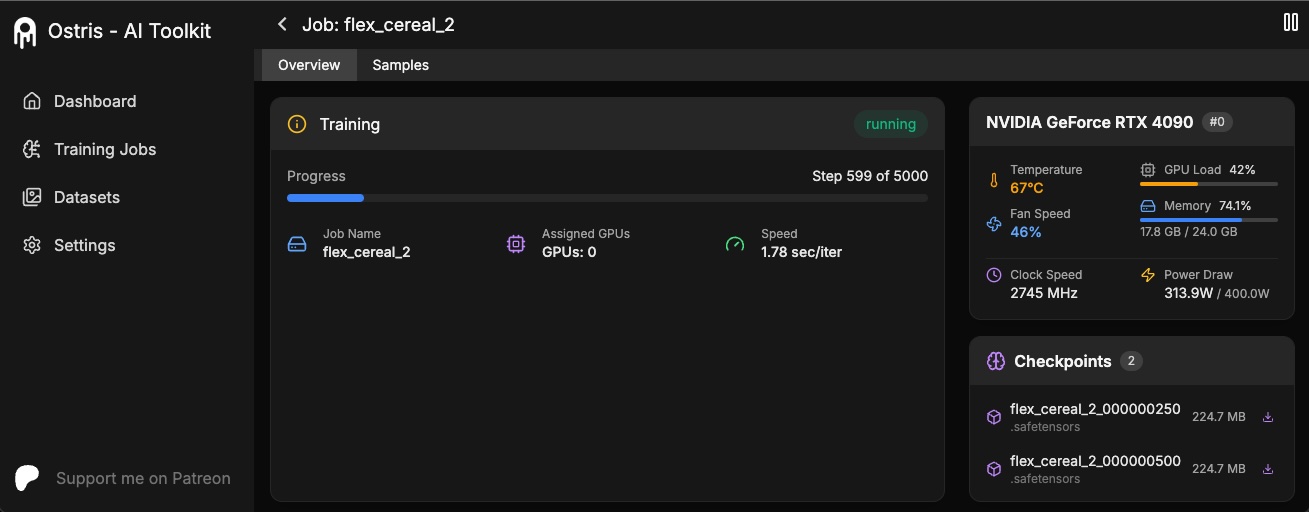
pip install -r requirements.txtThe AI Toolkit UI is a web interface for the AI Toolkit. It allows you to easily start, stop, and monitor jobs. It also allows you to easily train models with a few clicks. It is still in early beta and will likely have bugs and frequent breaking changes. It is currently only tested on linux for now.
WARNING: The UI is not secure and should not be exposed to the internet. It is only meant to be run locally or on a server that does not have ports exposed. Adding additional security is on the roadmap.
Requirements:
- Node.js > 18
You will need to do this with every update as well.
cd ui
npm install
npm run build
npm run update_dbMake sure you built it as shown above. The UI does not need to be kept running for the jobs to run. It is only needed to start/stop/monitor jobs.
cd ui
npm run startYou can now access the UI at http://localhost:8675 or http://<your-ip>:8675 if you are running it on a server.
To get started quickly, check out @araminta_k tutorial on Finetuning Flux Dev on a 3090 with 24GB VRAM.
You currently need a GPU with at least 24GB of VRAM to train FLUX.1. If you are using it as your GPU to control
your monitors, you probably need to set the flag low_vram: true in the config file under model:. This will quantize
the model on CPU and should allow it to train with monitors attached. Users have gotten it to work on Windows with WSL,
but there are some reports of a bug when running on windows natively.
I have only tested on linux for now. This is still extremely experimental
and a lot of quantizing and tricks had to happen to get it to fit on 24GB at all.
FLUX.1-dev has a non-commercial license. Which means anything you train will inherit the non-commercial license. It is also a gated model, so you need to accept the license on HF before using it. Otherwise, this will fail. Here are the required steps to setup a license.
- Sign into HF and accept the model access here black-forest-labs/FLUX.1-dev
- Make a file named
.envin the root on this folder - Get a READ key from huggingface and add it to the
.envfile like soHF_TOKEN=your_key_here
FLUX.1-schnell is Apache 2.0. Anything trained on it can be licensed however you want and it does not require a HF_TOKEN to train. However, it does require a special adapter to train with it, ostris/FLUX.1-schnell-training-adapter. It is also highly experimental. For best overall quality, training on FLUX.1-dev is recommended.
To use it, You just need to add the assistant to the model section of your config file like so:
model:
name_or_path: "black-forest-labs/FLUX.1-schnell"
assistant_lora_path: "ostris/FLUX.1-schnell-training-adapter"
is_flux: true
quantize: trueYou also need to adjust your sample steps since schnell does not require as many
sample:
guidance_scale: 1 # schnell does not do guidance
sample_steps: 4 # 1 - 4 works well- Copy the example config file located at
config/examples/train_lora_flux_24gb.yaml(config/examples/train_lora_flux_schnell_24gb.yamlfor schnell) to theconfigfolder and rename it towhatever_you_want.yml - Edit the file following the comments in the file
- Run the file like so
python run.py config/whatever_you_want.yml
A folder with the name and the training folder from the config file will be created when you start. It will have all checkpoints and images in it. You can stop the training at any time using ctrl+c and when you resume, it will pick back up from the last checkpoint.
IMPORTANT. If you press crtl+c while it is saving, it will likely corrupt that checkpoint. So wait until it is done saving
Please do not open a bug report unless it is a bug in the code. You are welcome to Join my Discord and ask for help there. However, please refrain from PMing me directly with general question or support. Ask in the discord and I will answer when I can.
To get started training locally with a with a custom UI, once you followed the steps above and ai-toolkit is installed:
cd ai-toolkit #in case you are not yet in the ai-toolkit folder
huggingface-cli login #provide a `write` token to publish your LoRA at the end
python flux_train_ui.pyYou will instantiate a UI that will let you upload your images, caption them, train and publish your LoRA

Example RunPod template: runpod/pytorch:2.2.0-py3.10-cuda12.1.1-devel-ubuntu22.04
You need a minimum of 24GB VRAM, pick a GPU by your preference.
- 1x A40 (48 GB VRAM)
- 19 vCPU 100 GB RAM
Custom overrides (you need some storage to clone FLUX.1, store datasets, store trained models and samples):
- ~120 GB Disk
- ~120 GB Pod Volume
- Start Jupyter Notebook
git clone https://github.com/ostris/ai-toolkit.git
cd ai-toolkit
git submodule update --init --recursive
python -m venv venv
source venv/bin/activate
pip install torch
pip install -r requirements.txt
pip install --upgrade accelerate transformers diffusers huggingface_hub #Optional, run it if you run into issues
- Create a new folder in the root, name it
datasetor whatever you like. - Drag and drop your .jpg, .jpeg, or .png images and .txt files inside the newly created dataset folder.
- Get a READ token from here and request access to Flux.1-dev model from here.
- Run
huggingface-cli loginand paste your token.
- Copy an example config file located at
config/examplesto the config folder and rename it towhatever_you_want.yml. - Edit the config following the comments in the file.
- Change
folder_path: "/path/to/images/folder"to your dataset path likefolder_path: "/workspace/ai-toolkit/your-dataset". - Run the file:
python run.py config/whatever_you_want.yml.

git clone https://github.com/ostris/ai-toolkit.git
cd ai-toolkit
git submodule update --init --recursive
python -m venv venv
source venv/bin/activate
pip install torch
pip install -r requirements.txt
pip install --upgrade accelerate transformers diffusers huggingface_hub #Optional, run it if you run into issues
- Run
pip install modalto install the modal Python package. - Run
modal setupto authenticate (if this doesn’t work, trypython -m modal setup).
- Get a READ token from here and request access to Flux.1-dev model from here.
- Run
huggingface-cli loginand paste your token.
- Drag and drop your dataset folder containing the .jpg, .jpeg, or .png images and .txt files in
ai-toolkit.
- Copy an example config file located at
config/examples/modalto theconfigfolder and rename it towhatever_you_want.yml. - Edit the config following the comments in the file, be careful and follow the example
/root/ai-toolkitpaths.
-
Set your entire local
ai-toolkitpath atcode_mount = modal.Mount.from_local_dirlike:code_mount = modal.Mount.from_local_dir("/Users/username/ai-toolkit", remote_path="/root/ai-toolkit") -
Choose a
GPUandTimeoutin@app.function(default is A100 40GB and 2 hour timeout).
- Run the config file in your terminal:
modal run run_modal.py --config-file-list-str=/root/ai-toolkit/config/whatever_you_want.yml. - You can monitor your training in your local terminal, or on modal.com.
- Models, samples and optimizer will be stored in
Storage > flux-lora-models.
- Check contents of the volume by running
modal volume ls flux-lora-models. - Download the content by running
modal volume get flux-lora-models your-model-name. - Example:
modal volume get flux-lora-models my_first_flux_lora_v1.

Datasets generally need to be a folder containing images and associated text files. Currently, the only supported
formats are jpg, jpeg, and png. Webp currently has issues. The text files should be named the same as the images
but with a .txt extension. For example image2.jpg and image2.txt. The text file should contain only the caption.
You can add the word [trigger] in the caption file and if you have trigger_word in your config, it will be automatically
replaced.
Images are never upscaled but they are downscaled and placed in buckets for batching. You do not need to crop/resize your images. The loader will automatically resize them and can handle varying aspect ratios.
To train specific layers with LoRA, you can use the only_if_contains network kwargs. For instance, if you want to train only the 2 layers
used by The Last Ben, mentioned in this post, you can adjust your
network kwargs like so:
network:
type: "lora"
linear: 128
linear_alpha: 128
network_kwargs:
only_if_contains:
- "transformer.single_transformer_blocks.7.proj_out"
- "transformer.single_transformer_blocks.20.proj_out"The naming conventions of the layers are in diffusers format, so checking the state dict of a model will reveal
the suffix of the name of the layers you want to train. You can also use this method to only train specific groups of weights.
For instance to only train the single_transformer for FLUX.1, you can use the following:
network:
type: "lora"
linear: 128
linear_alpha: 128
network_kwargs:
only_if_contains:
- "transformer.single_transformer_blocks."You can also exclude layers by their names by using ignore_if_contains network kwarg. So to exclude all the single transformer blocks,
network:
type: "lora"
linear: 128
linear_alpha: 128
network_kwargs:
ignore_if_contains:
- "transformer.single_transformer_blocks."ignore_if_contains takes priority over only_if_contains. So if a weight is covered by both,
if will be ignored.