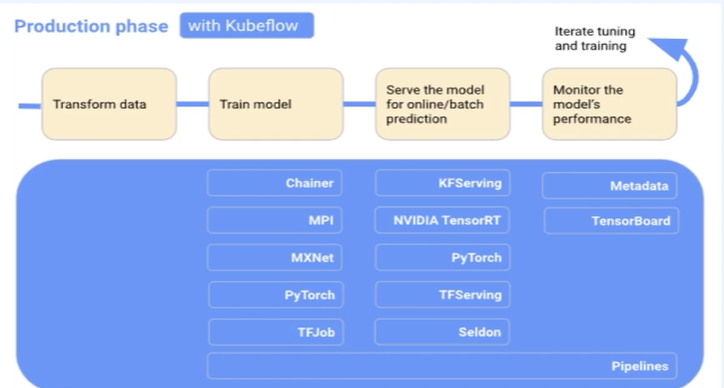
- 실행환경
- 머신러닝 스케쥴관리 , 병렬처리 , 유후자원관리
- 장애 대응, 트래픽 대응
- 컨테이너의 분산처리 및 load balancing
- 작업이 끝났을때 notice 기능도 사용
- 쿠버네티스에 익숙하지 않은 사람이 쿠버네티스를 활용해서 작업을 하고싶을때
- ex) 공유 GPU 사용등
- 정의 → 문제연구 + 데이터 → 훈련 → 하이퍼파라미터 튜닝
- test data → 훈련 → 배포 → 반복
- pytorch, scikit-learn ,tf, xgboost등 z쿠버네티스 위에서 돌릴수 있게 해줌
- data modeling 단계에서
- jupyter notebook, fairing (모듈 패키징) , pipelines
- 하이퍼파라미터 조정을 위해
- Katib
- 외부 serving framework를 쿠버네티스와 쉽게 연동할수있게 도와줌
- web 을 통해 각 요소들 접근가능
- 통합 dash board
- 쿠버네티스위에서 주피터 노트북 실행
- 사용자별 네임스페이스에서 노트북 서버 띄움
- 하지만 결국의 pod형식이기때문에 stateless하다
- 내부에서 작업한 내용을 보존해주지는 않음
- Pvc 기능으로 mount해서 사용해야함
- 가장 중요한 구성요소
- serving 용
- beta 버젼 , 안정되지 않음
- bentoml, seldom core등 연동시켜 사용할수있음
- 가장 리소스많이 필요함
- 하이퍼파라미터 튜닝으로 상당한 시간아낄수있음
- AutoML이라는것
- Job들을 하나로 공통화시킨것
- ex) TFjob
- tensorflow로 작성된 코드를 감싸 job으로 만들고 쿠버네티스위에서 돌리는것
- 각 이런 job들을 모두 합침
- 인증기능
- 유저에게 자원내에서 사용성을 주는것
- 재사용가능한 단위로 나누는 것
- 직접작성하기 어려움
- python code로 작성하면 SDK와 dsl 컴파일러로 ml 파일로 작성해줌
- 다음과같은 4가지 방식으로 실행가
- UI
- python 코드로 작성
- 실행정보 담긴 yaml 파일로 컴파일
- 각각의 step은 pod단위로 구성되어있음
- 결과물들은 airitifact storage에 저장하는 것
- kustomize
- Helm 과 비슷한 역할을 담당
- 여러 개의 yaml 파일들을 쉽게 관리하기 위한 도구
- 여러 resource 들의 configuration 을 템플릿(base)과 커스터마이제이션한 부분(overlay)을 나누어서 관리할 수 있는 도구
kustomize build명령을 통해, base + overlay 가 merge 된 형태의 yaml 파일들을 generate 할 수 있음
- Helm 과 비슷한 역할을 담당
- Kfctl
- v1.2 이후로는 공식적으로 지원하지 않음
- Minikf
- 아직 v1.3 까지만 릴리즈
- kubeflow 가 이미 설치되어있는 VM 이미지를 사용하여 Vagrant 쉽게 설치 가능
- Kubeflow manifests
- 공식 릴리즈 관리용 Repository
- Kustomize v3 기반으로 manifests 파일 관리
- 가장 정석적인 방법
- Kubernetes 환경
- 버전 : v1.17 ~ v1.21
- v1.19.3 사용
- Default StorageClass
- Dynamic provisioning 지원하는 storageclass
- TokenRequest API 활성화
- alpha version 의 API 이므로, k8s APIServer 에 해당 feature gate 를 설정해주어야 함
- 버전 : v1.17 ~ v1.21
- Kustomize
- 버전 : v3.x
- v3.2.0 사용
- 버전 : v3.x
# 바이너리 다운 (for linux amd64)
# 이외의 os 는 https://github.com/kubernetes-sigs/kustomize/releases/tag/v3.2.0 경로에서 binary 링크 확인
wget https://github.com/kubernetes-sigs/kustomize/releases/download/v3.2.0/kustomize_3.2.0_linux_amd64
# file mode 변경
chmod +x kustomize_3.2.0_linux_amd64
# file 위치 변경
sudo mv kustomize_3.2.0_linux_amd64 /usr/local/bin/kustomize
# 버전 확인
kustomize version# minikube start
# docker driver option
# cpu 4 개 할당
# memory 7g 할당
# kubernetes version v.19.3 설정
# --extra-config 부분은 tokenRequest 활성화 관련 설정
minikube start --driver=docker \
--cpus='4' --memory='7g' \
--kubernetes-version=v1.19.3 \
--extra-config=apiserver.service-account-signing-key-file=/var/lib/minikube/certs/sa.key \
--extra-config=apiserver.service-account-issuer=kubernetes.default.svc- 다음과같이 default-storageclass는 기본 addon 활성화
kubeflow/manifests Repository 를 로컬 폴더에 git clone 합니다.
https://github.com/kubeflow/manifests
cd ~/fast-campus-demo/kubeflow-tutorial
# git clone
git clone git@github.com:kubeflow/manifests.git
# 해당 폴더로 이동
cd manifests
# v1.4.0 태그 시점으로 git checkout
git checkout tags/v1.4.0이번 실습에서 사용하지 않는 일부 구성요소는 설치를 진행하지 않습니다.
- Knative, KFServing, Training Operator, MPI Operator
GitHub - kubeflow/manifests at v1.4.0
- kustomize build 의 동작 확인해보기
kustomize build common/cert-manager/cert-manager/base|pipe 연산자를 활용하여, kustomize build 의 결과물을 kubectl apply -f - 하여 적용
- 모든 구성요소가 Running 이 될 때까지 대기
kubectl get po -n kubeflow -w- 상당히 많은 구성요소들의 docker image 를 로컬 머신에 pull 받기 때문에, 최초 실행 시에는 네트워크 상황에 따라 약 30 분 정도까지도 소요될 수 있음
- 여러 구성요소들의 상태가
PodInitializing→ContainerCreating으로 진행되지만 시간이 오래걸리는 경우라면 정상적인 상황이지만, 상태가ErrororCrashLoopBackOff라면 minikube start 시의 설정을 다시 확인해주시기 바랍니다.
- 포트 포워딩
kubectl port-forward svc/istio-ingressgateway -n istio-system 8080:80- gateway 를 포트포워딩하여 localhost:8080 으로 kubeflow 대시보드에 접속
- 접속 정보
- kubeflow manifests 배포 시, user 접속 정보 관련 설정을 변경하지 않은 경우의 default 접속 정보
- ID : [email protected]
- PW : 12341234
- kubeflow manifests 배포 시, user 접속 정보 관련 설정을 변경하지 않은 경우의 default 접속 정보
- kubectx & kubens
- https://github.com/ahmetb/kubectx
- Install 방법도 매우 간편
- kubernetes 의 current-context 와, kubernetes 의 current-namespace 를 변경할 수 있는 툴
- 여러 개의 context 나 namespace 를 다루는 경우에 유용하게 사용할 수 있음
- ex)
kubens kubeflow를 수행하면 현재 바라보고 있는 namespace 가 kubeflow 로 변경됨
- https://github.com/ahmetb/kubectx
- kubectl-alias
- https://github.com/ahmetb/kubectl-aliases
- kubectl 관련 여러 명령어에 대한 alias 를 자동 생성
- 자주 사용하는 명령을 쉽게 수행할 수 있음
- ex)
kubectl get pod→kgpokubectl get deployment -w→kgdepw
- 원하는 이미지로 노트북 pod 띄울수있음
- volum 지정안해주면 정보 다날아감
- object 가져와 Tensorboard 실행가능
- kfserving 등에 사용
- Katib에서 htpo를 1회
- 여러 pipeline을 실행한 결과를 관리
- 논리적인 단위로 grouping해서 모아볼수 있음
- 다양한 파이프라인 예시 튜토리얼많음
- create run으로 pipelineㅇ만들수 있음
- 이때 experiment를 지정해 보일수있음
- 위에서 생성한 pipeline의 형태 순차적으로 설계진행
- Recurring run :
- 스케쥴 정해서 각각 실행시킬수있음
- 동일한 클러스터 사용시 결과 공유
- python 가상환경
- 3.8.9
- pypi 패키지
- kfp
-
pip install kfp --upgrade --use-feature=2020-resolverkfp 1.8.6 kfp-pipeline-spec 0.1.13 kfp-server-api 1.7.0
-
정상 설치 확인
kfp --helpwhich dsl-compile
-
- kfp
- 이전 시간에 설치한 minikube with kubeflow 환경
-
Pipeline 과 Component 의 관계
-
쿠버네티스 관점에서는 다음과 같은 리소스에 매핑
- Pipeline : Workflow
- Component : Pod
-
Pipeline
- kfp sdk 를 사용하여 pipeline 을 구현한 뒤, kfp 의 dsl compiler 즉,
dsl-compile혹은kfp.compiler.Compiler().compile()명령을 사용해 컴파일하면 k8s 가 이해할 수 있는 형태의 yaml 파일이 생성- yaml 파일을 조금 자세히 살펴보면,
kind가 Workflow 로 되어있는 것을 확인할 수 있으며, 작성한 component code 들이 중간중간에 copy - Workflow 라는 리소스는 간단히 말하면 여러 개의 container 들을 정해진 순서에 따라 실행시키고, input/output 을 전달하는 것을 정의한 DAG
- Workflow 는 k8s 의 기본 리소스는 아니지만, kubeflow 설치 시 함께 설치된 여러 모듈중 argpopoj의 workflow-controller에 의해 관리되는 CR(custom Resource)
- yaml 파일을 조금 자세히 살펴보면,
- kfp sdk 를 사용하여 pipeline 을 구현한 뒤, kfp 의 dsl compiler 즉,
-
Component
- kfp sdk 를 사용하여 component 를 구현하면, 그 component 를 사용하는 pipeline 을 컴파일했을 때 생성되는 workflow yaml 파일의
spec.templates에 해당 컴포넌트를 감싼 (containerized) 부분이 추가됩니다.- 하나의 component 는 k8s 상에서는 하나의 독립적인 pod 으로 생성되어 component 내부에 작성된 코드를 component decorator 에 작성한 base_image 환경에서 실행하게 됩니다.
- base_image 지정을 통해 항상 동일한 환경에서 정해진 코드가 실행되는 것을 보장할 수 있습니다.
- 따라서 하나의 pipeline 내에서 연속된 component 라고 하더라도 memory 를 공유하는 일은 일어나지 않으며, 일반적으로 서로 다른 component 간의 data 공유는 input/output 변수 혹은 파일경로로 넘겨주는 방식을 사용합니다.
- (pvc 를 공유하는 방식을 사용할 수도 있습니다.)
- 하나의 component 는 k8s 상에서는 하나의 독립적인 pod 으로 생성되어 component 내부에 작성된 코드를 component decorator 에 작성한 base_image 환경에서 실행하게 됩니다.
- kfp sdk 를 사용하여 component 를 구현하면, 그 component 를 사용하는 pipeline 을 컴파일했을 때 생성되는 workflow yaml 파일의
간단한 python code 를 component 와 pipeline 으로 만들어 본 뒤, kubeflow 에 배포하여 사용해봅니다.
-
먼저 간단한 kubeflow pipeline 을 만드는 example code 를 함께 보며, python code 로 kubeflow pipeline 을 만드는 방법을 살펴봅니다.
-
Add Example.py 코드
# Python 함수를 Component 로 바꿔주는 함수 # decorator 로도 사용할 수 있으며, 여러 옵션을 argument 로 설정할 수 있음 # add_op = create_component_from_func( # func=add, # base_image='python:3.7', # Optional : component 는 k8s pod 로 생성되며, 해당 pod 의 image 를 설정 # output_component_file='add.component.yaml', # Optional : component 도 yaml 로 compile 하여 재사용하기 쉽게 관리 가능 # packages_to_install=['pandas==0.24'], # Optional : base image 에는 없지만, python code 의 의존성 패키지가 있으면 component 생성 시 추가 가능 # ) from kfp.components import create_component_from_func """ kfp.components.create_component_from_func : Python 함수를 Component 로 바꿔주는 함수 decorator 로도 사용할 수 있으며, 여러 옵션을 argument 로 설정할 수 있음 add_op = create_component_from_func( func=add, base_image='python:3.7', # Optional : component 는 k8s pod 로 생성되며, 해당 pod 의 image 를 설정 output_component_file='add.component.yaml', # Optional : component 도 yaml 로 compile 하여 재사용하기 쉽게 관리 가능 packages_to_install=['pandas==0.24'], # Optional : base image 에는 없지만, python code 의 의존성 패키지가 있으면 component 생성 시 추가 가능 ) """ def add(value_1: int, value_2: int) -> int: """ 더하기 """ ret = value_1 + value_2 return ret def subtract(value_1: int, value_2: int) -> int: """ 빼기 """ ret = value_1 - value_2 return ret def multiply(value_1: int, value_2: int) -> int: """ 곱하기 """ ret = value_1 * value_2 return ret # Python 함수를 선언한 후, kfp.components.create_component_from_func 를 사용하여 # ContainerOp 타입(component)으로 convert add_op = create_component_from_func(add) subtract_op = create_component_from_func(subtract) multiply_op = create_component_from_func(multiply) from kfp.dsl import pipeline @pipeline(name="add example") def my_pipeline(value_1: int, value_2: int): task_1 = add_op(value_1, value_2) task_2 = subtract_op(value_1, value_2) # component 간의 data 를 넘기고 싶다면, # output -> input 으로 연결하면 DAG 상에서 연결됨 # compile 된 pipeline.yaml 의 dag 파트의 dependency 부분 확인 # uploaded pipeline 의 그래프 확인 task_3 = multiply_op(task_1.output, task_2.output)
-
pipeline 을 compile 한 뒤, 생성되는 add_pipeline.yaml 을 간단하게 살펴보겠습니다.
- 단, 해당 python code 의 주석에 한글이 들어가면 encoding 문제로 pipeline upload 가 되지 않을 수 있으니, 컴파일 전에는 한글 주석을 모두 제거해주시기 바랍니다.
dsl-compile --py [add.py](http://add.py) --output add_pipeline.yaml
-
add-pipeline.yaml을 kubeflow 에 업로드하고 run 해본 뒤, 결과를 함께 확인해보겠습니다.- graph 를 확인해보고, run 하여 input, output 이 어떻게 넘겨지는지, 최종 output 과 log 는 어떻게 확인할 수 있는지 함께 확인해보겠습니다.
앞서 Quick Start 를 통해 pipeline 을 만들었던 순서를 정리해보고, 앞으로 pipeline 을 만들 때마다 참고하도록 합니다.
- Python 함수를 구현합니다.
- 해당 함수 밖에서 선언된 코드를 사용해서는 안 됩니다.
- import 문까지도 함수 안에 작성되어야 합니다.
- 단, 해당 python 함수를 component 로 만들 때, base_image 로 사용하는 Docker 이미지에 들어있는 코드는 함수 내부에 선언하지 않아도 사용할 수 있습니다.
- 복잡한 로직을 모두 Python 함수 단위로 모듈화를 하기는 어렵기 때문에, 이런 경우에는 Component 의 base image 로 사용할 docker image 를 만들어두고 base_image 로 지정하는 방식을 주로 사용합니다.
- 자세한 사용 방법은 다음 링크를 참고합니다.
- pipeline 으로 엮을 수 있도록 input, output 을 잘 지정하여 구현합니다.
- component 간에 input, output 을 넘기는 방식은 추후 다른 예제로 함께 살펴보겠습니다.
- 해당 함수 밖에서 선언된 코드를 사용해서는 안 됩니다.
[kfp.components.create_component_from_func](https://kubeflow-pipelines.readthedocs.io/en/latest/source/kfp.components.html#kfp.components.create_component_from_func)함수를 사용하여, Python 함수를 kubeflow Component (ContainerOp) 로 변환합니다.- decorator 로 사용할 수도 있고, base_image, extar_packages 등 여러 argument 를 지정할 수도 있습니다.
kfp.dsl.pipeline데코레이터 함수를 사용하여, 각 component 들간의 input-output 을 엮습니다.- kfp.dsl 의 여러 메소드들을 사용하여, 컴포넌트 실행 시의 Condition 등을 지정할 수도 있습니다. 이는 추후 다른 예제로 함께 살펴보겠습니다.
kfp.compiler.Compiler().compile혹은dsl-compile을 사용하여 pipeline python code 를 k8s 의 Workflow yaml 파일로 컴파일합니다.- 컴파일된 yaml 파일을 UI 를 통해 업로드하고 run 합니다. 혹은
kfp.Client를 사용하거나 kfp CLI, HTTP API 를 사용해서 run 할 수도 있습니다.
-
Add Example 코드
import kfp.compiler from kfp.components import create_component_from_func def add(value_1: int, value_2: int) -> int: """ 더하기 """ ret = value_1 + value_2 return ret def subtract(value_1: int, value_2: int) -> int: """ 빼기 """ ret = value_1 - value_2 return ret def multiply(value_1: int, value_2: int) -> int: """ 곱하기 """ ret = value_1 * value_2 return ret add_op = create_component_from_func(add) subtract_op = create_component_from_func(subtract) multiply_op = create_component_from_func(multiply) from kfp.dsl import pipeline @pipeline(name="add example") def my_pipeline(value_1: int, value_2: int): task_1 = add_op(value_1, value_2) task_2 = subtract_op(value_1, value_2) task_3 = multiply_op(task_1.output, task_2.output) if __name__ == "__main__": kfp.compiler.Compiler().compile(my_pipeline, "./add_pipeline_2.yaml")
-
위의 add example pipeline 과 동일한 코드이지만, compile 할 때,
dsl-compile대신,kfp.compiler를 사용하는 코드가 추가된 버전입니다.python add_2.py를 실행시키면add_pipeline_2.yaml이 정상적으로 생성되는 것을 확인할 수 있습니다.
- Python Code로 pipeline설계
- Compile해서 Yaml 파일 생성후 kubeflow에 올림
- kubeflow에는 KFP가 존재해야하며 Pipeline 생성후 만들고 KFP 와 연결한후 RUN 진행가능
- RUN에들어가보면 컨테이너 생성과 각각의 LOG 볼수있음
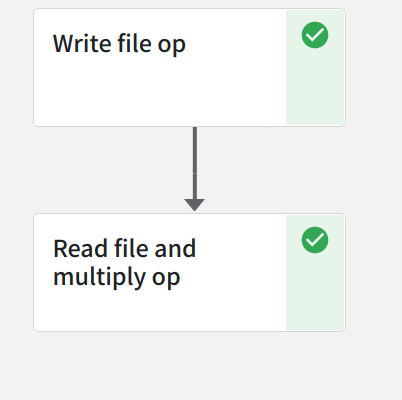
첫 번째 컴포넌트에서 file 에 data 를 쓴 뒤, 두 번째 컴포넌트에서는 해당 file 로부터 데이터를 읽어 두 수의 곱을 구하는 pipeline 예제입니다.
- Component 간에 데이터를 주고 받는 방법에는 위의 add_example 의 예시처럼 변수를 통해서 넘겨줄 수도 있지만, 데이터의 사이즈가 큰 경우에는 파일에 저장한 뒤, 파일 경로를 전달하는 방식으로 데이터를 넘겨줄 수 있습니다.
-
data_passing_file.py
import kfp from kfp.components import InputPath, OutputPath, create_component_from_func # decorator 사용 @create_component_from_func def write_file_op( # _path 라는 suffix 를 붙이고, type annotaion 은 OutputPath 로 선언해야 합니다. data_output_path: OutputPath("dict") ): # package import 문은 함수 내부에 선언 import json # dict data 선언 data = { "a": 300, "b": 10, } # file write to data_output_path with open(data_output_path, "w") as f: json.dump(data, f) @create_component_from_func def read_file_and_multiply_op( # input 역시, _path 라는 suffix 를 붙이고, type annotation 은 InputPath 로 선언해야 합니다. data_input_path: InputPath("dict") ) -> float: # package import 문은 함수 내부에 선언 import json # file read to data_output_path with open(data_input_path, "r") as f: data = json.load(f) # multiply result = data["a"] * data["b"] print(f"Result: {result}") return result @kfp.dsl.pipeline(name="Data Passing by File Example") def data_passing_file_pipeline(): write_file_task = write_file_op() _ = read_file_and_multiply_op(write_file_task.outputs["data_output"]) if __name__ == "__main__": kfp.compiler.Compiler().compile( data_passing_file_pipeline, "./data_passing_file_pipeline.yaml" )
-
정해진 Rule 대로 component, pipeline 을 작성하면 kubeflow pipeline SDK 가 관련 부분을 file passing 으로 인식하여 pipeline 컴파일 시에 관련 처리를 자동화해줍니다.
- Rule :
- component 의 argument 를 선언할 때, argument name 의 suffix 로
_path를 붙이고, type annotation 을kfp.components.InputPath혹은kfp.components.OutputPath로 선언합니다.
- component 의 argument 를 선언할 때, argument name 의 suffix 로
- Rule :
-
컴파일된 Workflow yaml 파일을 확인하여,
add_pipeline.yaml와 어떤 점이 다른지 확인해봅니다.- yaml 파일의
dag부분을 보면,arguments의 value 로parameter가 아닌,artifacts로 선언되어 있는 것을 확인할 수 있습니다.
- yaml 파일의
-
UI 를 통해 pipeline 업로드 후, 실행해봅니다. 컴포넌트 간의 input, output 이 어떻게 연결되는지 확인합니다.
컴포넌트에서 metrics 를 남기는 pipeline 예제입니다.
- 하나의 컴포넌트에서 metrics 를 export 하는 예제입니다.
-
export_metrics.py
import kfp from kfp.components import OutputPath, create_component_from_func @create_component_from_func def export_metric_op( mlpipeline_metrics_path: OutputPath("Metrics"), ): # package import 문은 함수 내부에 선언 import json # 아래와 같이 정해진 형태로, key = "metrics", value = List of dict # 단, 각각의 dict 는 "name", "numberValue" 라는 key 를 가지고 있어야 합니다. # "name" 의 value 로 적은 string 이 ui 에서 metric 의 name 으로 parsing 됩니다. # 예시이므로, 특정 모델에 대한 값을 직접 계산하지 않고 const 로 작성하겠습니다. metrics = { "metrics": [ # 개수는 따로 제한이 없습니다. 하나의 metric 만 출력하고 싶다면, 하나의 dict 만 원소로 갖는 list 로 작성해주시면 됩니다. { "name": "auroc", "numberValue": 0.8, # 당연하게도 scala value 를 할당받은 python 변수를 작성해도 됩니다. }, { "name": "f1", "numberValue": 0.9, "format": "PERCENTAGE", # metrics 출력 시 포맷을 지정할 수도 있습니다. Default 는 "RAW" 이며 PERCENTAGE 를 사용할 수도 있습니다. }, ], } # 위의 dict 타입의 변수 metrics 를 mlpipeline_metrics_path 에 json.dump 합니다. with open(mlpipeline_metrics_path, "w") as f: json.dump(metrics, f) @kfp.dsl.pipeline(name="Export Metrics Example") def export_metrics_pipeline(): write_file_task = export_metric_op() if __name__ == "__main__": kfp.compiler.Compiler().compile( export_metrics_pipeline, "./export_metrics_pipeline.yaml" )
-
정해진 Rule 대로 component, pipeline 을 작성하면 kubeflow pipeline SDK 가 관련 부분을 export metrics 으로 인식하여 pipeline 컴파일 시에 관련 처리를 자동화해줍니다.
- Rule :
- component 의 argument 를 선언할 때, argument name 은
mlpipeline_metrics_path여야 하며, type annotation 은OutputPath('Metrics')로 선언합니다. - component 내부에서 metrics 를 위의 코드의 주석의 룰을 지켜 선언하고 json dump 하여 사용합니다.
- component 의 argument 를 선언할 때, argument name 은
- Rule :
-
컴파일된 Workflow yaml 파일을 확인하여,
add_pipeline.yaml와 어떤 점이 다른지 확인해봅니다.- yaml 파일의
dag부분을 보면,arguments의 value 로parameter가 아닌,artifacts로 선언되어 있는 것을 확인할 수 있습니다.
- yaml 파일의
-
주의사항
- metrics 의 name 은 반드시 다음과 같은 regex pattern 을 만족해야 합니다.
^[a-zA-Z]([-_a-zA-Z0-9]{0,62}[a-zA-Z0-9])?$
- metrics 의 numberValue 의 value 는 반드시 numeric type 이어야 합니다.
- metrics 의 name 은 반드시 다음과 같은 regex pattern 을 만족해야 합니다.
-
UI 를 통해 pipeline 업로드 후, 실행해봅니다. Run output 을 눌러 Metrics 가 어떻게 출력되는지 확인합니다.
- metrics 를 출력한 component 의 이름, 그리고 해당 component 에서의 key, value 를 확인할 수 있습니다.
하나의 컴포넌트에서, k8s resource 들을 직접 지정하여 사용하는 방법을 간단히 다룹니다. 컴포넌트 별로, 필요한 리소스를 할당할 수 있습니다. 이번 파트는 실습은 하지 않고 사용법만 알아보겠습니다.
-
CPU, Memory 할당
-
다음과 같은 형태로
ContainerOp에 메소드 체이닝 형태로 작성하면, 해당 component 를 run 할 때, pod 의 리소스가 지정되어 생성@dsl.pipeline() def pipeline(): ... training_task = training_op(learning_rate, num_layers, optimizer).set_cpu_request(2).set_cpu_limit(4).set_memory_request('1G').set_memory_limit('2G') ...
-
-
GPU 할당
-
cpu, memory 와 동일한 방법으로 작성
@dsl.pipeline() def pipeline(): ... training_task = training_op(learning_rate, num_layers, optimizer).set_gpu_limit(1) ...
-
단, 해당 component 의 base_image 에 cuda, cudnn, tensorflow-gpu 등 GPU 를 사용할 수 있는 docker image 를 사용해야 정상적으로 사용 가능
-
-
PVC 할당
-
k8s 의 동일한 namespace 에 pvc 를 미리 생성해둔 뒤, 해당 pvc 의 name 을 지정하여 다음과 같은 형태로
ContainerOp의 argument 로 직접 작성@dsl.pipeline() def pipeline(): ... vop = dsl.VolumeOp( name="v1", resource_name="mypvc", size="1Gi" ) use_volume_op = dsl.ContainerOp( name="test", ... pvolumes={"/mnt": vop.volume} # 이렇게 ContainerOp 생성 시, argument 로 지정 ) ...
-
혹은, 다음과 같이
add_pvolumes를 사용하여 작성@dsl.pipeline() def pipeline(): ... vop = dsl.VolumeOp( name="v2", resource_name="mypvc", size="1Gi" ) use_volume_op = dsl.ContainerOp( name="test" ) # 이렇게 위의 CPU, MEMORY, GPU 처럼 내장 메소드 사용 use_volume_task = use_volume_op("name").add_pvolumes({"/mnt": vop.volume})
-
-
Secret 를 Env variable 로 사용
-
k8s 의 동일한 namespace 에 secret 를 미리 생성해둔 뒤, 해당 secret 의 name 과 value 지정하여 다음과 같은 형태로
add_env_variable사용하여 작성@dsl.pipeline() def pipeline(): ... env_var = V1EnvVar(name='example_env', value='env_variable') use_secret_op = dsl.ContainerOp( name="test" ) use_secret_task = use_secret_op("name").add_env_variable(env_var) ...
-
사용할 정보를 담은 secret 을 미리 만들어두고, 위의 예시처럼
add_env_variable함수를 사용해서 component(pod) 에서 붙이면, component python code 내부에서는 그냥os.environ.get()등을 사용하여 활용할 수 있습니다.
-
-
kfp Pipeline, component 에서 자주 활용하는 쿠버네티스의 리소스별 사용법은 위와 같으나, 이외에도 대부분의 k8s resource 를 사용할 수 있습니다.
- 더 다양한 기능은 Official API Reference 를 참고해주시기 바랍니다.
- ML모델에서 필요한 다양한 feature들
- 단순한 데이터가 아니라 병합,가공 ,정제를 거쳐서 나온것들
- 모델이 인식할수있는 feature vector로 변환되어야한다.
- 여러 데이터들을 합쳐 feature column등을 만들어내고 합쳐서 feature들을 다시 가공해 들어간다
- 새로운 데이터가 생겼을때
- Feature A, Feature B에 대해서
- 다시 Feature 생성
- 주요 업무
- 코드완성후 자동 test및 자동 배포
- 여기서 Feature Engineering이후 Featuer Store에 전달
- 매우 많은 데이터를 대상으로 하게됌
- Data Engineer쪽에서 Feature Engineering과 Feature Store쪽을 담당
- 다양한 시간대로 Feature가 저장이 된다.
- 각각의 data가 전부 다르기 때문에 일정한 Feature Pipeline이 필요함
- 미리 정의해서 입력형식을 맞추는 것이 중요함
- 생각보다 잘 알려진 Tool이 별로 없음
- 보조적인 수단으로만 주로 사용됨
-
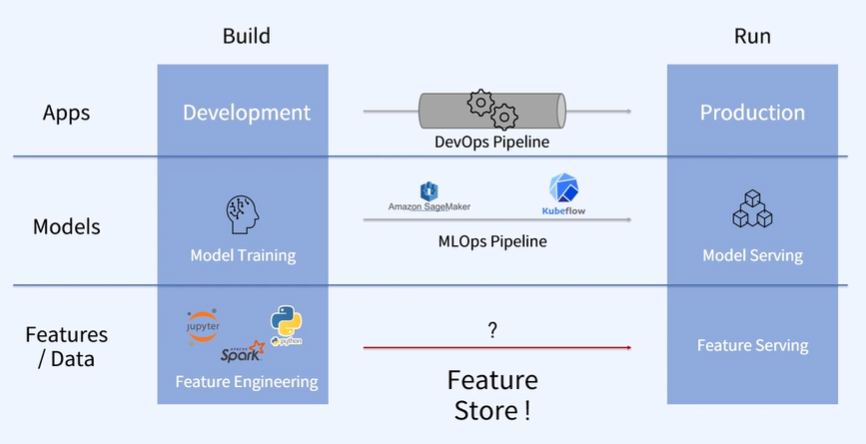
모델 훈련과 배포과정의 중복을 줄이기 위해 생겨난 관리형 플랫폼
-
Feature Pipeline을 공유하여 같이 활용함
-
Feature 활용측면에서 반복을 줄일 수있는 Feature Store
- batch data
- 여러개를 하나의 묶음으로 데이터가 묶인것
- Steram data
- 바로바로 들어오는 data
- 여러 데이터가 합쳐짐
- 다양한 변형마다 범위랑 데이터 빈도가 다르다
- 지원되는 변형이 혼재됌
- 데이터의 단위가 매우 크므로 0.1초단위의 latency가 일어남
- Data store로 미리 feature를 계산해 data store에 저장된 feature를 바탕으로 model이 예측결과를 내보내줌
- 그러나 24시간전 데이터이기 때문에 최신데이터에 민감하다면 쓸모없는 feature일수도 있음
- Data 처리비용을 줄이면서 ㅚ신 feature를 data store에 적재하는 것이 필요
- 모델링 지연과 훈련/제공 데이터의 차이가 발생함
- 미리 Pipeline을 구성해놓고 데이터가 들어오면 자동적으로 feature를 생성한다.
- 데이터 누수의 문제위험성도 줄어든다
- 모델이 바뀌게 되면 모델의 feature들도 바뀔수있고 feature 가공방법까지 협업을 해야함
- 각자의 디스크에서 편리하게 사용하지만 관리가 힘듬
- 다시 복잡한 feature pipeline 생성 → ML 제작
- 모델의 완성도가 떨어짐
- 해결법
- 데이터사이언티스트가 직접 feature tore를 통해 운영에 필요한 feature들을 배포하게 됌
- 약간의 pipeline수정만으로 feature들을 제공할수있음
- 다양한 feature들의 원천데이터 활용이 다 다름
- Resource들이 다 다르다
- feature store에서 데이터 사용의 중복 및 관ㄹ이ㅔ 용이
- 데이터의 분포변화를 막고 데이터 품질 신뢰를 얻을수있다
- https://www.featurestore.org/
- site에 다양한 정보 사례있음
- Eats의 ㅂ달시간예측 ML 모델 서비스
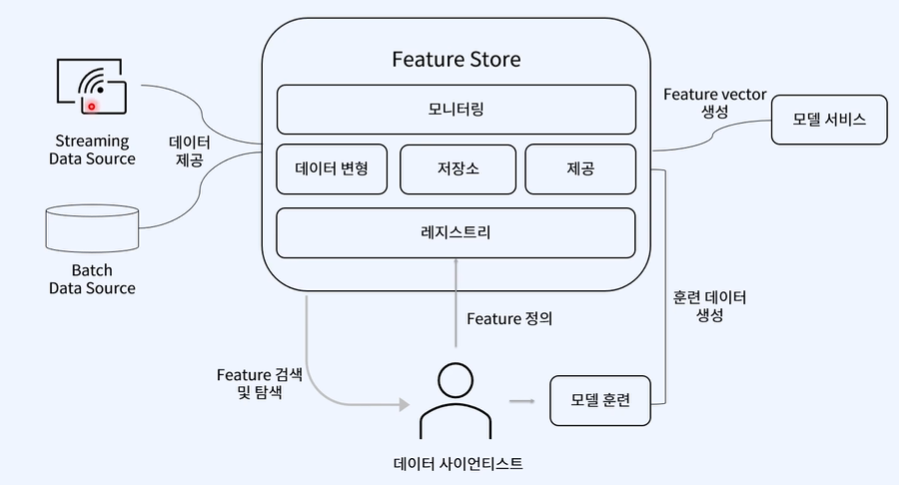
- Data lake :
- spark
- Hive Feature Store
- spark
- Kafka
- Streaming
- Hive Feature
- Sampling되고 다시 모니터링 spark담당→ 모니터링시스템으로 넘김
- 많은 App들의 ML기반 서비스
- 데이터주입
- feature generation → 본인들이 필요한 feature 생성
- online table → feature를 생성
- Kubeflow 사용해 MLOps주로
- 주크박스
- 3가지 분류
- Feature Registery And Gallery
- Feature Prepration
- Features serving
- 다양한 형태변환 loader 존재
- Online serving
- 간편함
- FEAST 방식을 잘 이해하면 다른 것들도 이해 잘 이해 가능
- 한눈에 알아보기 쉬움
- 어떻게 다른 plugin들과 연결할수 있는가
- 과거에 다 component를 띄워야했지만 지금은 한번에 연계해 작업
- 별도의 sdk 환경으로 아키텍쳐 구성
실습 1. Feast 기본 예제 - (1) Store 생성과 배포
실습 2. Feast 기본 예제 - (2) Feature 추출 및 추론
실습 5. Feast 와 MLFlow 를 활용한 머신러닝 프로젝트 적용
적용하지 않는경우
데이터 웨어하우스에서 바로 모델에게 적용하는 end2end
- 적용하는 경우
Feature Pipeline을 미리 구성하고 Feast에 접근해서 모델에 필요한 feature만 뽑아옴
- Feast 에 방식 경우
Feast로 할수있는일
새로운 데이터 발생 즉시 feature로 변환?
- Batch 변형
- 실시간 변형
- On-demand 변형
- 모니터링
- ML지표들을 모니터링하고 운영시스템관리한 Tool 관리
- Feature 제공시 지표확인가ㅡㄴㅇ
- 레지스트리
- 표준화된 Feature 정의와 메타데이터 전용 레지스트리
- 저장소
- S3, BigQuery ,SnowFalke ,RedShift같은 다양한 Feature 제공시스템의 요구사항 지원
- key-value 타입의 저장소를 낮은 lattency로 추론할수있는 feature 제공
할수없는일?>?
작업흐름 관리 X
- 데이터 탐색 X
- Feature Enginerring 불가능
- DVC, Pachyderm등 데이터버젼관리 X
- 모델 제공 메타데이터 관리 X , seldom ,bento등
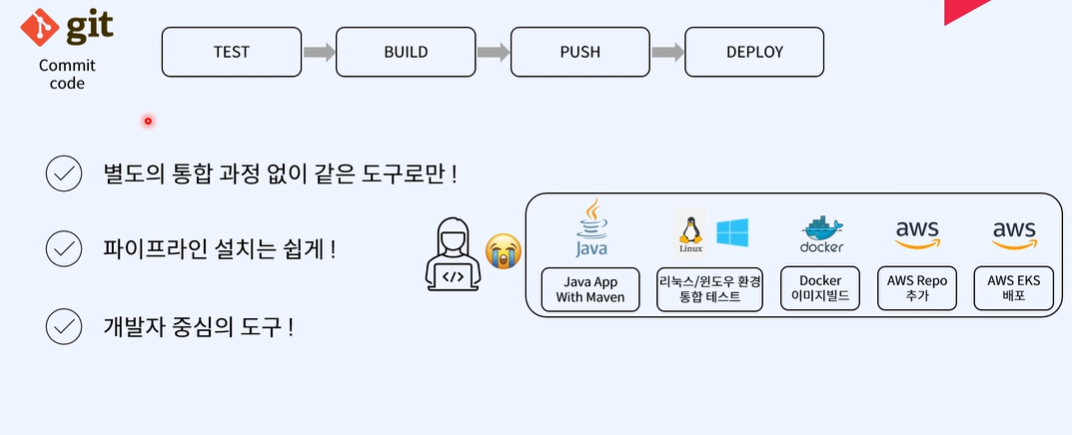
파이프라인 생성 : kubeflow
Gihub Action ?
개발자들을 workflow를 자동화하기 위한 플랫폼
단순 CI/CD가 아닌 자동화에 초점
- build자동화 ,production 자동화
Workflow 자동화 tool
github : 오픈소스 프로젝트를 위한 플랫폼
- github flow
개선사항 → 새로운 branch안에서 개선사항 안에서 요청
- 요청한 후 괜찮다 싶으면 → merge branch를 통해 master branch로 통합 가능
- git hub issue
issue를 통해서 겪은 문제점들 사용자들 공유
- issue 해결- > 개선 → pull request → bug 고쳐졌는가 검증후 master branch 로 merge
- CI/CD pipeline에서
배포를 할수있게 하는 방법
- Realease notes
- Version Number 업데이트
- 전체적인 CI/CD Pipeline 과정
굉장히 많은 workflow가 이루어짐
- workflow를 통해 issue 극복 및 realease
- 이 workflow를 자동화하는것
다양한 event등이 있음
github event 발생시 자동 작업
자동화 과정
Github actions 기반 CI/CD - Build 및 Push
할것들
- github action을 활용한 docker image build
- 생성한 docker image를 docker hub에 push
Github actions 활용해 Docker image Build
github repo 생성
- actions 선택
-
python application 선택(이건 자율)
- 다양한 workflow 존재 → 개인선택
-
Workflow file 생성
# This workflow will install Python dependencies, run tests and lint with a single version of Python # For more information see: https://docs.github.com/en/actions/automating-builds-and-tests/building-and-testing-python name: Python application on: push: branches: [ "main" ] pull_request: branches: [ "main" ] permissions: contents: read jobs: build: runs-on: ubuntu-latest steps: - uses: actions/checkout@v3 - name: Set up Python 3.10 uses: actions/setup-python@v3 with: python-version: "3.10" - name: Install dependencies run: | python -m pip install --upgrade pip pip install flake8 pytest if [ -f requirements.txt ]; then pip install -r requirements.txt; fi - name: Lint with flake8 run: | # stop the build if there are Python syntax errors or undefined names flake8 . --count --select=E9,F63,F7,F82 --show-source --statistics # exit-zero treats all errors as warnings. The GitHub editor is 127 chars wide flake8 . --count --exit-zero --max-complexity=10 --max-line-length=127 --statistics - name: Test with pytest run: | pytest
- yml or yaml 파일
Github event 알아보기
name [optional] on [required] events : workflow 를 시작하게 할 수 있는 Github event 의 이름 : jobs [required] jobs.<job_id> : one or more jobs : sequence of tasks (steps) : steps 1) can run commands, 2) setup tasks 3) run an action - uses : selects an action (actions/ 다음에는 재사용 가능 코드 위치) - run : runs a command-line command
name: Python application
on: push: branches: [ python-ci-workflow ] pull_request: branches: [ python-ci-workflow ]
jobs: build: steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v2
- name: Set up Python uses: actions/setup-python@v2 with: python-version: "3.8"
- name: Display Python version run: python -c "import sys; print(sys.version)"
actions
- https://github.com/actions
- checkout - action.yaml
- Start commit → Create a new branch.. → 이름을 'python-ci-workflow' 로 변경 → Create pull request
- Details 클릭 → build
- 이 코드들은 어디서 실행되는 걸까?
- Github 에 의해 관리된다
- Workflow 의 각 jobs 은 새로운 가상 환경에서 실행된다
- runs-on 필요
jobs: build: runs-on: ubuntu-latest strategy: matrix: os: [ubuntu-latest, windows-latest, macOS-latest]
운영체제 개별로 build
name: Python application on: push: branches: [ python-ci-workflow ] pull_request: branches: [ python-ci-workflow ] jobs: build: runs-on: **${{ matrix.os }}** strategy: matrix: os: **[ubuntu-latest, macos-latest, windows-latest]** python-version: ['3.6', '3.8'] exclude: - os: macos-latest python-version: '3.8' - os: windows-latest python-version: '3.6' steps: - uses: actions/checkout@v2 - name: Set up Python uses: actions/setup-python@v2 with: python-version: ${{ matrix.python-version }} - name: Display Python version run: python -c "import sys; print(sys.version)"
아직 APP build 하지 않음
- Docker의 docs의 Build your Python Image 보기
- https://docs.docker.com/language/python/build-images/
- app.py
from flask import Flask
app = Flask(__name__)
@app.route('/')
def hello_world():
return 'Hello, Docker!'Dockerfile
# syntax=docker/dockerfile:1
FROM python:3.8-slim-buster
WORKDIR /app
COPY requirements.txt requirements.txt
RUN pip3 install -r requirements.txt
COPY . .
CMD [ "python3", "-m" , "flask", "run", "--host=0.0.0.0"]requirements.txt
Flask==2.3.2-
Workflow 설명
- 작성한 App 빌드
- Docker image로 생성
- Docker repo로 추가
-
Docker Image 빌드
- Docker hub 에 자기 repo 생성
docker build and push actions 검색
- 다양한 Inputs
추가할 Dockerfile
- name: Build & push Docker image uses: mr-smithers-excellent/docker-build-push@v5 with: image: docker-hub-repo/image-name tags: v2, latest registry: docker.io username: ${{ secrets.DOCKER_USERNAME }} password: ${{ secrets.DOCKER_PASSWORD }}
반영결과
- ci.yml 수정
name: Python application
on:
push:
branches: [ python-ci-workflow ]
pull_request:
branches: [ python-ci-workflow ]
jobs:
build:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v2
- name: Set up Python
uses: actions/setup-python@v2
with:
python-version: "3.8"
- name: Display Python version
run: python -c "import sys; print(sys.version)"
- name: Build & push Docker image
uses: mr-smithers-excellent/docker-build-push@v5
with:
image: yunjjun/github-actions-app
tags: v3, latest
registry: docker.io
username: ${{ secrets.DOCKER_USERNAME }}
password: ${{ secrets.DOCKER_PASSWORD }}(https://github.com/marketplace/actions/docker-build-push-action)
- Docker hub 지원
- Secrets 설정필요 -github action에서
- github - settings - Secrets - New
- Name : DOCKER_USERNAME - yunjjun
- Name : DOCKER_PASSWORD - dockerhub 에서 access token 생성
tag와 생성 이미지 build 됌
💡 **실습 목표 1. Github Actions 를 활용하여 예제 머신러닝 코드 실행하여 성능 지표 출력하기 2. CML 을 사용하여 성능 지표를 레포트 형태로 출력하기 3. 분석 코드 변경 후 재배포 시 레포트 재생성 하기 4. DVC 를 활용하여 Metric 의 변화 추적하기**실습 2. CML 과 DVC 연계를 통한 Model Metric Tracking
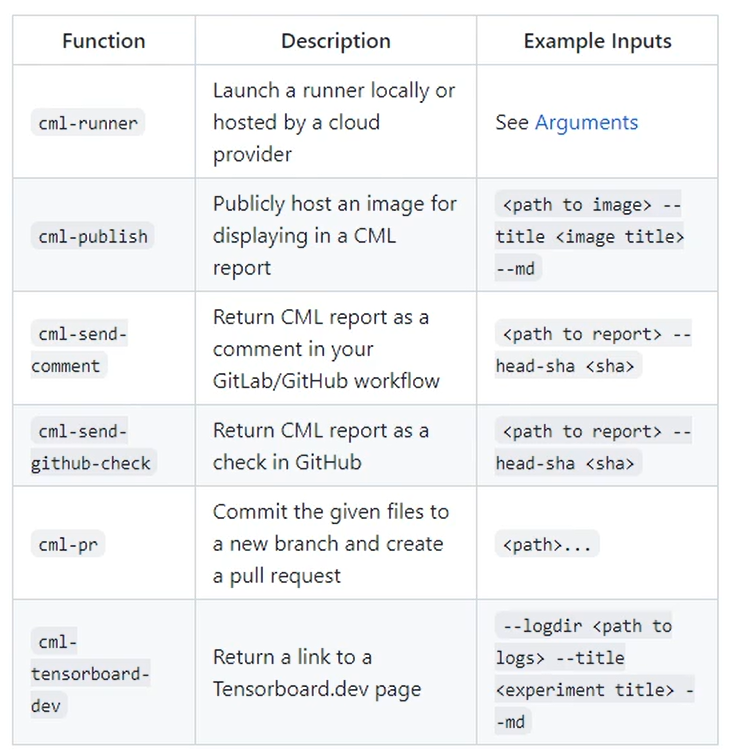
시각화 Report 오픈소스 : CML
report 해주는 오픈소스
- pull request를 action마다 수행해서 시각화해서보여줄수 있음
여기서 cml-publish, cml-send-comment 사용
- version 바뀌어 cml comment create, cml check reate등으로 바뀜
CML 을 사용하여 성능 지표를 레포트 형태로 출력하기
CML : 데이터 사이언스 프로젝트를 지속적으로 통합시키기 위한 오픈소스
https://github.com/iterative/cml
Markdown 형식으로 내보내기YAML복사
echo "## MODEL METRICS" > report.md
cat metrics.txt >> report.md- CML Command 를 사용하여 분석 결과 이미지를 Markdown 형식으로 내보내기
echo "## Data viz" >> report.md
cml-publish feature_importance.png --md >> report.md
cml-publish residuals.png --md >> report.md
cml-send-comment report.md분석코드 report.md → commit에 들어감
github의 commit에서 살펴볼수 있음
장점
github에 파라미터를 바꾸거나 어떤 값을 바꿔서 넣어도 바로바로 report를 기록하고 확인할수있다는 장점 : 자동화
최종 YAML : cml version바뀌어서 윗부분과 다
name: model-training
on: [push]
jobs:
run:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- uses: actions/setup-node@v1
with:
node-version: '16'
- uses: actions/checkout@v3
- uses: actions/setup-python@v2
- uses: iterative/setup-cml@v1
- name: Train model
env:
REPO_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.TOKEN }}
run: |
pip install -r requirements.txt
python train.py
echo "## MODEL METRICS" >> report.md
cat metrics.txt >> report.md
echo "## Data viz" >> report.md
echo "" >> report.md
echo "" >> report.md
cml comment create report.mdgithub actinons의 secret의 token추가해주기
DVC는 왜쓰는걸까?
Model Metrics의 변화를 한눈에 보기위해서
- 쓰지 않게된다면 각 commit을 눌러서 보게되는 불편함 존재
-
Github Repo Fork
-
데이터 확인 및 다운로드
-
process_data.py 실행
-
train.py 실행
## AttributeError: 'Series' object has no attribute 'to_numpy' 에러 시 참고 pip install --upgrade pandas # numpy==1.23.0
-
-
Metric 의 변화는 어떻게 알 수 있을까?
-
- 수치 비교보다는 코드의 변화를 알기 위해 보통 사용하므로 활용이 어렵다.
- 파일 변경 이력을 알기 어렵다 → 모델링 전략 변경을 알기 어렵다.
-
DVC 사용!
- install dvc
pip install dvc==2.0.3
-
파이프라인 빌드
-
초기화
# 초기화 dvc init # dvc.yaml 생성 dvc run -n process -d process_data.py -d data_raw.csv -o data_processed.csv --no-exec python process_data.py
-
전체 코드
stages: process: cmd: python process_data.py deps: - process_data.py - data_raw.csv outs: - data_processed.csv train: cmd: python train.py deps: - train.py - data_processed.csv outs: - by_region.png metrics: - metrics.json: cache: false
-
-
# 각 단계별로 재생성 dvc repro -
.github/workflows/train.yaml 생성
name: dvc-cml on: [push] jobs: run: runs-on: [ubuntu-latest] container: docker://dvcorg/cml-py3:latest steps: - uses: actions/checkout@v2 - name: cml_run env: repo_token: ${{ secrets.TOKEN }} run: | pip install -r requirements.txt dvc repro git fetch --prune ## https://git-scm.com/docs/git-fetch dvc metrics diff --show-md master > report.md echo "## Validating results by region" cml-publish by_region.png --md >> report.md cml-send-comment report.md
docker file쓰기때문에 그냥 version신경없이 해도된다.
-
모델링 변경하여 테스트
-
새로운 branch (experiment) 생성
-
train.py 수정 (LogisticRegression → QuadraticDiscriminantAnalysis)
# from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression from sklearn.discriminant_analysis import QuadraticDiscriminantAnalysis ... # clf = LogisticRegression() clf = QuadraticDiscriminantAnalysis()
-
commit → build
-
변경값 확인 !
변경값 확인가능
-
-
Jenkins란?
코드 변경사항 직접확인하고 변경사항발견하고 반영
-
Jenkins가 있다면?
- commit 시에 감지후 바로 서버에 자동반영
일련의 작업들이 서버에서 자동화 가능
- actions랑 다른게뭐징?
-
여러 장점
Jenkins 파이프라인 → jenkinsfile
jenkinsfile로 일반 소스코드를 다루는 github, vscode로 수정하는 것으로 파일 이용가능
기본적으로 jenkinsfile을 통해 jenkins 실행가능
Scripted Pipeline
jenkins 관련 구조를 자세히 가지지 않고 프로그램의 흐름을 자바와 유사한 Groovy라는 동적객체 지향프로그래밍언어를 이용해 관맇되었음
- 유연하지만 시작하기 어려웠음
node { ## 빌드를 수행할 node 또는 agent를 의미한다. stage("Stage 1"){ echo "Hello" } stage("Stage 2"){ echo "World" sh "sleep 5" } stage("Stage 3"){ echo "Good to see you!" } }
-
Declarative Pipeline (선언적 파이프라인)
- 2016년 경 Cloudbees 에서 개발
- 사전에 정의된 구조만 사용할 수 있기 때문에 CI/CD 파이프라인이 단순한 경우에 적합하며 아직은 많은 제약사항이 따른다.
- 공식 문서
pipeline { agent any stages { stage('Stage 1') { steps { script { echo 'Hello' } } }
stage('Stage 2') { steps { script { echo 'World' sh 'sleep 5' } } } stage('Stage 3') { steps { script { echo 'Good to see you!' } } } }}
-
실습 1. Jenkins 설치
!version 바뀌어서 jenkins공식 홈페이지 참조함 : 아래 버전 안됌
💡 **실습 목표 1. Jenkins 를 Local 과 Docker 로 각각 설치한 후 기본 사용법을 익혀 본다. 2. 생성한 Docker Image 를 Docker Hub 에 Push 한다.**- Local 에 직접 설치해보기
-
JDK 설치
sudo apt install openjdk-11-jre-headless
-
Key 다운로드
wget -q -O - https://pkg.jenkins.io/debian/jenkins.io.key | sudo apt-key add - echo deb http://pkg.jenkins.io/debian-stable binary/ | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/jenkins.list
-
Jenkins 설치하기
# sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get install jenkins -
정상여부 확인
sudo systemctl status jenkins # 재시작 : sudo service jenkins restart -
초기 패스워드 확인
sudo cat /var/lib/jenkins/secrets/initialAdminPassword
-
브라우저 접속 (localhost:8080)
- 초기 비밀번호 사용하여 로그인
-
플러그인 설치
-
계정 만들기
- admin_user / 1234
-
- Local 에 직접 설치해보기
Jenkins CI Pipeline 생성
기본 구조
pipeline : 반드시 맨위
-
agent : 어디서 실행할것인지 정의
- any, none, label,node, docker, dockerfile, kubernetes
- agent가 none인 경우 stage에 포함해야함
pipeline { agent none stages { stage('Example Build') { agent { docker 'maven:3-alpine' } steps { echo 'Hello, Maven' sh 'mvn --version' } } stage('Example Test') { agent { docker 'openjdk:8-jre' } steps { echo 'Hello, JDK' sh 'java -version' } } } }
stages : 하나이상의 stage에 대한 모음
- pipeline블록안에서 한번만 실행 가능
pipeline {
agent any
stages {
stage("build") {
steps {
echo 'building the applicaiton...'
}
}
stage("test") {
steps {
echo 'testing the applicaiton...'
}
}
stage("deploy") {
steps {
echo 'deploying the applicaiton...'
}
}
}
}깃허브에 repo 생성
- local에서 Jenkinsfile 생성 하여 github에 업로드
Post를 이용해 모든 stage가 실행된 후 명령정의가능
post : 후 조건
- alwayss ,changed ,fixed, regression, aborted, success, unsuccessful , unstable, failure, notBuilt, cleanup 등
pipeline {
agent any
stages {
stage("build") {
steps {
echo 'building the applicaiton...'
}
}
stage("test") {
steps {
echo 'testing the applicaiton...'
}
}
stage("deploy") {
steps {
echo 'deploying the applicaiton...'
}
}
}
post {
always {
echo 'building..'
}
success {
echo 'success'
}
failure {
echo 'failure'
}
}
}when으로 stage가 실행되는 조건 추가
test stage에서 branch이름에 따른 조건
- build stage에서 branch이름에 따른 조건등
pipeline {
agent any
stages {
stage("build") {
when {
expression {
env.GIT_BRANCH == 'origin/master'
}
}
steps {
echo 'building the applicaiton...'
}
}
stage("test") {
when {
expression {
env.GIT_BRANCH == 'origin/test' || env.GIT_BRANCH == ''
}
}
steps {
echo 'testing the applicaiton...'
}
}
stage("deploy") {
steps {
echo 'deploying the applicaiton...'
}
}
}
}- Jenkinsfile 자체 환경변수 목록 보기
Custom env 사용
echo 사용시에는 큰따옴표
pipeline {
agent any
**environment {
NEW_VERSION = '1.0.0'
}**
stages {
stage("build") {
steps {
echo 'building the applicaiton...'
echo "building version ${NEW_VERSION}"
}
}
stage("test") {
steps {
echo 'testing the applicaiton...'
}
}
stage("deploy") {
steps {
echo 'deploying the applicaiton...'
}
}
}
}-
Credentials 자격 증명 환경 변수로 사용하기
- Jenkins credential 추가
- [Jenkins 관리]-[Manage Credentials]-[Global credentials]-[Add credentials]
- Username : admin_user / Password : 1234 / ID : admin_user_credentials
- Jenkinsfile 에서 환경변수로 사용
pipeline { agent any environment { NEW_VERSION = '1.0.0' ADMIN_CREDENTIALS = credentials('admin_user_credentials') } stages { stage("build") { steps { echo 'building the applicaiton...' echo "building version ${NEW_VERSION}" } } stage("test") { steps { echo 'testing the applicaiton...' } } stage("deploy") { steps { echo 'deploying the applicaiton...' echo "deploying with ${ADMIN_CREDENTIALS}" sh 'printf ${ADMIN_CREDENTIALS}' } } } }jenkins plugin에서 credentials plugin설치되어야함
pipeline { agent any environment { NEW_VERSION = '1.0.0' } stages { stage("build") { steps { echo 'building the applicaiton...' echo "building version ${NEW_VERSION}" } } stage("test") { steps { echo 'testing the applicaiton...' } } stage("deploy") { steps { echo 'deploying the applicaiton...' withCredentials([[$class: 'UsernamePasswordMultiBinding', credentialsId: 'admin_user_credentials', usernameVariable: 'USER', passwordVariable: 'PWD' ]]) { sh 'printf ${USER}' } } } } } - Jenkins credential 추가
jenkinsfile에 parameters 추가
pipeline {
agent any
parameters {
string(name: 'VERSION', defaultValue: '', description: 'deployment version')
choice(name: 'VERSION', choices: ['1.1.0','1.2.0','1.3.0'], description: '')
booleanParam(name: 'executeTests', defaultValue: true, description: '')
}
stages {
stage("build") {
steps {
echo 'building the applicaiton...'
}
}
stage("test") {
steps {
echo 'testing the applicaiton...'
}
}
stage("deploy") {
steps {
echo 'deploying the applicaiton...'
}
}
}
}executeTests 가 true 인 경우의 조건 추가해보기
pipeline {
agent any
parameters {
choice(name: 'VERSION', choices: ['1.1.0','1.2.0','1.3.0'], description: '')
booleanParam(name: 'executeTests', defaultValue: true, description: '')
}
stages {
stage("build") {
steps {
echo 'building the applicaiton...'
}
}
stage("test") {
when {
expression {
params.executeTests
}
}
steps {
echo 'testing the applicaiton...'
}
}
stage("deploy") {
steps {
echo 'deploying the applicaiton...'
echo "deploying version ${params.VERSION}"
}
}
}
}Grooby script 만들어서 사용
groovy script 추가
- script.groovy
def buildApp() {
echo 'building the applications...'
}
def testApp() {
echo 'testing the applications...'
}
def deployApp() {
echo 'deploying the applicaiton...'
echo "deploying version ${params.VERSION}"
}
return thispipeline {
agent any
parameters {
choice(name: 'VERSION', choices: ['1.1.0','1.2.0','1.3.0'], description: '')
booleanParam(name: 'executeTests', defaultValue: true, description: '')
}
stages {
stage("init") {
steps {
script {
gv = load "script.groovy"
}
}
}
stage("build") {
steps {
script {
gv.buildApp()
}
}
}
stage("test") {
when {
expression {
params.executeTests
}
}
steps {
script {
gv.testApp()
}
}
}
stage("deploy") {
steps {
script {
gv.deployApp()
}
}
}
}
}Jenkinsfile 의 모든 환경변수는 groovy script 에서 사용 가능하다.
- replay에서 수정후 재빌드 가능
앞에서 배운 Jenkins CI Pipeline 생성을 Python 어플리케이션에 적용해 본다.
FastAPI 예제 코드를 생성하여 서버에서 Docker Container 를 실행해 본다.
app/main.py
Python
복사
from fastapi import FastAPI
app = FastAPI()
@app.get("/") def read_root(): return {"Hello": "MLOps"}
@app.get("/items/{item_id}") def read_item(item_id: int, q: str = None): return {"item_id": item_id, "q": q}
app/requirements.txt
Python
복사
fastapi uvicorn
서버에 docker-compose 설치
Shell
복사
sudo apt install docker-compose
Dockerfile 작성
Docker
복사
FROM python:3.9
WORKDIR /app
COPY ./app/requirements.txt /app/requirements.txt
RUN pip install --no-cache-dir --upgrade -r /app/requirements.txt
COPY ./app /app
CMD ["uvicorn", "main:app", "--host", "0.0.0.0", "--port", "80"]
docker-compose.yml 작성
Docker
복사
version: "3"
services: web: build: . container_name: fastapi-app volumes: - .:/code ports: - "80:80"
서버에서 Docker Container 생성해 보기
Shell
복사
docker-compose build web docker images docker-compose up -d docker ps -a
localhost:80 접속하여 확인
Jenkinsfile 을 작성하여 Jenkins 에서 배포해 본다.
docker group 에 jenkins 등록
sudo gpasswd -a jenkins docker
sudo vi /usr/lib/systemd/system/docker.service (에러 발생 시에만 시도)
Python
복사
ExecStart=/usr/bin/dockerd -H fd:// -H tcp://0.0.0.0:2376 --containerd=/run/containerd/containerd.sock
sudo systemctl daemon-reload
sudo systemctl restart docker
sudo service jenkins restart
YAML
복사
pipeline { agent any parameters { choice(name: 'VERSION', choices: ['1.1.0','1.2.0','1.3.0'], description: '') booleanParam(name: 'executeTests', defaultValue: true, description: '') } stages { stage("init") { steps { script { gv = load "script.groovy" } } } stage("Checkout") { steps { checkout scm } } stage("Build") { steps { sh 'docker-compose build web' } } stage("test") { when { expression { params.executeTests } } steps { script { gv.testApp() } } } stage("deploy") { steps { sh "docker-compose up -d" } } } }
Github 에 Push 시 자동으로 배포하는 trigger 를 설정해 본다.
Jenkins pipeline 에 Github 을 바로 가도록 설정해 본다.
Poll SCM 은 매 시간마다 소스가 변경되었는지 확인한다.
예) H/3 * * * * → 3분마다 소스가 변경되었는지 확인
우리는 'GitHub hook trigger for GITScm polling' 선택
Github Webhook 설정을 위한 VirtualBox 네트워크 설정 변경
[설정]-[네트워크]-[어댑터에 브리지]로 변경-[가상머신 재시작]
sudo service jenkins restart
ifconfig 명령으로 public ip 확인
Jenkins 로 배포하여 접근 확인
Github Webhook 설정
Github Repository - Settings - Webhooks - Add webhook
Payload URL : http://:8080/github-webhook/
Content type : application/json
Acitve 활성화
코드 변경 후 push 하여 확인해 보기
배포된 Docker image 를 Docker Hub 로 올리기
Credentials 생성
Kind : Username with password
Username : docker hub 아이디
password : docker hub access key
ID : docker-hub / Description : docker-hub
Jenkinsfile 작성
YAML
복사
pipeline { agent any parameters { choice(name: 'VERSION', choices: ['1.1.0','1.2.0','1.3.0'], description: '') booleanParam(name: 'executeTests', defaultValue: true, description: '') } stages { stage("init") { steps { script { gv = load "script.groovy" } } } stage("Checkout") { steps { checkout scm } } stage("Build") { steps { sh 'docker-compose build web' } } stage("test") { when { expression { params.executeTests } } steps { script { gv.testApp() } } } stage("Tag and Push") { steps { withCredentials([[$class: 'UsernamePasswordMultiBinding', credentialsId: 'docker-hub', usernameVariable: 'DOCKER_USER_ID', passwordVariable: 'DOCKER_USER_PASSWORD' ]]) { sh "docker tag jenkins-pipeline_web:latest ${DOCKER_USER_ID}/jenkins-app:${BUILD_NUMBER}" sh "docker login -u ${DOCKER_USER_ID} -p ${DOCKER_USER_PASSWORD}" sh "docker push ${DOCKER_USER_ID}/jenkins-app:${BUILD_NUMBER}" } } } stage("deploy") { steps { sh "docker-compose up -d" } } } }
-
FastAPI 예제 코드를 생성하여 서버에서 Docker Container 를 실행해 본다.
-
app/main.py
from fastapi import FastAPI app = FastAPI() @app.get("/") def read_root(): return {"Hello": "MLOps"} @app.get("/items/{item_id}") def read_item(item_id: int, q: str = None): return {"item_id": item_id, "q": q}
-
app/requirements.txt
fastapi uvicorn
-
서버에 docker-compose 설치
sudo apt install docker-compose
- Dockerfile 작성
FROM python:3.9 WORKDIR /app COPY ./app/requirements.txt /app/requirements.txt RUN pip install --no-cache-dir --upgrade -r /app/requirements.txt COPY ./app /app CMD ["uvicorn", "main:app", "--host", "0.0.0.0", "--port", "80"]- docker-compose.yml 작성
version: "3" services: web: build: . container_name: fastapi-app volumes: - .:/code ports: - "80:80"
- 서버에서 Docker Container 생성해 보기
docker-compose build web docker images docker-compose up -d docker ps -a
- localhost:80 접속하여 확인
-
-
Jenkinsfile 을 작성하여 Jenkins 에서 배포해 본다.
- docker group 에 jenkins 등록
-
sudo gpasswd -a jenkins docker -
sudo vi /usr/lib/systemd/system/docker.service(에러 발생 시에만 시도)ExecStart=/usr/bin/dockerd -H fd:// -H tcp://0.0.0.0:2376 --containerd=/run/containerd/containerd.sock
-
sudo systemctl daemon-reload -
sudo systemctl restart docker -
sudo service jenkins restart
-
pipeline { agent any parameters { choice(name: 'VERSION', choices: ['1.1.0','1.2.0','1.3.0'], description: '') booleanParam(name: 'executeTests', defaultValue: true, description: '') } stages { stage("init") { steps { script { gv = load "script.groovy" } } } stage("Checkout") { steps { checkout scm } } stage("Build") { steps { sh 'docker-compose build web' } } stage("test") { when { expression { params.executeTests } } steps { script { gv.testApp() } } } stage("deploy") { steps { sh "docker-compose up -d" } } } }
Github 에 Push 시 자동으로 배포하는 trigger 를 설정해 본다.
- Jenkins pipeline 에 Github 을 바로 가도록 설정해 본다.
- Poll SCM 은 매 시간마다 소스가 변경되었는지 확인한다.
- 예) H/3 * * * * → 3분마다 소스가 변경되었는지 확인
- 우리는 'GitHub hook trigger for GITScm polling' 선택
- Github Webhook 설정을 위한 VirtualBox 네트워크 설정 변경
- [설정]-[네트워크]-[어댑터에 브리지]로 변경-[가상머신 재시작]
sudo service jenkins restart- ifconfig 명령으로 public ip 확인
- Jenkins 로 배포하여 접근 확인
- Github Webhook 설정
- Github Repository - Settings - Webhooks - Add webhook
- Payload URL : http://:8080/github-webhook/
- Content type : application/json
- Acitve 활성화
- 코드 변경 후 push 하여 확인해 보기
- 바뀐점
ngrok으로 app 배포
- ngrok url을 webhook으로 전달해야함
Github WebHooks 연동하여 Jenkins 빌드 자동화
배포된 Docker image 를 Docker Hub 로 올리기
- Credentials 생성
- Kind : Username with password
- Username : docker hub 아이디
- password : docker hub access key
- ID : docker-hub / Description : docker-hub
- Jenkinsfile 작성
pipeline { agent any parameters { choice(name: 'VERSION', choices: ['1.1.0','1.2.0','1.3.0'], description: '') booleanParam(name: 'executeTests', defaultValue: true, description: '') } stages { stage("init") { steps { script { gv = load "script.groovy" } } } stage("Checkout") { steps { checkout scm } } stage("Build") { steps { sh 'docker-compose build web' } } stage("test") { when { expression { params.executeTests } } steps { script { gv.testApp() } } } stage("Tag and Push") { steps { withCredentials([[$class: 'UsernamePasswordMultiBinding', credentialsId: 'docker-hub', usernameVariable: 'DOCKER_USER_ID', passwordVariable: 'DOCKER_USER_PASSWORD' ]]) { sh "docker tag jenkins-pipeline_web:latest ${DOCKER_USER_ID}/jenkins-app:${BUILD_NUMBER}" sh "docker login -u ${DOCKER_USER_ID} -p ${DOCKER_USER_PASSWORD}" sh "docker push ${DOCKER_USER_ID}/jenkins-app:${BUILD_NUMBER}" } } } stage("deploy") { steps { sh "docker-compose up -d" } } } }commit 만 하면 자동 push
- docker group 에 jenkins 등록
전체적인 구조
ML App 생성
- 표준화 & 모델링 하고 모델파일 나옴→ joblib 아티팩트로 저장
fast api ,pydantic으로 검사후 serving
- 이렇게 github에 commit을 하면 jenkins가 감지후 app build 및 docker conatiner run
- contianer를 push하고 locust 가 simulation
- prometheus가 jenkins의 metric수집하고 locust에서도 수집
- grafana로 보내 ML 모니터링 대쉬보드 생성
RUN ["python","train.py"] 추가
- joblib형태로 저장해 load를 사용하고 있기때문에 docker container안에서 한번 실행시켜 코드를 저장해야함
-
FastAPI-Prometheus 연동
[app/api.py]
from .monitoring import instrumentator
[app/monitoring.py]
-
패키지 로드, NAMESPACE, SUBSYSTEM 생성
import os from typing import Callable import numpy as np from prometheus_client import Histogram from prometheus_fastapi_instrumentator import Instrumentator, metrics from prometheus_fastapi_instrumentator.metrics import Info NAMESPACE = os.environ.get("METRICS_NAMESPACE", "fastapi") SUBSYSTEM = os.environ.get("METRICS_SUBSYSTEM", "model")
-
instrumentator 생성
- excluded_handlers : "/metrics"
- env_var_name : "ENABLE_METRICS"
- 참고 문서
instrumentator = Instrumentator( should_group_status_codes=True, should_ignore_untemplated=True, should_respect_env_var=True, should_instrument_requests_inprogress=True, excluded_handlers=["/metrics"], env_var_name="ENABLE_METRICS", inprogress_name="fastapi_inprogress", inprogress_labels=True, ) ## ENABLE_METRICS 가 true 인 Runtime 에서만 동작하게 됨 instrumentator.add( metrics.request_size( should_include_handler=True, should_include_method=True, should_include_status=True, metric_namespace=NAMESPACE, metric_subsystem=SUBSYSTEM, ) ) instrumentator.add( metrics.response_size( should_include_handler=True, should_include_method=True, should_include_status=True, metric_namespace=NAMESPACE, metric_subsystem=SUBSYSTEM, ) ) instrumentator.add( metrics.latency( should_include_handler=True, should_include_method=True, should_include_status=True, metric_namespace=NAMESPACE, metric_subsystem=SUBSYSTEM, ) ) instrumentator.add( metrics.requests( should_include_handler=True, should_include_method=True, should_include_status=True, metric_namespace=NAMESPACE, metric_subsystem=SUBSYSTEM, ) )
-
새로운 Metric 생성
- prometheus_client 의 Histogram 활용
- Metric 유형 참고 사이트 [from PromLabs]
- bucket : 임의로 지정해 둔 측정 범위를 의미
- Histogram : bucket 안에 있는 metric 의 빈도 측정
- info object 에 instrumentation 에 필요한 모든 것이 있음
- request, response, modified_handler, modified_status, modified_duration 등
def regression_model_output( metric_name: str = "regression_model_output", metric_doc: str = "Output value of regression model", metric_namespace: str = "", metric_subsystem: str = "", buckets=(0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, float("inf")), ) -> Callable[[Info], None]: METRIC = Histogram( metric_name, metric_doc, buckets=buckets, namespace=metric_namespace, subsystem=metric_subsystem, ) def instrumentation(info: Info) -> None: if info.modified_handler == "/predict": predicted_quality = info.response.headers.get("X-model-score") if predicted_quality: METRIC.observe(float(predicted_quality)) return instrumentation buckets = (*np.arange(0, 10.5, 0.5).tolist(), float("inf")) instrumentator.add( regression_model_output(metric_namespace=NAMESPACE, metric_subsystem=SUBSYSTEM, buckets=buckets) )
- prometheus_client 의 Histogram 활용
-
api 에 연동 부분 추가
from .monitoring import instrumentator ... instrumentator.instrument(app).expose(app, include_in_schema=False, should_gzip=True)
-
docker-compose.yml 내용 변경
version: "3" services: web: build: . container_name: js-fastapi-monitoring volumes: - .:/code ports: - "5000:80" **environment: - ENABLE_METRICS=true** -
로컬에서 git push
-
서버에서 git pull
-
docker-compose build web && docker-compose up -d
-
-
prometheus 로컬 설치
-
prometheus.yml 작성 (참고)
- global.scrape_interval : 몇 초마다 Metric 을 수집할 지 설정
- global.evaluation_interval : AlertRule 을 어느 주기마다 evaluate 할 것인지 설정
- evaluate 하게 되면 inactive, pending, firing 의 3가지 state 로 구분이 되고, 이를 기반으로 alertmanager에서의 알람 발송 여부를 정할 수 있다.
- alertmanager의 rule은 expression을 사용해서 설정할 수 있다.
- scrape_config
- job_name : 메트릭을 수집해서 구분을 할 네이밍을 지정
- static_configs.targets : Metric 을 수집할 서버 주소를 지정한다.
# prometheus.yml global: scrape_interval: 15s evaluation_interval: 30s # scrape_timeout is set to the global default (10s). scrape_configs: - job_name: fastapi honor_labels: true static_configs: - targets: - localhost:5000 # metrics from model
-
prometheus.yml 을 volume 으로 참조해서 실행
docker run -d --name prom-docker --network=host -v <서버 경로>/prometheus.yml:/etc/prometheus/prometheus.yml prom/prometheus
-
localhost:9090/targets 에 접속하여 확인
- grafana 로컬 설치/ prometheus metric 연결 확인
docker run -d --name grafana-docker --network=host grafana/grafana- localhost:3000 접속
- 초기 아이디/비밀번호 : admin/admin
- prometheus 연결 확인
-
- 수행 절차
- Locust 란?
- 구축된 서버의 성능을 측정하기 위한 스트레스 테스트 도구
- API Testing 서비스
- 특징
- @task 데코레이터의 인자값을 이용해 어느 task 를 더 많이 실행할 지 정의
- 구축된 서버의 성능을 측정하기 위한 스트레스 테스트 도구
- 코드 작성
-
locust 폴더, locustfile.py 생성
-
Feature 와 dataset 정의
[locustfile.py]
from locust import HttpUser, task import pandas as pd import random feature_columns = { "fixed acidity": "fixed_acidity", "volatile acidity": "volatile_acidity", "citric acid": "citric_acid", "residual sugar": "residual_sugar", "chlorides": "chlorides", "free sulfur dioxide": "free_sulfur_dioxide", "total sulfur dioxide": "total_sulfur_dioxide", "density": "density", "pH": "ph", "sulphates": "sulphates", "alcohol": "alcohol_pct_vol", } dataset = ( pd.read_csv( "winequality-red.csv", delimiter=",", ) .rename(columns=feature_columns) .drop("quality", axis=1) .to_dict(orient="records") )
-
test class 생성
class WinePredictionUser(HttpUser): @task(1) def healthcheck(self): self.client.get("/healthcheck") @task(10) def prediction(self): record = random.choice(dataset).copy() self.client.post("/predict", json=record) @task(2) def prediction_bad_value(self): record = random.choice(dataset).copy() corrupt_key = random.choice(list(record.keys())) record[corrupt_key] = "bad data" self.client.post("/predict", json=record)
-
locust 폴더에 winequality-red.csv 복사해서 넣기
-
Git 반영
-
서버에서 locust 실행
pip install locust==1.4.1 pip install pandas==0.23.3 docker pull origin master locust -f locust/locustfile.py --host http://127.0.0.1:5000
-
localhost:8089 접속하여 확인
-
- Grafana Dashboard 생성
-
localhost:3000 에 접속
-
-
→ Import → Import via panel json 에 아래 json 입력하고 Load
{ "annotations": { "list": [ { "builtIn": 1, "datasource": "-- Grafana --", "enable": true, "hide": true, "iconColor": "rgba(0, 211, 255, 1)", "name": "Annotations & Alerts", "target": { "limit": 100, "matchAny": false, "tags": [], "type": "dashboard" }, "type": "dashboard" } ] }, "editable": true, "fiscalYearStartMonth": 0, "gnetId": null, "graphTooltip": 0, "id": 3, "links": [], "liveNow": false, "panels": [ { "collapsed": false, "datasource": null, "fieldConfig": { "defaults": {}, "overrides": [] }, "gridPos": { "h": 1, "w": 24, "x": 0, "y": 0 }, "id": 18, "panels": [], "title": "Model Metrics", "type": "row" }, { "datasource": null, "gridPos": { "h": 9, "w": 5, "x": 0, "y": 1 }, "id": 10, "options": { "content": "# Model Predictions\n\n와인 데이터를 이용한 ML 모델 성능 모니터링", "mode": "markdown" }, "pluginVersion": "8.2.5", "timeFrom": null, "timeShift": null, "type": "text" }, { "datasource": null, "fieldConfig": { "defaults": { "mappings": [], "max": 10, "min": 0, "noValue": "No Data", "thresholds": { "mode": "absolute", "steps": [ { "color": "red", "value": null }, { "color": "yellow", "value": 1 }, { "color": "green", "value": 3 }, { "color": "#EAB839", "value": 7 }, { "color": "red", "value": 9 } ] } }, "overrides": [] }, "gridPos": { "h": 9, "w": 4, "x": 5, "y": 1 }, "id": 8, "options": { "orientation": "auto", "reduceOptions": { "calcs": [ "mean" ], "fields": "", "values": false }, "showThresholdLabels": false, "showThresholdMarkers": true, "text": {} }, "pluginVersion": "8.2.5", "targets": [ { "exemplar": true, "expr": "sum(rate(fastapi_model_regression_model_output_sum[3m])) / sum(rate(fastapi_model_regression_model_output_count[3m]))", "interval": "", "legendFormat": "", "refId": "A" } ], "timeFrom": null, "timeShift": null, "title": "Model Score (3m avg)", "type": "gauge" }, { "cards": { "cardPadding": null, "cardRound": null }, "color": { "cardColor": "#F2495C", "colorScale": "sqrt", "colorScheme": "interpolateViridis", "exponent": 0.5, "mode": "spectrum" }, "dataFormat": "tsbuckets", "datasource": null, "description": "Average per second count of predictions which fall into each bucket.", "gridPos": { "h": 9, "w": 15, "x": 9, "y": 1 }, "heatmap": {}, "hideZeroBuckets": true, "highlightCards": true, "id": 6, "legend": { "show": true }, "pluginVersion": "7.2.1", "reverseYBuckets": false, "targets": [ { "exemplar": true, "expr": "sum(rate(fastapi_model_regression_model_output_bucket[1m])) by (le)", "format": "heatmap", "interval": "", "legendFormat": "{{le}}", "refId": "A" } ], "timeFrom": null, "timeShift": null, "title": "Model Prediction Distribution", "tooltip": { "show": true, "showHistogram": false }, "type": "heatmap", "xAxis": { "show": true }, "xBucketNumber": null, "xBucketSize": null, "yAxis": { "decimals": null, "format": "short", "logBase": 1, "max": null, "min": null, "show": true, "splitFactor": null }, "yBucketBound": "auto", "yBucketNumber": null, "yBucketSize": null }, { "collapsed": false, "datasource": null, "fieldConfig": { "defaults": {}, "overrides": [] }, "gridPos": { "h": 1, "w": 24, "x": 0, "y": 10 }, "id": 16, "panels": [], "title": "Service Metrics", "type": "row" }, { "datasource": null, "gridPos": { "h": 9, "w": 5, "x": 0, "y": 11 }, "id": 12, "options": { "content": "# Request Throughput\n\n전체 Reqeust 중 5xx 에러로 돌아오지 않는 비율", "mode": "markdown" }, "pluginVersion": "8.2.5", "timeFrom": null, "timeShift": null, "type": "text" }, { "datasource": null, "fieldConfig": { "defaults": { "mappings": [], "max": 1, "min": 0.8, "noValue": "No Data", "thresholds": { "mode": "absolute", "steps": [ { "color": "red", "value": null }, { "color": "yellow", "value": 0.95 }, { "color": "green", "value": 0.99 } ] }, "unit": "percentunit" }, "overrides": [] }, "gridPos": { "h": 9, "w": 4, "x": 5, "y": 11 }, "id": 14, "options": { "orientation": "auto", "reduceOptions": { "calcs": [ "mean" ], "fields": "", "values": false }, "showThresholdLabels": false, "showThresholdMarkers": true, "text": {} }, "pluginVersion": "8.2.5", "targets": [ { "exemplar": true, "expr": "sum(rate(fastapi_model_http_requests_total{status!=\"5xx\"}[3m])) / sum(rate(fastapi_model_http_requests_total[3m]))", "interval": "", "legendFormat": "", "refId": "A" } ], "timeFrom": null, "timeShift": null, "title": "HTTP Success Rate (3m avg)", "type": "gauge" }, { "aliasColors": {}, "bars": false, "dashLength": 10, "dashes": false, "datasource": null, "fieldConfig": { "defaults": { "unit": "reqps" }, "overrides": [] }, "fill": 10, "fillGradient": 0, "gridPos": { "h": 9, "w": 15, "x": 9, "y": 11 }, "hiddenSeries": false, "id": 2, "legend": { "alignAsTable": false, "avg": false, "current": false, "hideEmpty": false, "hideZero": false, "max": false, "min": false, "show": true, "total": false, "values": false }, "lines": true, "linewidth": 1, "nullPointMode": "null", "options": { "alertThreshold": true }, "percentage": false, "pluginVersion": "8.2.5", "pointradius": 2, "points": false, "renderer": "flot", "seriesOverrides": [], "spaceLength": 10, "stack": true, "steppedLine": false, "targets": [ { "exemplar": true, "expr": "sum(rate(fastapi_model_http_requests_total[1m])) by (status) ", "interval": "", "legendFormat": "", "refId": "A" } ], "thresholds": [], "timeFrom": null, "timeRegions": [], "timeShift": null, "title": "Requests", "tooltip": { "shared": true, "sort": 0, "value_type": "individual" }, "type": "graph", "xaxis": { "buckets": null, "mode": "time", "name": null, "show": true, "values": [] }, "yaxes": [ { "format": "reqps", "label": null, "logBase": 1, "max": null, "min": "0", "show": true }, { "format": "short", "label": null, "logBase": 1, "max": null, "min": null, "show": true } ], "yaxis": { "align": false, "alignLevel": null } }, { "datasource": null, "description": "", "gridPos": { "h": 9, "w": 5, "x": 0, "y": 20 }, "id": 20, "options": { "content": "# Request Latencies ", "mode": "markdown" }, "pluginVersion": "8.2.5", "timeFrom": null, "timeShift": null, "type": "text" }, { "datasource": null, "fieldConfig": { "defaults": { "mappings": [], "min": 0, "thresholds": { "mode": "absolute", "steps": [ { "color": "green", "value": null }, { "color": "red", "value": 80 } ] } }, "overrides": [] }, "gridPos": { "h": 9, "w": 4, "x": 5, "y": 20 }, "id": 23, "options": { "colorMode": "value", "graphMode": "area", "justifyMode": "auto", "orientation": "auto", "reduceOptions": { "calcs": [ "last" ], "fields": "", "values": false }, "text": {}, "textMode": "auto" }, "pluginVersion": "8.2.5", "targets": [ { "exemplar": true, "expr": "sum(fastapi_inprogress)", "instant": false, "interval": "", "legendFormat": "", "refId": "A" } ], "timeFrom": null, "timeShift": null, "title": "Requests In Progress", "type": "stat" }, { "aliasColors": {}, "bars": false, "dashLength": 10, "dashes": false, "datasource": null, "fieldConfig": { "defaults": { "unit": "s" }, "overrides": [] }, "fill": 1, "fillGradient": 0, "gridPos": { "h": 9, "w": 15, "x": 9, "y": 20 }, "hiddenSeries": false, "id": 4, "legend": { "avg": false, "current": false, "max": false, "min": false, "show": true, "total": false, "values": false }, "lines": true, "linewidth": 1, "nullPointMode": "null", "options": { "alertThreshold": true }, "percentage": false, "pluginVersion": "8.2.5", "pointradius": 2, "points": false, "renderer": "flot", "seriesOverrides": [], "spaceLength": 10, "stack": false, "steppedLine": false, "targets": [ { "exemplar": true, "expr": "histogram_quantile(0.99, \n sum(\n rate(fastapi_model_http_request_duration_seconds_bucket[1m])\n ) by (le)\n)", "interval": "", "legendFormat": "99th percentile", "refId": "A" }, { "expr": "histogram_quantile(0.95, \n sum(\n rate(fastapi_http_request_duration_seconds_bucket[1m])\n ) by (le)\n)", "interval": "", "legendFormat": "95th percentile", "refId": "B" }, { "expr": "histogram_quantile(0.50, \n sum(\n rate(fastapi_http_request_duration_seconds_bucket[1m])\n ) by (le)\n)", "interval": "", "legendFormat": "50th percentile", "refId": "C" } ], "thresholds": [], "timeFrom": null, "timeRegions": [], "timeShift": null, "title": "Latency", "tooltip": { "shared": true, "sort": 0, "value_type": "individual" }, "type": "graph", "xaxis": { "buckets": null, "mode": "time", "name": null, "show": true, "values": [] }, "yaxes": [ { "format": "s", "label": null, "logBase": 1, "max": null, "min": null, "show": true }, { "format": "short", "label": null, "logBase": 1, "max": null, "min": null, "show": true } ], "yaxis": { "align": false, "alignLevel": null } }, { "datasource": null, "gridPos": { "h": 9, "w": 5, "x": 0, "y": 29 }, "id": 29, "options": { "content": "# Request Size ", "mode": "markdown" }, "pluginVersion": "8.2.5", "timeFrom": null, "timeShift": null, "type": "text" }, { "datasource": null, "fieldConfig": { "defaults": { "mappings": [], "noValue": "No Data", "thresholds": { "mode": "absolute", "steps": [ { "color": "green", "value": null }, { "color": "#EAB839", "value": 500 } ] }, "unit": "decbytes" }, "overrides": [] }, "gridPos": { "h": 9, "w": 4, "x": 5, "y": 29 }, "id": 31, "options": { "colorMode": "value", "graphMode": "none", "justifyMode": "auto", "orientation": "auto", "reduceOptions": { "calcs": [ "mean" ], "fields": "", "values": false }, "text": {}, "textMode": "auto" }, "pluginVersion": "8.2.5", "targets": [ { "exemplar": true, "expr": "sum(rate(fastapi_model_http_request_size_bytes_sum{handler=\"/predict\"}[3m])) / sum(rate(fastapi_model_http_request_size_bytes_count{handler=\"/predict\"}[3m]))", "interval": "", "legendFormat": "", "refId": "A" } ], "timeFrom": null, "timeShift": null, "title": "Request Size (3m avg)", "type": "stat" }, { "aliasColors": {}, "bars": false, "dashLength": 10, "dashes": false, "datasource": null, "fieldConfig": { "defaults": { "unit": "decbytes" }, "overrides": [] }, "fill": 1, "fillGradient": 0, "gridPos": { "h": 9, "w": 15, "x": 9, "y": 29 }, "hiddenSeries": false, "id": 30, "legend": { "avg": false, "current": false, "max": false, "min": false, "show": true, "total": false, "values": false }, "lines": true, "linewidth": 1, "nullPointMode": "null", "options": { "alertThreshold": true }, "percentage": false, "pluginVersion": "8.2.5", "pointradius": 2, "points": false, "renderer": "flot", "seriesOverrides": [], "spaceLength": 10, "stack": false, "steppedLine": false, "targets": [ { "exemplar": true, "expr": "sum(rate(fastapi_model_http_request_size_bytes_sum{handler=\"/predict\"}[1m])) / sum(rate(fastapi_model_http_request_size_bytes_count{handler=\"/predict\"}[1m]))", "interval": "", "legendFormat": "", "refId": "A" } ], "thresholds": [], "timeFrom": null, "timeRegions": [], "timeShift": null, "title": "Request Size", "tooltip": { "shared": true, "sort": 0, "value_type": "individual" }, "type": "graph", "xaxis": { "buckets": null, "mode": "time", "name": null, "show": true, "values": [] }, "yaxes": [ { "format": "decbytes", "label": null, "logBase": 1, "max": null, "min": "0", "show": true }, { "format": "short", "label": null, "logBase": 1, "max": null, "min": null, "show": true } ], "yaxis": { "align": false, "alignLevel": null } }, { "collapsed": false, "datasource": null, "fieldConfig": { "defaults": {}, "overrides": [] }, "gridPos": { "h": 1, "w": 24, "x": 0, "y": 38 }, "id": 25, "panels": [], "title": "Resource Metrics", "type": "row" } ], "refresh": "5s", "schemaVersion": 32, "style": "dark", "tags": [], "templating": { "list": [] }, "time": { "from": "now-5m", "to": "now" }, "timepicker": {}, "timezone": "", "title": "Model Dashboard", "uid": "K1ZW-uxGz", "version": 2 }
-
-
결과 화면
-
- Locust 란?
-
Jenkins 재시작
sudo service jenkins restart
-
Jenkins Pipeline 생성
- [새로운 item] - [Pipeline : monitoring-pipeline]
- Jenkins 설정
-
Jenkinsfile 생성
pipeline { agent any stages { stage("Checkout") { steps { checkout scm } } stage("Build") { steps { sh 'docker-compose build web' } } stage("deploy") { steps { sh "docker-compose up -d" } } stage("Update model") { steps { sh "docker exec -i js-fastapi-monitoring python train.py" } } } }
-
Jenkins 빌드 실행
-
'GitHub hook trigger for GITScm polling' 선택
-
Github Webhook 설정을 위한 VirtualBox 네트워크 설정 변경
- [설정]-[네트워크]-[어댑터에 브리지]로 변경-[가상머신 재시작]
sudo service jenkins restart- ifconfig 명령으로 public ip 확인
- Jenkins 로 배포하여 접근 확인
-
Github Webhook 설정
- Github Repository - Settings - Webhooks - Add webhook
- Payload URL : http://:8080/github-webhook/
- Content type : application/json
- Acitve 활성화
- 코드 변경 후 push 하여 확인해 보기
-
HistGradientBoostingRegressor 를 RandomForestRegressor 로 변경해 보기
-
import 에 추가
from sklearn.ensemble import HistGradientBoostingRegressor, RandomForestRegressor ... model = RandomForestRegressor(max_depth=30).fit(X_train, y_train)
-
max_depth=30
-
Jenkins 자동 빌드 및 배포 확인
-
Granfana Dashboard 변화 확인
-
Jenkins Monitoring