Table of Contents generated with DocToc
- Lipidnotater
- Viktig prinsipp for regulering:
- Cahpter 6 fatty acid synthesis - Forholdet mellom Karbohydrat og Lipid-syntese - Likheter mellom oksidasjon og syntese: - Oversikt - Regulering
- Chap 5. Oxidation of fatty acids in eukaryotes - Generell bakgrunn: - Beta oksidasjon - 3.3 β-oxidation of unsaturated fatty acids - Regulering
- Chapter 7 Desaturation and chain elongation. - Elongering - Viktige enzymer - Desaturering - Desaturaser og samhandling med Elovl enzymer - Regulering av desaturaser og Elongaser
- Lipprotein Oversikt
- Lipoprotein structure - Main apolipoprotein function
- Lipoprotein Receptors - LDL receptors - Mutations
- PPAR-alfa- induserer fettsyreoksiderings-gener
- Derav gener for: fatty acid transport, fatty binding and activation, and peroxisomal and mitochondrial fatty acid β-oxidation. (including PDK4, ACOX1, and CPT1.)
- PPARS aktiveres av LCFA.
- SREBP-1 induserer syntese gener. SREBP-1c is responsible for regulating the genes required for de novo lipogenesis. SREBP er også oppregulert av insulin og kolesterol derivater. Anabole hormoner. I ku kan det virke som PPARg er med å nedregulere SREBP og dermed lipogenese.
Først og fremst:
Bakgrunn:
Substratet for Fettsyresyntese er Acetyl-CoA. Et produkt i sitronsyresyklus der glukose omdannes til energi.
Dette kommer via citrat som passerer mitokondriemembranen.
Citrat tar veien over til cytosol.
- I simpleste form handler FAS om å kombinere Acetyl-CoA (2 C) til Palmitin-Syre (16 C) i en energikrevende sirkelreaksjon. ATP + H20 -> ADP + H+
Regnskapet for en hel runde fra Acetyl-CoA til palmitate blir da:
- Palmitinsyre brukes videre som utgangspunkt for å lage lengre fettsyrer og for å legge til dobbeltbindinger.
Fatty acid synthesis starts with the carboxylation of acetyl CoA to malonyl CoA. This irreversible reaction is the committed step in fatty acid synthesis
- The enzyme system that catalyzes the synthesis of saturated long-chain fatty acids from acetyl CoA, malonyl CoA, and NADPH is called the fatty acid synthase
- Fatty acids are synthesized by the repetition of the following reaction sequence: condensation, reduction, dehydration, and reduction.
- The growing fatty acid chain is elongated by the sequential addition of two-carbon units derived from acetyl CoA. The activated donor of twocarbon units in the elongation step is malonyl ACP.(Acyl carrier protein)
- Fatty acids are synthesized in the cytosol, whereas acetyl CoA is formed from pyruvate in mitochondria. Hence, acetyl CoA must be transferred from mitochondria to the cytosol. The barrier to acetyl CoA is bypassed by citrate, which carries acetyl groups across the inner mitochondrial membrane
- Elongation by the fatty acid synthase complex stops on formation of palmitate (C16). Further elongation and the insertion of double bonds are carried out by other enzyme systems.
Endelig skjebne Fettsyrene blir koblet på glycerol til triaceyl-glyserider og syntetisert til VLDL i leveren og transportert til resten av kroppen
Acetyl-CoA karboksylase Rate limiting enzyme..
* Legger til karboksylgruppe til Acetyl-CoA --> Malonyl-CoA.
Pos regulering:
- Alosterisk (molekyl fester seg på anne sted på enzymet) ved Citrat Regulerer oppover/fremover-
- Hormonell: Insulin (Trenger fettsyresyntese etter høy glukose i blodet)
Neg Regulering:
- Hormonell:Glukagon (Bryter ned fettsyrer for energi.)
- Alosterisk: Langkjedede fettsyrer. (Neg tilbakekobling)
- Fettsyrer trenger å transporteres fra cytosol til Mitokondriemembran.
- Carnitine Acyl transferase I.
- Aktivere Fettsyren.
- Legge til Carnitin
- Transport inn i mitokondriell matrix.
- Beta-oksidasjon
- Lager NADH og FADH2 til elktrontransportkjeden og prod av ATP.
All produksjon av energi skjer i mitokondriet, både Oksidering samt celleånding. Krebs-syklus.
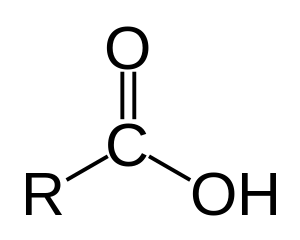
Fettsyre: Karboksylsyre med lang karbonkjede. Karboksylsyre
General Fatty Acid Formula
General chemical structure of an acyl-CoA, where R is a fatty acid side chain -->
NADH
In metabolism, NAD+ is involved in redox reactions, carrying electrons from one reaction to another.
FADH2
flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD) is a redox cofactor involved in several important reactions in metabolism.
Hvert andre C fra karbonyl-ende av acyl-CoA bli oksydert til Acetyl CoA og prod Reduksjonsagenter for ATP-prod.
FA oxidation on Wikpedia In the words of Wikipedia:
"Beta-oxidation is the process by which fatty acid molecules are broken down in the mitochondria to generate acetyl-coA, which enters the citric acid cycle, and NADH and FADH2, which are used by the electron transport chain."
-
Reaction 1: The Initial Dehydrogenation (Diagram, Figure 18.17) Catalyzed by fatty acyl-CoA dehydrogenase Electrons passed to enzyme-bound FAD and then to Coenzyme Q (like succinate dehydrogenase)
-
Reactions 2 and 3: Hydration and Dehydrogenation Catalyzed by enoyl-CoA hydratase and 3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase, respectively. Electrons passed to NAD+
-
Reaction 4: Thiolytic Cleavage Catalyzed by -ketothiolase (thiolase)
Enoyl-CoA Hydratase, a key enzyme in -oxidation of saturated fatty acids, acts on trans double bonds, but cannot act on the cis double bonds of unsaturated fatty acids. Instead, cells must rely on two additional enzymes, enoyl-CoA isomerase and 2,4-dienoyl-CoA reductase, to complete the -oxidation of unsaturated fatty acids. The activity of these enzymes is shown in Figure 18.18.
-
Enoyl-CoA Isomerase catalyzes conversion of cis double bonds at positions 3-4 to trans double bonds at positions 2-3.
-
2,4-Dienoyl-CoA Reductase catalyzes the reduction of the conjugated double bonds, cis 4-5 and trans 2-3 to a single cis double bond between carbons 3-4. This reaction uses electrons from NADPH.
-
In each case, enoyl-CoA isomerase and 2,4-dienoyl-CoA reductase converts an intermediate with a cis double bond into an intermediate with a trans double bond. Moreover, the trans double bond has the appropriate structure to be handled by the enzymes involved in the -oxidation of saturated fatty acids.
-
It should be noted that enoyl-CoA isomerase and 2,4-dienoyl-CoA reductase only help metabolize dietary unsaturated fatty acids with double bonds in the cis configuration. Dietary fatty acids with trans double bonds are not readily metabolized and may pose a health hazard.
Take home message
- Enoyl CoA hydratase må ha hjelp av ytterligere to enzymer for okisdasjon av umettede fettsyrer. Kun cis bindinger er brukbare, og trans-bindinger vil ikke brytes ned til energi og med sin mettede struktur skaper de problemer i kroppen.
- Positiv: I hovedsak styres graden av oksidasjon i cellene av substratetts tilgjengelighet. Dette er igjen avhengig av hormonell aktivitet. Glucagon og Ephinephrine stimulerere release av fettsyrer og opphopning av disse i celler og økt oksidasjon.
- Negativ: Malonyl-CoA alosterisk hemmer av Carnitine Acyl transferase I som fører fettsyrer fra Cytosol til Mitokondire-Matrix. Malonyl-CoA er også prod av Acetyl-CoA karboksylase første steg i fettsyresyntese.
- Malonyl-CoA vil altså øke syntese ved å aktivere syntese i Cytosol, og hemme opptak av Fatty-Acyl-Carnitine, det første steget i Beta-oksidasjon.
Fettsyrer med 16C eller mer, blir modifisert i:
- ER
- Mitokondrier
- Perixosomer
"The major product of the fatty acid synthase is palmitate. In eukaryotes, longer fatty acids are formed by elongation reactions catalyzed by enzymes on the cytosolic face of the endoplasmic reticulum membrane. These reactions add two-carbon units sequentially to the carboxyl ends of both saturated and unsaturated fatty acyl CoA substrates. Malonyl CoA is the two-carbon donor in the elongation of fatty acyl CoAs. Again, condensation is driven by the decarboxylation of malonyl CoA."
"Uses acyl-CoAs, Malonyl-CoAs, and NADPH (Diagram 1, #2)"
Elongation of very long chain fatty acids
- Elovl 1-7
- Elovl 1,3 og 6 (Elongering av SFA og MUFA. (C16 opp til c24)
- Elovl 2 og 4 (PUFA synthetis)
Fatty acid desaturation system
Tre beskrevne gen-klasser
- DELTA-9 desuturaser SCD1, SCD5 mest viktig i Menneske
- DELTA 5 og DELTA 6 desaturaser D5D og D6D
- FADS3 Ukjent Funksjon når boken ble skrevet.
-
DELTA-9 desauturase eller Steroyl-CoA desaturase som katalyserer mettede Acyl-Coa-fettsyrer til umettede fettsyrer. Most notably:
18-karbon-fettsyre (Acyl-CoA) 18:0 til oljesyre, 18:1. Lager en dobbeltbinding 9 karboner fra karboksyl-gruppen (COO-). Er under kopleks hormonell kontroll. *Desaturerer også :0 fettsyrer med C12-19 karboner -
SCD1 og SDC5 mest studert. SCD5 mest aktiv i hjernen og pankreas og mutasjoner er forbundet med hareskår hos mennesker.
- Enkelt sagt vil SCD konvertere C12 til C19 mettet til enumettet.
- Videre jobber Elovl sammen med D5D og D6D for å lage flerumettede fettsyrer som Omega-3 (DHA) og Omega-6.
Syntese av omega 3 og 6.
Esensielle fettsyrer Med dobbeltbindinger beyond DELTA-9 pos. Karbon nr. 9 etter kaboksylgruppen.
Linolenic acid is an unsaturated fatty acid that is an essential fatty acid in mammals because they cannot synthesize double bonds in fatty acids beyond position DELTA-9. This makes linoleic acid and linolenic acid essential in mammalian diets, since they have double bonds beyond position DELTA-9 (at positions 9,12 and at positions 9,12, and 15 for linoleic and linolenic acid, respectively).
The tran-scription factors, SREBP-Ic, PPAR-a, LXR, and carbohydrate response element binding protein (ChREBP) play key roles in the regulation of desaturases and elongases.
- Ekspresjon av desaturaser og elongaser er regulert av flere næringstoffer og hormoner.
MUFA
- Negativ regulering Faktorene under binder seg til til sitt regulatoriske element i promotoren Hemmer ekpresjon av desaturaser og elongaser.
- ChREBP
- SREBP
- LXR
- Density reflect sammensetning av lipider og proteiner.
Chylomicroner --> VLDL--> IDL (VLDL remains) --> LDL --> HDL --> (VHDL)
PHOSPHOLIPDIER + CHOLESTERYL ESTERS + TRIGLYCERIDER) + protein --> PROTEIN + lipids
- help solubilize neutral lipids in circulation
- receptor recognition
- modulation of enzyme activities
Involvement of LDL receptors in cholesterol uptake and metabolism
Phenotypes of the LDL receptor mutations in FH individuals are as follows:
- Reductions in amount of LDL receptor made;
- LDL receptor is made, but it fails to migrate to plasma membrane;
- LDL receptor is in plasma membrane, but it fails to bind LDL; and
- LDL receptor is in plasma membrane and binds LDL, but it fails to cluster in coated pits.