- Linux
$ sudo apt-get install git
$ sudo yum install git
- Windows and Mac
- Git is a free and open source version control system
- It's a system that keeps records of your changes
- Allows collaboration and lets you see who made what changes as well as when those changes were made
- Git lets you revert any changes and go back to a previous version of a project
- Distributed version control system
- Git doesn't rely on a central server to store all versions of a project
- Every developer gets and full history of the project when they "clone"
- Users can make any changes without an internet connection
- An internet connection is required only to push and pull from a remote server
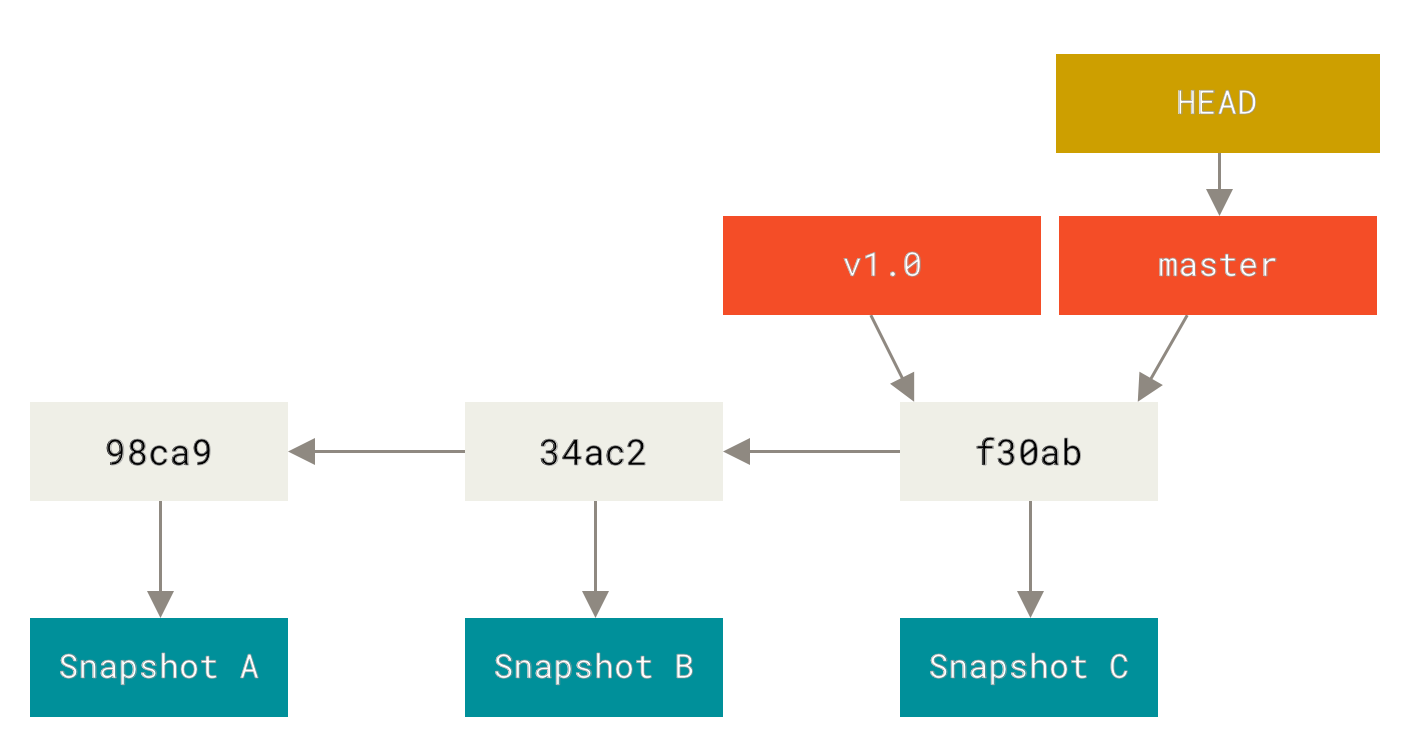
- Snapshot: The way git tracks changes to the code
- At a given time you can create a snapshot of the current version of the code
- Commit: The act of creating a snapshot. (Commits also keeps track of the previous commit that came before it)
- So an open source project is just made up of a bunch of commits
- Repository: Usually a collection of the project along with its full history (usually on a remote server, GitHub)
- Cloning: The act of copying a repository from a remote server
- Pulling: Downloading new changes from a remote repository that doesn't exist in your local repository
- Pushing: Adding your local changes to a remote repository
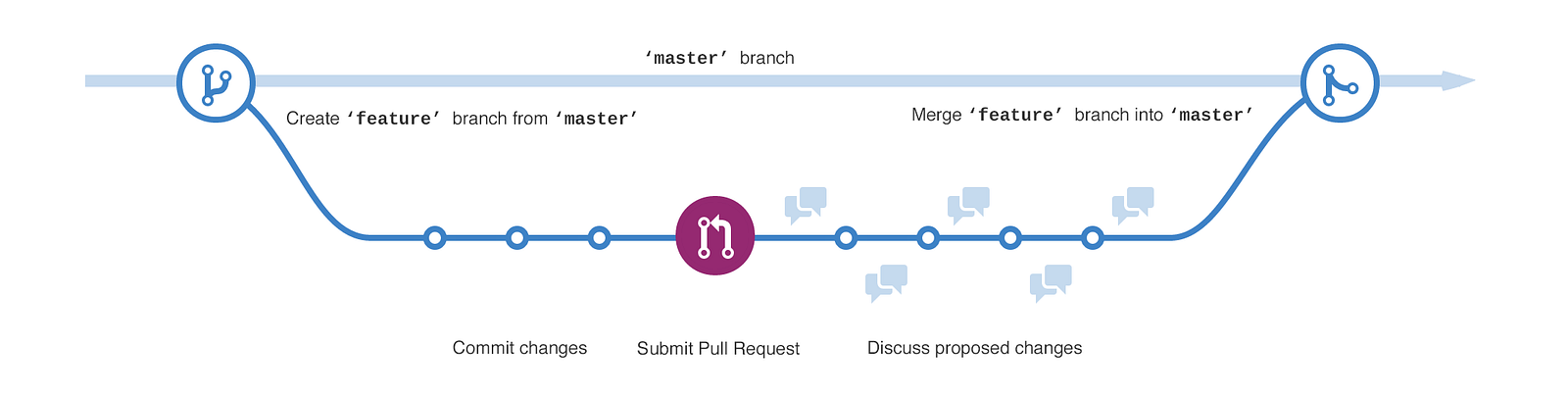
- Branches: All commits on git exists on a branch
- The main branch in a project is called the master branch
(https://www.atlassian.com/git/tutorials/using-branches)
(https://nvie.com/posts/a-successful-git-branching-model/)
(https://git-scm.com/book/en/v2/images/branch-and-history.png)
- Head: reference to the current branch in the workspace (in this case we are working in the master branch)
- It is also a reference to most recent commit (most of the time)
- Typically it is best to not directly work on master
- The master branch is the main branch, so it must be your most stable branch
- All developers who will work on a project will initially branch off of the master branch
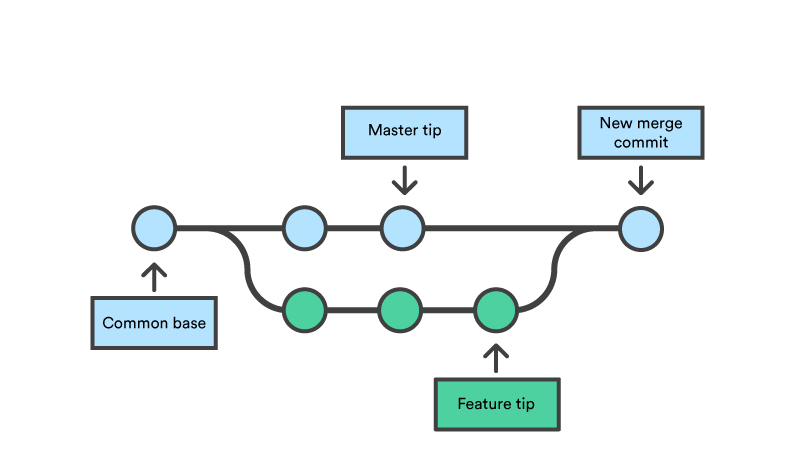
- Branching off: is the concept of making a new branch using the latest commit of another branch
(https://www.atlassian.com/git/tutorials/using-branches)
(https://services.github.com/on-demand/downloads/github-git-cheat-sheet.pdf)
- Pull latest code from the remote server
- Write some new code or edit some existing code
- Add file to the staging area
- Commit changes with readable commit message
- Push the commit
- Repeat
(https://www.atlassian.com/git/tutorials/comparing-workflows/gitflow-workflow)
- The largest git repository hosting service
- Allows code collaboration with anyone and has some handy UI tools to easily manage your repository
- There are hundreds of thousands of project available for developers to contribute
- Fork or Pull latest code from the remote server
- Write some new code or edit some existing code
- Add file to the staging area
- Commit changes with readable commit message
- Push the commit
- Create a Pull request to the original repository
- Repeat