-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 0
Commit
This commit does not belong to any branch on this repository, and may belong to a fork outside of the repository.
- Loading branch information
qingtong
committed
Jun 21, 2024
1 parent
5bb2bbe
commit 51970b0
Showing
3 changed files
with
199 additions
and
4 deletions.
There are no files selected for viewing
Loading
Sorry, something went wrong. Reload?
Sorry, we cannot display this file.
Sorry, this file is invalid so it cannot be displayed.
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| Original file line number | Diff line number | Diff line change |
|---|---|---|
| @@ -0,0 +1,195 @@ | ||
| --- | ||
| title: "AI 思考的快与慢" | ||
| date: "2024-06-12" | ||
| cta: "lowcode" | ||
| spoiler: "AI 思考的快与慢" | ||
| --- | ||
|
|
||
| ## 前言 | ||
|
|
||
| 2024 年,一位以心理学家身份获得诺贝尔经济学家的传奇人物——丹尼尔·卡尼曼去世,牵动了整个国外科技圈的关注。 | ||
|
|
||
| 卡尼曼教授在在著作《思考,快与慢》中提出了两种思考模式: | ||
|
|
||
| - 系统 1:快思考。依赖直觉,反应快速,更偏向于感性给出反馈 | ||
| - 系统 2:慢思考。深思熟虑,反馈时间长,基于逻辑和理性给出答案 | ||
|
|
||
| 我们每天都在不停地切换这两种思考模式,比如我们可以毫不费力在人潮中识别到朋友(系统 1)。而在撰写这篇文章时,我需要思考主题,搜集材料,整理结构,并持续调整(系统 2)。 | ||
|
|
||
| Open AI 创始成员 Karpathy 在一次公开演讲中提到,基于大模型的思维链(Chain Of Thought)模式背后的思想正是来源于「慢思考」理论,要想让大模型表现得更好,就需要引导大模型一步一步思考,循环往复,直到达成预定结束条件。 | ||
|
|
||
| 比如,即使是很简单的数学题,如果要求大模型一步到位给出答案,也很难获得理想的结果。 | ||
|
|
||
| 有研究人员给出一道数学题,定义了 ”Q 运算”,规则是 `a Q b = a + b - 1`(未在 prompt 中声明),要求大模型在按规律进行运算。结果 GPT4、Claude、Germini 这些先进大模型全军覆没。 | ||
|
|
||
|  | ||
|
|
||
| 只有让模型一步步推理,甚至需要不断地给出引导,才能让它输出正确结果。 | ||
|
|
||
|  | ||
|
|
||
| 像这样一步一步处理方式正是区别于 Agent(智能体)和 LLM 的核心,背后的原理也正是卡尼曼的「慢思考」理论。 | ||
|
|
||
| ## Agent 是什么 | ||
|
|
||
| 简而言之,AI agent 是有能力主动思考和行动的智能体。当我们提出需求时,agent 有能力自行感知环境、形成记忆、规划和决策行动,甚至与别的 agent 合作实现任务。对比之下,LLM 是被动的推理引擎,用户每 prompt 点拨一次才会回复一次。 | ||
|
|
||
| 具体到 AI Agent 的产品形态的可能性,目前社区主流有三种理解方式: | ||
|
|
||
| ### 1.AI Agent 是 AI Native 的开发范式 | ||
|
|
||
| 在 AI Native 之前,云原生(Cloud Native)的概念炙手可热。云原生并非指代具体的某一项技术,而是一套指导软件架构设计的方法论。首先软件天然就“生在云上,长在云上”,其次软件遵循一种新的开发、发布、运维模式,能够最大化发挥“云”的价值。 | ||
|
|
||
| AI Native 软件的设计架构也是类似,软件原生为 AI 而设计,更好地利用并适应 AI,而非传统的 AI 来适应软件。 | ||
|
|
||
| 未来 AI Native 应用的核心思路都有 Agent 的影子。Agent 是能够更好的辅助 AI 扬长避短,结构化思考的设计思想。 | ||
|
|
||
| ### 2. AI Agent 比传统软件更灵活,比 LLM 更可靠 | ||
|
|
||
| 传统软件基于规则和逻辑,带来的是高可靠性和确定性,但也使其难以解决灵活的长尾问题。AI Agent 可以基于用户的需求灵活定制,真正实现千人千面的定制化能力。优秀的 Agent 要充分发挥 LLM 的推理(Reasoning)、角色(Actor)和交互能力(Interact)。 | ||
|
|
||
| 短期内要实现灵活性,Agent 还是要牺牲一定的可靠性,对于容错度较低的场景,短期内并不推荐直接上 Agent。但在可预期未来,Agent 能够达到类似于传统软件的可靠性。 | ||
|
|
||
| ### 3. AI Agent 和 LLM-based 应用相比,存在一些不同点: | ||
|
|
||
| - 3.1 编排能力(Orchestration)。不同于 LLM 的一锤子买卖,Agent 可以实现多 Agent 编排,共同完成一个复杂的工作流场景。比如在编程场景下,有开发、测试角色。 | ||
|
|
||
| - 3.2 工具使用(Tool)。LLM 只适合文字补全(completion)的工作,而 Agent 基于 LLM 的理解能力,可以调用合适的外部工具,解决对应的问题。比如 LLM 并不擅长解决数学问题,而 Agent 基于 LLM 的理解,调用合适的外部数学工具,就能很好地解决数学难题。 | ||
|
|
||
| - 3.3 记忆能力(Memory)。LLM 的记忆能力只和上下文窗口(context window)相关。而 Agent 的记忆能力可以将 context window 和长期记忆结合,类似于内存(memory)和存储(Storage)的关系。未来的 Agent 能够记录用户偏好和使用习惯,使用越多就越了解用户。作为人类值得信任的工作伙伴。 | ||
|
|
||
| - 3.4 推理能力(Reasoning)。LLM 是一种建立在 next token 预测引擎之上的概率工具,这和人类的思考方式是截然相反的。比如我们在思考数学问题时,会对一系列的假设方案进行实验并得出最佳答案,而不可能从一开始就能获取最优解。Agent 的推理能力,就是模拟人类思考方式,通过不断地假设、试验、求证,并持续迭代这一个过程,最终获得最优解。 | ||
|
|
||
| 短期来看,一个优秀的 AI Agent 应用至少要具备 Orchestration 和 Tool 能力。LLM 应用还不够强大,需要在合适的场景下寻找合适的工具(Tool)来解决问题,这个过程需要人类专家参与工作流,进行设计和编排,使其成为可靠的合作伙伴。 | ||
|
|
||
| 中长期来看,Memory 是下一个需要突破的方向,如何让人机协助积累的数据,带来新的数据飞轮,是一个相当重要的问题,有了个性化的记忆,就是 Gen AI 时代个性化的推荐引擎。 | ||
|
|
||
| Reasoning 能力则是一个长期目标,需要大模型产品持续去提升,当前基于 next token 预测模型,很难让 AI 真正学会探索、试错。这方面需要 LLM 和 Agent 分别从模型推理和产品形态的双重进化。 | ||
|
|
||
| ## Agent 设计模式 | ||
|
|
||
| 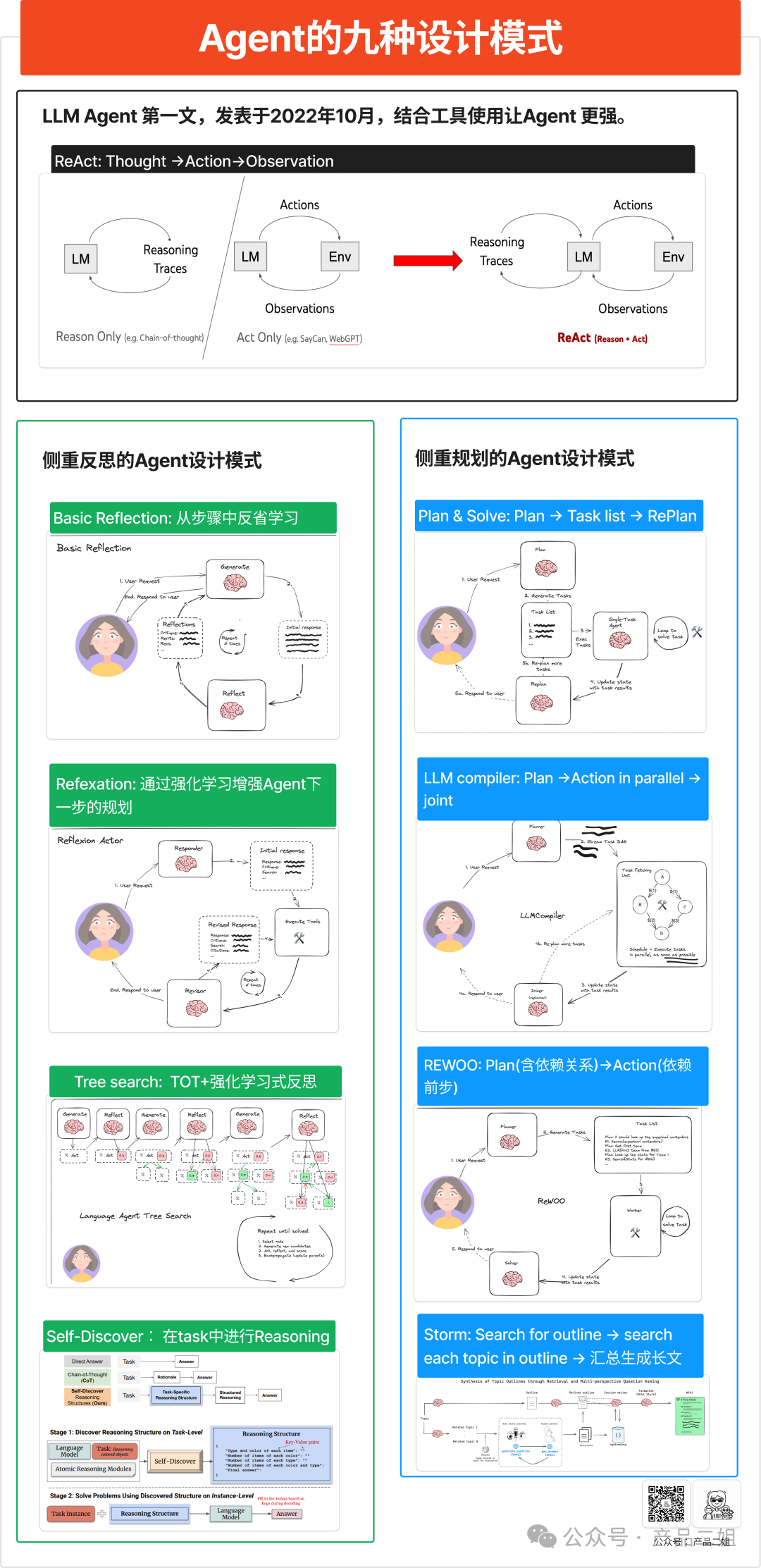 | ||
|
|
||
| ### 1. ReAct | ||
|
|
||
| ReAct 是 Agent 设计模式中最早提出的,发表于 2022 年 10 月,在 ChatGPT 发布之前就提出了让 LLM 学习外公不公使用,具有相当高的开创性。 | ||
|
|
||
| 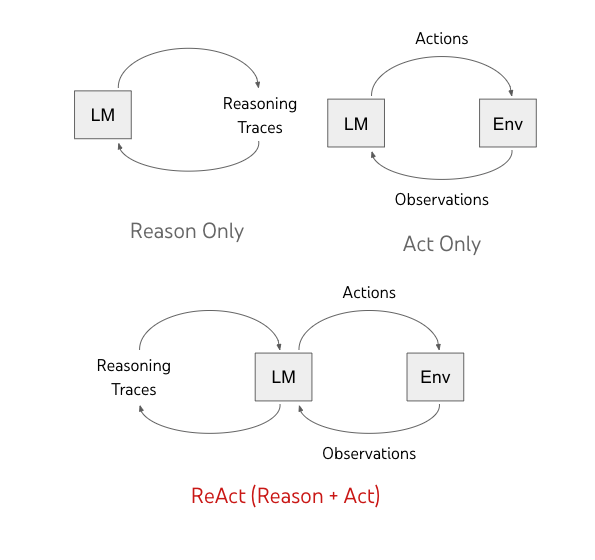 | ||
|
|
||
| ReAct 模式,是把 Reasoning(推理),Action(行动) 与 LLM 结合起来的 Agent 开发范式。 | ||
|
|
||
| 前面我们提到过 LLM 实际上是「系统 1」的思考方式,基于用户提问,快速给出答案,然后给出证明答案的证据。事实上,很多问题需要思考,提出若干解决思路,并一步一步得出最终答案,也就是「系统 2」的思考方式。 | ||
|
|
||
| ReAct 属于典型的「系统 2」思考方式。 | ||
|
|
||
| ### Prompt | ||
|
|
||
| 以 `langchain` 为例,官方提供了一套 ReAct system prompt 模板,[链接](https://smith.langchain.com/hub/hwchase17/react?organizationId=ebebe8d7-2f89-597e-90fa-f331000bbce3) | ||
|
|
||
| ``` | ||
| Answer the following questions as best you can. You have access to the following tools: | ||
| {tools} | ||
| Use the following format: | ||
| Question: the input question you must answer | ||
| Thought: you should always think about what to do | ||
| Action: the action to take, should be one of [{tool_names}] | ||
| Action Input: the input to the action | ||
| Observation: the result of the action | ||
| ... (this Thought/Action/Action Input/Observation can repeat N times) | ||
| Thought: I now know the final answer | ||
| Final Answer: the final answer to the original input question | ||
| Begin! | ||
| Question: {input} | ||
| Thought:{agent_scratchpad} | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| 首先,因为是一个通用的模板,所以给出了一个通用的解决问题的目标。 | ||
|
|
||
| 其次,定义`{tools}`,明确告诉 LLM 选择给定外部工具来执行 action。 | ||
|
|
||
| 然后又给出了 LLM 执行步骤: | ||
|
|
||
| - Question: 用户提问 | ||
| - Thought: 这是大模型擅长的领域,基于一个问题,给出解决问题的思考方向 | ||
| - Action: 从 `{tools}` 选择对应的工具 | ||
| - Action Input: 从问题中提取参数作为 `tool` 的输出 | ||
| - Observation: 观察 Action 输出 | ||
| ... (Thought/Action/Action Input/Observation 重复执行 N 次) | ||
| - Final Answer: 基于 Observation, LLM 判断任务已完成,输出结果 | ||
|
|
||
| 最后将 `input(用户提问)`和 `agent_scratchpad(agent 执行记录)` 传递给大模型,开始本次命运的齿轮 ⚙ 转动。 | ||
|
|
||
| 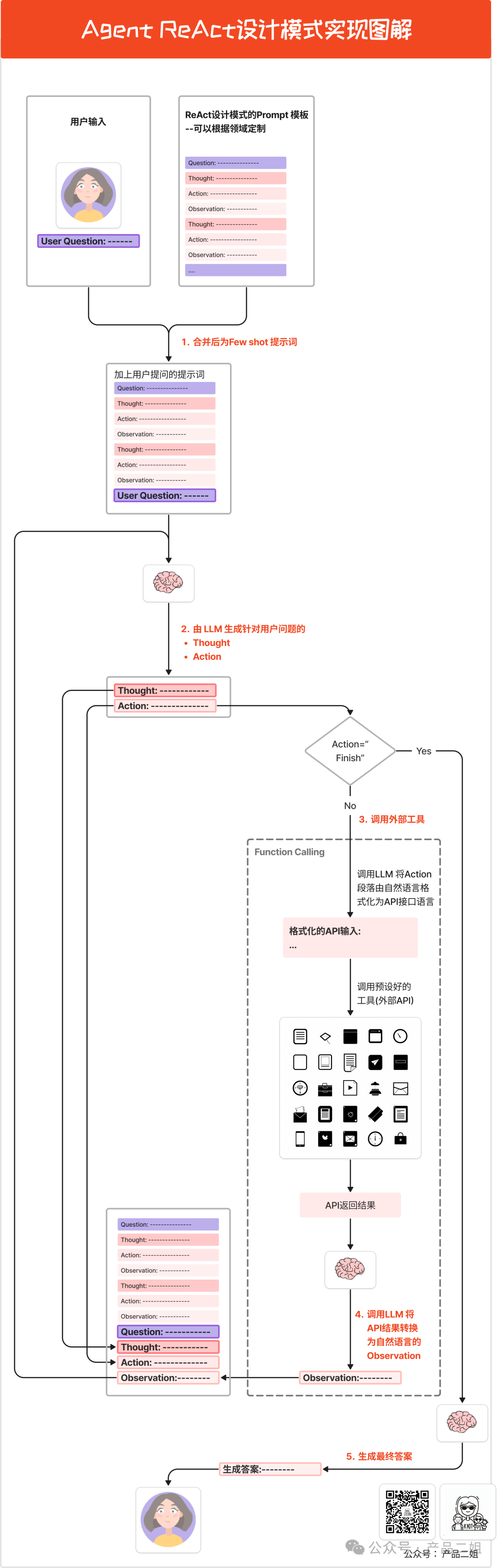 | ||
|
|
||
| ### 使用场景 | ||
|
|
||
| ``` | ||
| Question: 中国哪个省份面积最大,哪个面积最小,最大和最小差几倍 | ||
| --- | ||
| action:: I should use the search engine to find the largest and smallest provinces in China by area, and then use the calculator to find the difference in their sizes. | ||
| Action: tavily_search_results_json | ||
| Action Input: "largest province in China by area" | ||
| Observation: The largest province in China by area is Xinjiang | ||
| --- | ||
| Action: tavily_search_results_json | ||
| Action Input: "smallest province in China by area" | ||
| Observation: The smallest province in China by area is Macau | ||
| --- | ||
| Action: calculator | ||
| Action Input: area of Xinjiang / area of Macau | ||
| Observation: The area of Xinjiang is about 166 times larger than the area of Macau | ||
| --- | ||
| Thought: I now know the final answer | ||
| --- | ||
| Final Answer: Xinjiang is the largest province in China by area, Macau is the smallest, and Xinjiang's area is about 166 times larger than Macau's. | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| 接下来我们基于 `langchainjs` 是实现 ReAct: | ||
|
|
||
| ```typescript | ||
| import { AzureChatOpenAI } from "@langchain/azure-openai"; | ||
| import { AgentExecutor, createReactAgent } from "langchain/agents"; | ||
| import { pull } from "langchain/hub"; | ||
| import type { PromptTemplate } from "@langchain/core/prompts"; | ||
| import { TavilySearchResults } from "@langchain/community/tools/tavily_search"; | ||
| import { Calculator } from "@langchain/community/tools/calculator"; | ||
|
|
||
| // 定义模型 | ||
| const llm = new AzureChatOpenAI({ | ||
| temperature: 0, | ||
| }); | ||
|
|
||
| // 定义工具 | ||
| const tools = [new TavilySearchResults({ maxResults: 1 }), new Calculator()]; | ||
|
|
||
| // 拉取 prompt | ||
| const prompt = await pull<PromptTemplate>("hwchase17/react"); | ||
|
|
||
| // 定义 agent | ||
| const agent = await createReactAgent({ | ||
| llm, | ||
| tools, | ||
| prompt, | ||
| }); | ||
| // 生成 agent 实例 | ||
| const agentExecutor = new AgentExecutor({ | ||
| agent, | ||
| tools, | ||
| }); | ||
|
|
||
| const result = await agentExecutor.invoke({ | ||
| input: "中国哪个省份面积最大,哪个面积最小,最大和最小差几倍", | ||
| }); | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| ### 小结 | ||
|
|
||
| 从以上示例可以看出,ReAct 设计的核心有两点: | ||
|
|
||
| 1. 基于上下文推理能力,包括选择合适的工具,并提取出工具参数 | ||
| 2. 预设工具的丰富程度,能否和推理阶段相匹配 |
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters