If you are updating from v1.3 or earlier to v1.6, you must update your AlexaClientSDKConfig.json to include a Notifications database. An updated sample is available in the quickstart guides for Ubuntu Linux, Raspberry Pi, macOS, and Generic Linux.
The Alexa Voice Service (AVS) enables developers to integrate Alexa directly into their products, bringing the convenience of voice control to any connected device. AVS provides developers with access to a suite of resources to quickly and easily build Alexa-enabled products, including APIs, hardware development kits, software development kits, and documentation.
The AVS Device SDK provides C++-based (11 or later) libraries that leverage the AVS API to create device software for Alexa-enabled products. It is modular and abstracted, providing components for handling discrete functions such as speech capture, audio processing, and communications, with each component exposing the APIs that you can use and customize for your integration. It also includes a sample app, which demonstrates the interactions with AVS.
You can set up the SDK on the following platforms:
- Raspberry Pi (Raspbian Stretch)
- Download the install script. We recommend running these commands from the home directory (
~/) or Desktop; however, you can run the script anywhere.
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/xmos/avs-device-sdk/master/tools/Install/setup.sh
- Run the setup script:
sudo bash setup.sh
You can also prototype with a third party development kit:
- XMOS VocalFusion 4-Mic Kit - Learn More Here
Or if you prefer, you can start with our SDK API Documentation.
Watch this tutorial to learn about the how this SDK works and the set up process.
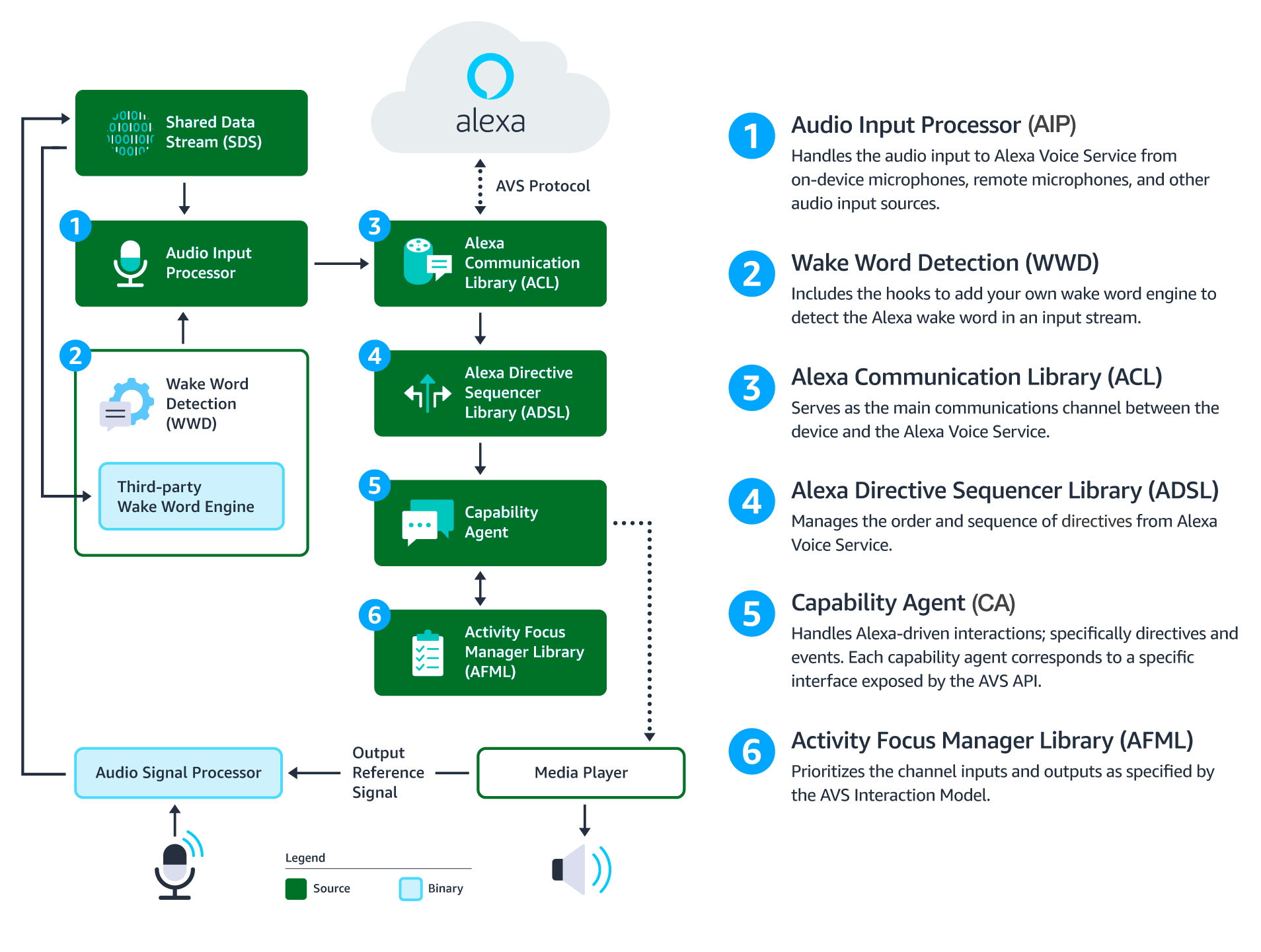
This diagram illustrates the data flows between components that comprise the AVS Device SDK for C++.
Audio Signal Processor (ASP) - Third-party software that applies signal processing algorithms to both input and output audio channels. The applied algorithms are designed to produce clean audio data and include, but are not limited to acoustic echo cancellation (AEC), beam forming (fixed or adaptive), voice activity detection (VAD), and dynamic range compression (DRC). If a multi-microphone array is present, the ASP constructs and outputs a single audio stream for the array.
Shared Data Stream (SDS) - A single producer, multi-consumer buffer that allows for the transport of any type of data between a single writer and one or more readers. SDS performs two key tasks:
- It passes audio data between the audio front end (or Audio Signal Processor), the wake word engine, and the Alexa Communications Library (ACL) before sending to AVS
- It passes data attachments sent by AVS to specific capability agents via the ACL
SDS is implemented atop a ring buffer on a product-specific memory segment (or user-specified), which allows it to be used for in-process or interprocess communication. Keep in mind, the writer and reader(s) may be in different threads or processes.
Wake Word Engine (WWE) - Software that spots wake words in an input stream. It is comprised of two binary interfaces. The first handles wake word spotting (or detection), and the second handles specific wake word models (in this case "Alexa"). Depending on your implementation, the WWE may run on the system on a chip (SOC) or dedicated chip, like a digital signal processor (DSP).
Audio Input Processor (AIP) - Handles audio input that is sent to AVS via the ACL. These include on-device microphones, remote microphones, an other audio input sources.
The AIP also includes the logic to switch between different audio input sources. Only one audio input source can be sent to AVS at a given time.
Alexa Communications Library (ACL) - Serves as the main communications channel between a client and AVS. The ACL performs two key functions:
- Establishes and maintains long-lived persistent connections with AVS. ACL adheres to the messaging specification detailed in Managing an HTTP/2 Connection with AVS.
- Provides message sending and receiving capabilities, which includes support JSON-formatted text, and binary audio content. For additional information, see Structuring an HTTP/2 Request to AVS.
Alexa Directive Sequencer Library (ADSL): Manages the order and sequence of directives from AVS, as detailed in the AVS Interaction Model. This component manages the lifecycle of each directive, and informs the Directive Handler (which may or may not be a Capability Agent) to handle the message.
Activity Focus Manager Library (AFML): Provides centralized management of audiovisual focus for the device. Focus is based on channels, as detailed in the AVS Interaction Model, which are used to govern the prioritization of audiovisual inputs and outputs.
Channels can either be in the foreground or background. At any given time, only one channel can be in the foreground and have focus. If multiple channels are active, you need to respect the following priority order: Dialog > Alerts > Content. When a channel that is in the foreground becomes inactive, the next active channel in the priority order moves into the foreground.
Focus management is not specific to Capability Agents or Directive Handlers, and can be used by non-Alexa related agents as well. This allows all agents using the AFML to have a consistent focus across a device.
Capability Agents: Handle Alexa-driven interactions; specifically directives and events. Each capability agent corresponds to a specific interface exposed by the AVS API. These interfaces include:
- SpeechRecognizer - The interface for speech capture.
- SpeechSynthesizer - The interface for Alexa speech output.
- Alerts - The interface for setting, stopping, and deleting timers and alarms.
- AudioPlayer - The interface for managing and controlling audio playback.
- Notifications - The interface for displaying notifications indicators.
- PlaybackController - The interface for navigating a playback queue via GUI or buttons.
- Speaker - The interface for volume control, including mute and unmute.
- System - The interface for communicating product status/state to AVS.
- TemplateRuntime - The interface for rendering visual metadata.
- Review the AVS Terms & Agreements.
- The earcons associated with the sample project are for prototyping purposes only. For implementation and design guidance for commercial products, please see Designing for AVS and AVS UX Guidelines.
- Please use the contact information below to-
- Contact Sensory for information on TrulyHandsFree licensing.
- Contact KITT.AI for information on SnowBoy licensing.
- IMPORTANT: The Sensory wake word engine referenced in this document is time-limited: code linked against it will stop working when the library expires. The library included in this repository will, at all times, have an expiration date that is at least 120 days in the future. See Sensory's GitHub page for more information.
Note: Feature enhancements, updates, and resolved issues from previous releases are available to view in CHANGELOG.md.
v1.6.0 released 03/08/2018:
Enhancements
rapidJsonis now included with "make install".- Updated the
TemplateRuntimeObserverInterfaceto support clearing ofdisplayCards. - Added Windows SDK support, along with an installation script (MinGW-w64).
- Updated
ContextManagerto ignore context reported by a state provider. - The
SharedDataStreamobject is now associated by playlist, rather than by URL. - Added the
RegistrationManagercomponent. Now, when a user logs out all persistent user-specific data is cleared from the SDK. The log out functionality can be exercised in the sample app with the new command:k.
Bug Fixes
- Issue 400 Fixed a bug where the alert reminder did not iterate as intended after loss of network connection.
- Issue 477 Fixed a bug in which Alexa's weather response was being truncated.
- Fixed an issue in which there were reports of instability related to the Sensory engine. To correct this, the
portAudiosuggestedLatencyvalue can now be configured.
Known Issues
- The
ACLmay encounter issues if audio attachments are received but not consumed. SpeechSynthesizerStatecurrently usesGAINING_FOCUSandLOSING_FOCUSas a workaround for handling intermediate state. These states may be removed in a future release.- Music playback doesn't immediately stop when a user barges-in on iHeartRadio.
- The Windows sample app hangs on exit.
- GDB receives a
SIGTRAPwhen troubleshooting the Windows sample app. make integrationdoesn't work on Windows. Integration tests will need to be run individually.