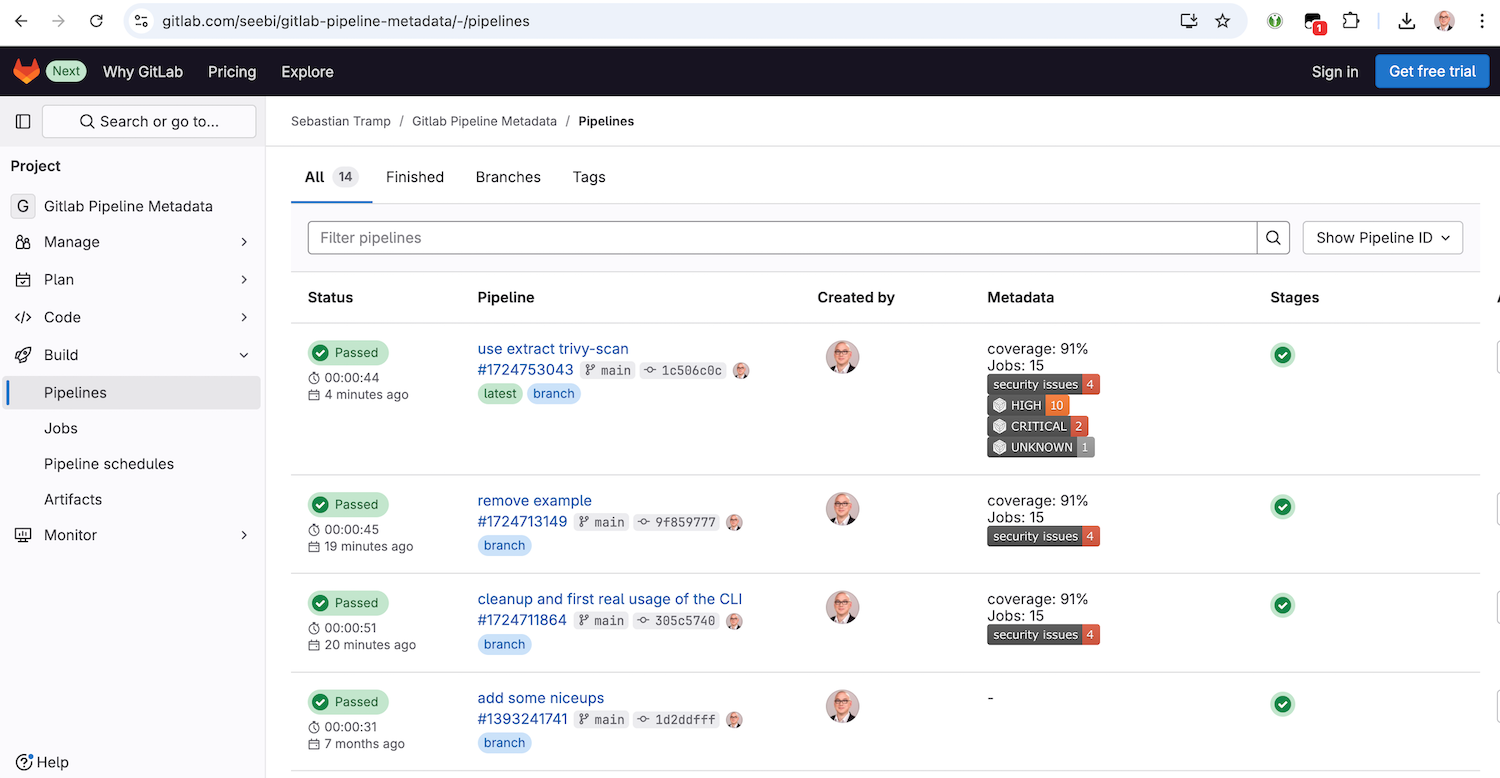
cimd is about collecting and sharing structured metadata of CI/CD processes.
cimd is an acronym for Continuous Integration Meta Data.
🤓 Motivation ··· 🚀 Features ··· ⚙️ Installation
🐍 Development ··· 📄 Specification ··· ℹ️ Similar Project
To enable a fast overview of recent pipelines and their metadata in a GitLab-managed repository, this project provides the backend and frontend capabilities to extend the GitLab pipeline list with a custom metadata column.
GitLab already has some metadata mechanisms (e.g. coverage patterns), but they are limited to a specific scope.
The basic idea of this project is to prepare and provide extensible metadata artefacts on a well-known position, which can be easily fetched and parsed by a custom user script to extend the pipeline list with metadata item representations.
cimd contains of a command line tool (CLI) and a frontend user script.
The frontend is available as a single JavaScript file in the js folder.
It is currently tested with Tampermonkey on Google Chrome only 🙈.
Once activated, it will extend the pipeline view of your 
The CLI is used to prepare and manipulate metadata items in a __metadata__.json document.
It has the following features:
- commands for basic CRUD operations:
add- add a metadata itemdelete- delete metadata itemsget- get data of a metadata itemlist- list metadata items
extractcommand group, which collects commands to extract metadata items from different sources:coverage-xml- extract metadata from a Coverage XML output filesjunit-xml- extract metadata from JUnit XML output filespipeline-logs- extract metadata from gitlab pipeline job logstrivy-scan- extract metadata from Trivy scan JSON output files
extendcommand group, which collects commands to extend metadata items in a special way:gitlab-link- extend metadata items with a raw gitlab artifact linkshields-badge- extend metadata items with a shields.io badge
To install the frontend userscript with a user script manager such as Tampermonkey, you have the following options:
- Recommended: Go to the greasyfork.org entry of cimd and click the install button.
- Create a new script entry and copy/paste the content of the script from the js folder.
After installation, feel free to go to the example pipeline list at gitlab.com/seebi/gitlab-pipeline-metadata.
To install and use the cimd command line interface, you have all the options the python ecosystem provides:
-
Recommended ... via pipx
pipx install cimd
-
The cool way ... via uv
uvx cimd
-
There is also a docker image ...
docker run -i -t --rm -v $(pwd):/data seebi/cimd
- Run task to see all major development tasks.
- Use pre-commit to avoid errors before commit.
- This repository was created with this copier template.
This section describes the details about the JSON data artifact (__metadata__.json) which holds your pipeline metadata.
In your pipeline description, create a job which provides a JSON artifact adhering to the schema at the path __metadata__.json.
An example .gitlab-ci.yml, which creates some basic metadata items, is available at gitlab.com/seebi/gitlab-pipeline-metadata.
The content of the __metadata__.json is a simple structure to describe separate metadata items.
{
"items": {
"coverage": {
"value": "87%"
}
}
}In addition to that, the following optional keys can be used for a metadata item: label, description, image, link and comment.
{
"items": {
"coverage": {
"value": "87",
"comment": "'value' is the only mandatory key of a metadata item."
},
"jobs": {
"value": "15",
"label": "Jobs",
"description": "Number of overall jobs executed in the pipeline.",
"comment": "'label' and 'description' can be used to enhance the UI."
},
"security_issues": {
"value": "4",
"image": "https://img.shields.io/badge/security%20issues-4-red",
"link": "https://example.org/security_issues",
"comment": "We all love badges - and clickable badges are even better."
}
}
}Hereinafter you will find some comments on the optional field:
label- A human readable label for a metadata item. If present, it should be used by the frontend instead of the item identifier.description- A description of the metadata item. If present, can be used as on-hover text in the frontend for an item.image- An optional link to an image representation of the item (e.g. a shields.io image). If present, it should be used instead of the ID/Label/Value representation of the item. Images should be rendered with max-height/width.link- If present, the metadata item representation is click-able.comment- will be ignored by the frontend, for debugging only.
The proposed JSON structure is formalized as a JSON Schema which is available at schema/schema.json or can be visualized in the [email protected].
💬 Drop me a note if you miss a project here ...
- github-action-benchmark - is a GitHub Action for continuous benchmarking to keep performance