Roslyn-based analyzer to provide diagnostics of static fields and properties initialization and more.
- Wrong order of static field and property declaration
- Partial type member reference across files
- Cross-Referencing Problem of static field across type
Enumtype analysis to prevent user-level value conversion & morestructparameter-less constructor misuse analysisDisposableanalyzer to detect missing using statementTSelfgeneric type argument & type constraint analysis- Annotating and underlining field, property or etc with custom message
- Find out all diagnostic rules: RULES.md
Restrict both cast from/to integer number! Disallow user-level enum value conversion completely!!
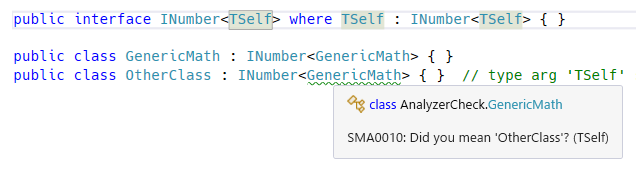
Analyze TSelf type argument mismatch and where clause mismatch.
There is fancy extra feature to take your attention while coding in Visual Studio. No more need to use Obsolete attribute in case of annotating types, methods, fields and properties.
See the following section for details.
- NuGet
- https://www.nuget.org/packages/SatorImaging.StaticMemberAnalyzer
-
PM> Install-Package SatorImaging.StaticMemberAnalyzer
Analyzer is tested on Visual Studio 2022.
You could use this analyzer on older versions of Visual Studio. To do so, update Vsix project file by following instructions written in memo and build project.
This analyzer can be used with Unity 2020.2 or above. See the following page for detail.
SatorImaging.StaticMemberAnalyzer.Unity/
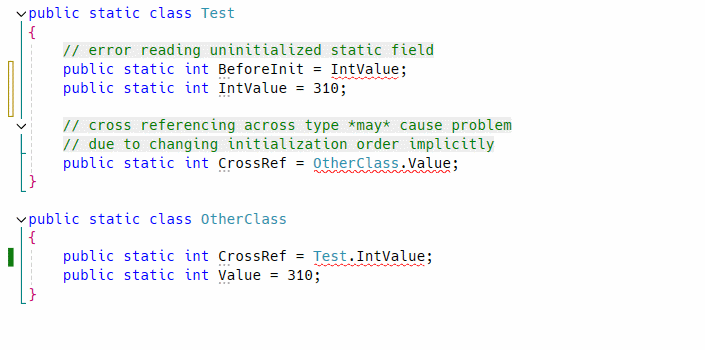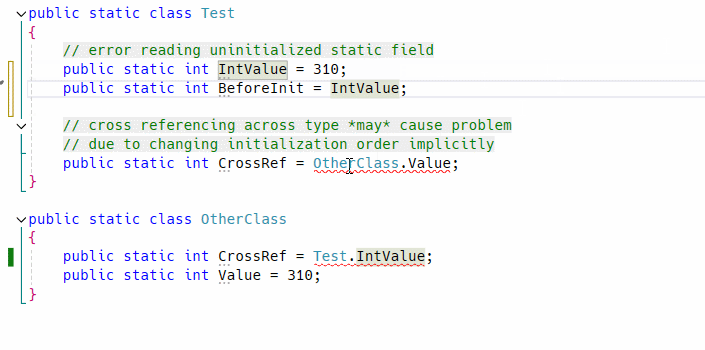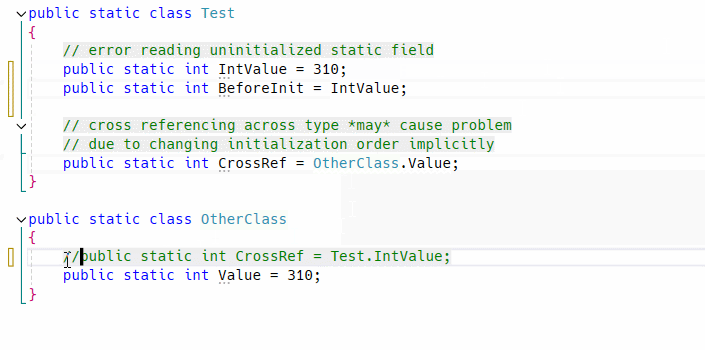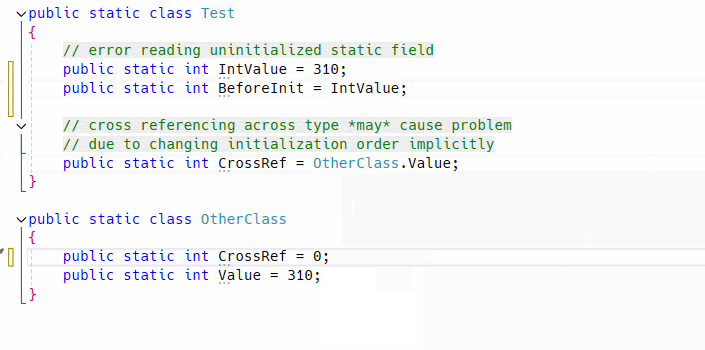
It is a design bug makes all things complex. Not only that but also it causes initialization error only when meet a specific condition.
So it must be fixed even if app works correctly at a moment, to prevent simple but complicated potential bug which is hard to find in large code base by hand. As you know static fields will never report error when initialization failed!!
class A {
public static int Value = B.Other;
public static int Other = 310;
}
class B {
public static int Other = 620;
public static int Value = A.Other; // will be '0' not '310'
}
public static class Test
{
public static void Main()
{
System.Console.WriteLine(A.Value); // 620
System.Console.WriteLine(A.Other); // 310
System.Console.WriteLine(B.Value); // 0 👈👈👈
System.Console.WriteLine(B.Other); // 620
// when changing class member access order, it works correctly 🤣
// see the following section for detailed explanation
//System.Console.WriteLine(B.Value); // 310 👈 correct!!
//System.Console.WriteLine(B.Other); // 620
//System.Console.WriteLine(A.Value); // 620
//System.Console.WriteLine(A.Other); // 310
}
}C# Compiler Initialization Sequence
A.Value = B.Other;- // 'B' initialization is started by member access
B.Other = 620;B.Value = A.Other;// BUG: B.Value will be 0 because reading uninitializedA.Other- // then, assign
B.Othervalue (620) toA.Value
A.Other = 310;// initialized here!! this value is not assigned to B.Value
When reading B value first, initialization order is changed and resulting value is also changed accordingly:
B.Other = 620;B.Value = A.Other;- // 'A' initialization is started by member access
A.Value = B.Other;// correct: B.Other is initialized before reading valueA.Other = 310;
Enum type handling is really headaching. To make enum operation under control, good to avoid user-level enum handling such as converting to integer or string, parse from string and etc.
This analyzer will help centerizing and encapsulating enum handling in app's central enum utility.
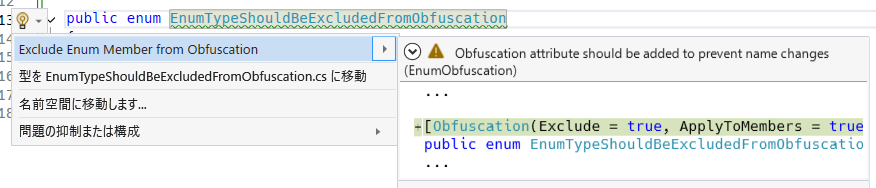
Helpful annotation and code fix for enum types to prevent modification of string representation by obfuscation tool.
Note
Obfuscation attribute is from C# base library and it does NOT provide feature to obfuscate compiled assembly. It just provides configuration option to obfuscation tools which recognizing this attribute.
Analysis to help implementing Kotlin-style enum class.
Enum-like type requirements:
MyEnumLike[]orReadOnlyMemory<MyEnumLike>field(s) exist- analyzer will check field initializer correctness if name is starting with
Entries(case-sensitive) or ending withentries(case-insensitive)
- analyzer will check field initializer correctness if name is starting with
sealedmodifier on typeprivateconstructor onlypublic staticmember calledEntriesexistspublic bool Equalsmethod should not be declared/overridden
public class EnumLike
// ~~~~~~~~ WARN: no `sealed` modifier on type and public constructor exists
// * this warning appears only if type has member called 'Entries'
{
public static readonly EnumLike A = new("A");
public static readonly EnumLike B = new("B");
public static ReadOnlySpan<EnumLike> Entries => EntriesAsMemory.Span;
// 'Entries' must have all of 'public static readonly' fields in declared order
static readonly EnumLike[] _entries = new[] { B, A };
// ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ wrong order!!
// 'ReadOnlyMemory<T>' can be used instead of array
public static readonly ReadOnlyMemory<EnumLike> EntriesAsMemory = new(new[] { A, B });
/* === Kotlin style enum template === */
static int AUTO_INCREMENT = 0; // iota
public readonly int Ordinal;
public readonly string Name;
private EnumLike(string name) { Ordinal = AUTO_INCREMENT++; Name = name; }
public override string ToString()
{
const string SEP = ": ";
Span<char> span = stackalloc char[Name.Length + 32];
Ordinal.TryFormat(span, out var written);
SEP.AsSpan().CopyTo(span.Slice(written));
written += SEP.Length;
Name.AsSpan().CopyTo(span.Slice(written));
written += Name.Length;
return span.Slice(0, written).ToString();
}
}Benefits
Kotlin-like enum (algebraic data type) can prevent invalid value creation.
var invalid = Activator.CreateInstance(typeof(EnumLike));
if (EnumLike.A == invalid || EnumLike.B == invalid)
{
// this code path won't be reached
// each enum like entry is a class instance and ReferenceEquals match required
}Unfortunately, use in switch statement is a bit weird.
var val = EnumLike.A;
switch (val)
{
// pattern matching with case guard...!!
case EnumLike when val == EnumLike.A:
System.Console.WriteLine(val);
break;
case EnumLike when val == EnumLike.B:
System.Console.WriteLine(val);
break;
}
// this pattern generates same AOT compiled code
switch (val)
{
// typeless case guard
case {} when val == EnumLike.A:
System.Console.WriteLine(val);
break;
case {} when val == EnumLike.B:
System.Console.WriteLine(val);
break;
}var d = new Disposable();
// ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ no `using` statement found
d = (new object()) as IDisposable;
// ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ cast from/to disposableAnalyzer won't show warning in the following condition:
- instance is created on
returnstatementreturn new Disposable();
- assign instance to field or property
m_field = new Disposable();
- cast between disposable types
var x = myDisposable as IDisposable;
To suppress analysis for specified types, declare attribute named DisposableAnalyzerSuppressor and add it to assembly.
[assembly: DisposableAnalyzerSuppressor(typeof(Task), typeof(Task<>))] // Task and Task<T> are ignored by default
[Conditional("DEBUG"), AttributeUsage(AttributeTargets.Assembly, AllowMultiple = true)]
sealed class DisposableAnalyzerSuppressor : Attribute
{
public DisposableAnalyzerSuppressor(params Type[] _) { }
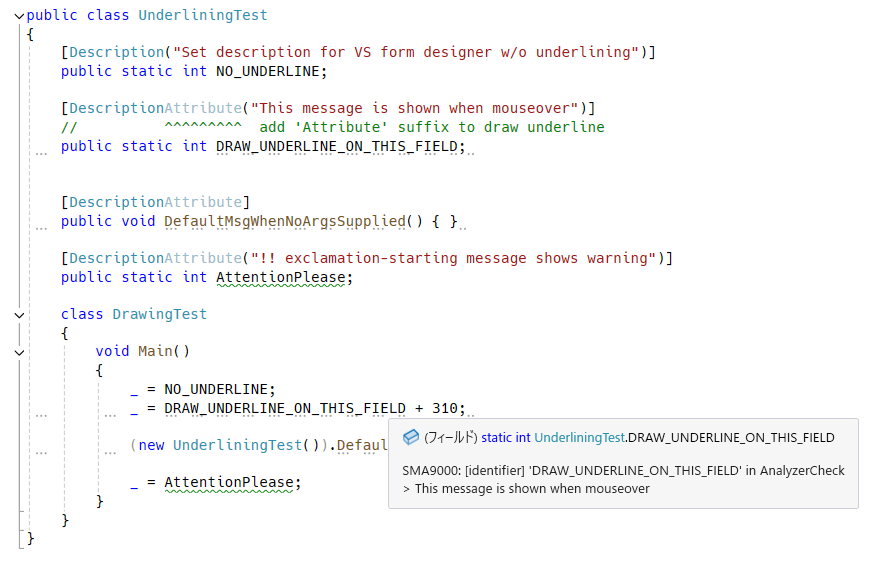
}There is optional feature to draw underline on selected types, fields, properties, generic type/method arguments and parameters of method, delegate and lambda function.
As of Visual Studio's UX design, Info severity diagnostic underlines are drawn only on a few leading chars, not drawn whole marked area. So for workaround, underline on keyword is dashed.
Tip
!-starting message will add warning annotation on keyword instead of info diagnostic annotation.
To avoid dependency to this analyzer, required attribute for underlining is chosen from builtin System.ComponentModel assembly so that syntax is little bit weird.
Analyzer is checking identifier keyword in C# source code, not checking actual C# type. DescriptionAttribute in C# attribute syntax is the only keyword to draw underline. Omitting Attribute or adding namespace are not recognized.
Tip
CategoryAttribute can be used instead of DescriptionAttribute.
By contrast from Description, CategoryAttribute draws underline only on exact type reference and constructors including base(). Any inherited types, variables, fields and properties don't get underline.
using System.ComponentModel;
[DescriptionAttribute("Draw underline for IDE environment and show this message")]
// ^^^^^^^^^ `Attribute` suffix is required to draw underline
public class WithUnderline
{
[DescriptionAttribute] // parameter-less will draw underline with default message
public static void Method() { }
}
// C# language spec allows to omit `Attribute` suffix but when omitted, underline won't be drawn
// to avoid conflict with originally designed usage for VS form designer
[Description("No Underline")]
public class NoUnderline { }
// underline won't be drawn when namespace is specified
[System.ComponentModel.DescriptionAttribute("...")]
public static int Underline_Not_Drawn = 0;
// this code will draw underline. 'Trivia' is allowed to being added in attribute syntax
[ /**/ DescriptionAttribute ( "Underline will be drawn" ) /* hello, world. */ ]
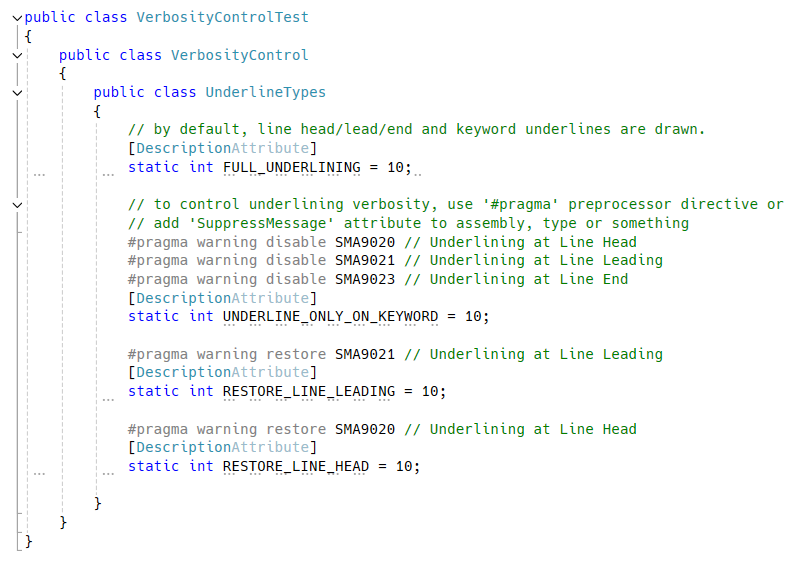
public static int Underline_Drawn = 310;There are 4 types of underline, line head, line leading, line end and keyword.
By default, static field analyzer will draw most verbose underline.
You can omit specific type of underline by using #pragma preprocessor directive or adding SuppressMessage attribute or etc.
Underlining is achieved by using Description attribute designed for Visual Studio's visual designer, formerly known as form designer.
To remove unnecessary attribute from Unity build, add the following link.xml file in Unity project's Assets folder.
<linker>
<assembly fullname="System.ComponentModel">
<type fullname="System.ComponentModel.DescriptionAttribute" preserve="nothing"/>
</assembly>
</linker>
Steps to publish new version of nuget package
- update nuget package version in
.props - upload source code to github
- run build action for test
- merge pull request sent from build action
- create github release
- run nuget packaging action to push new version
- lambda return statement
MethodArg(() => DisposableProperty);MethodArg(() => { return DisposableProperty; });
?:operatorDisposableProperty = condition ? null : disposableList[index];
- implicit cast suppressor attribute
[assembly: EnumAnalyzer(SuppressImplicitCast = true)]- DO NOT suppress cast to
objectEnumstringintor other blittable types - (implicit cast operator is designed function in almost cases. it should be suppressed by default?)
- DO NOT suppress cast to
- allow internal only entry for Enum-like types
sealed class MyEnumLike { public static readonly MyEnumLike PublicEntry = new(); internal static readonly MyEnumLike ForDebuggingPurpose = new(); }
- features not supported
ITypeParameterObjectCreationOperationIDefaultValueOperation
- unnecessary optimization...??
ts_singleLocation-->ImmutableArray.Create(loc)- https://github.com/dotnet/runtime/blob/main/src/libraries/System.Collections.Immutable/src/System/Collections/Immutable/ImmutableArray.cs#L37
- entry method has many
ifstatements. seems that ready to be separated- underlining by
CategoryAttribute - lambda analysis
- ...and other if statements can be made more simple by separating analyzer action registration
- underlining by
- Implement
IViewTaggerProviderfor underlining analyzer.