-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 195
6LBR Modes
6LBR runs in three categories of modes: bridge, router and transparent bridge. These three categories are declined into the following modes :
- Bridge
- SmartBridge
- Router
- Router
- NDP-Router
- 6LR
- RPL-Root
- Transparent Bridge
- RPL-Replay
- FullTransparentBridge
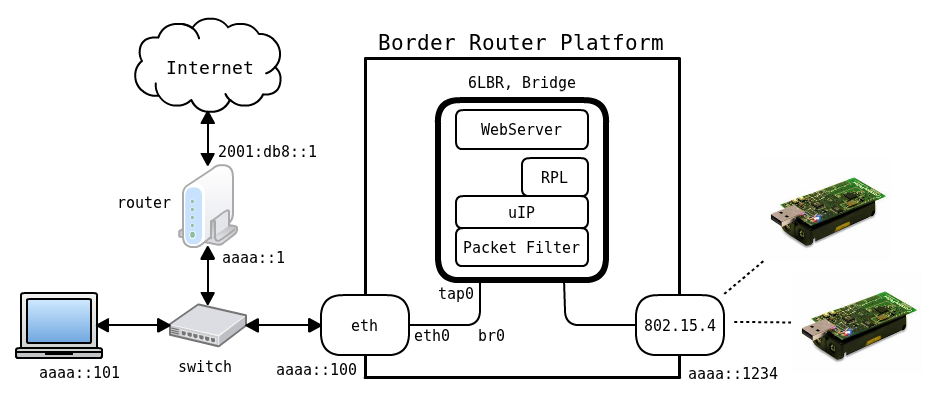
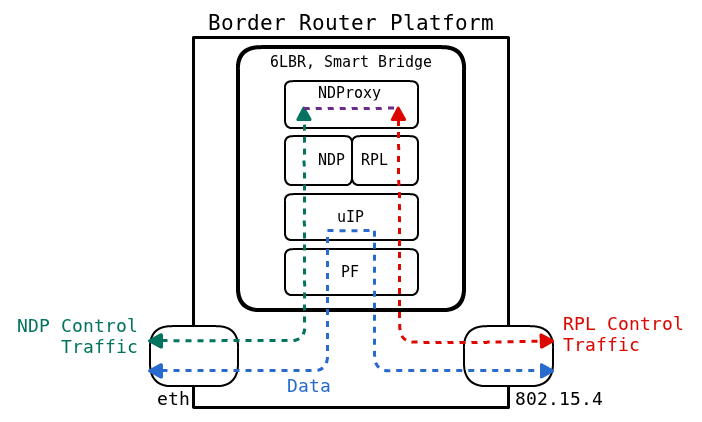
In this mode, the 6LBR acts as a Smart bridge, allowing to interconnect a standard IPv6 based network with a RPL based WSN mesh. The SmartBridge is acting as a NDP proxy on the Ethernet side and is using NDP parameters to configure the WSN mesh. Source and destination MAC addresses are translated and addresses present in ICMPv6 packets are also translated. The SmartBridge mode allows you to :
- seamlessly integrate a WSN mesh into an existing NDP based IPv6 network, the SmartBridge will use the NDP provided configuration to set up the WSN mesh accordingly.
- aggregate several WSN meshes with their own DODAG into one virtual IPv6 subnet. Node mobility is supported, in the case of two WSN overlaps, one node can switch from one WSN to the other if it gets a better link, as seen from the virtual IPv6 subnet, this switch will be almost invisible thanks to the NDP proxy.
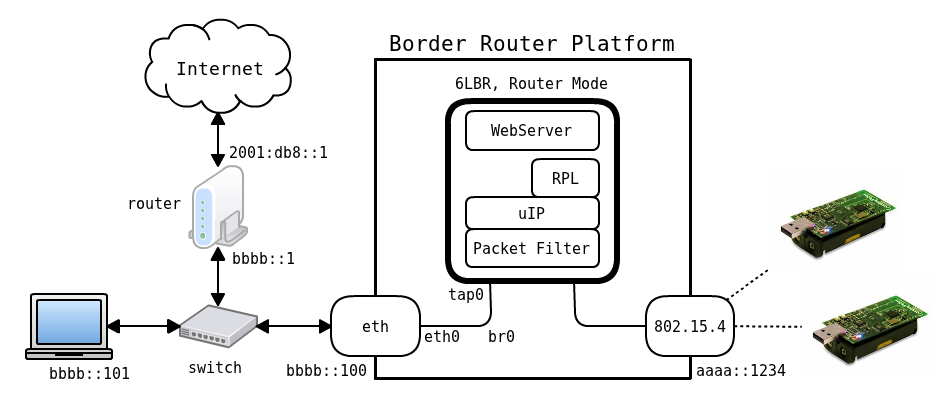
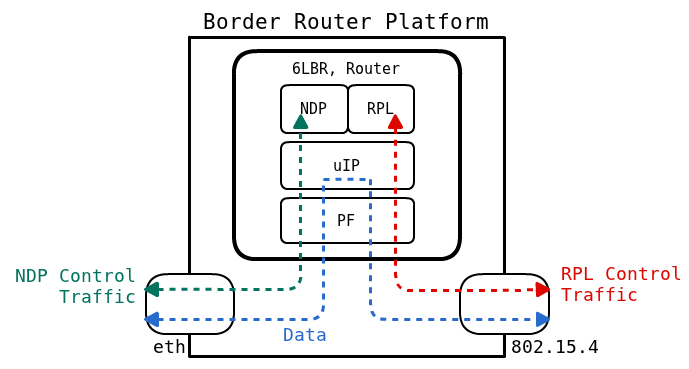
In this mode, the 6LBR acts as a full fledged IPv6 Router, interconnecting two IPv6 subnets. The WSN subnet is managed by the RPL protocol and the Ethernet subnet is managed by IPv6 NDP. In this mode, the 6LBR provides a virtual second interface to Contiki thanks to the packet filter module. This mode works more like a Gateway between Ethernet and 6Lowpan RPL. Outgoing packets source address from RPL side will be updated as eth_ip_local_addr.
The Router moder allows you to :
- Isolate WSN mesh into its own subnet, therefore clearly identifying the WSN nodes.
- ...
Note: Node mobility across different WSN subnets is supported thanks to the prefix switching capability. In that case the nodes will get a new address, based on the prefix of the new WSN.
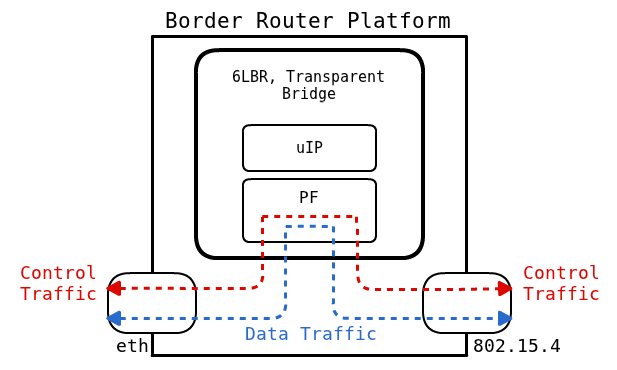
In these modes, the 6LBR acts as a standalone bridge, providing basic switching capabilities. All incoming packets targeting a 802.15.4 interface or incoming multicast packets on the Ethernet interface are forwarded to the WSN segment. Conversely, all incoming packets targeting an Ethernet interface or incoming multicast packets on the 802.15.4 interface are forwarded to the Ethernet segment. The 6LBR has its own address and act as a host. Source and destination MAC addresses are translated and addresses present in ICMPv6 packets are also translated. The transparent Bridge Mode allows you to :
- aggregate sub-WSN meshes into one global DODAG, managed by an external RPL Root node (When using RPL-Relay)
- bridge a one-hop mesh with an IPv6 network using NDP (When using FullTransparentBridge)
- bridge a statically routed mesh with an IPv6 network (When using FullTransparentBridge)
- ...
Note that we intentionally omitted labelling the type of control traffic, as both RPL and NDP are mentionned in the possible use cases.
To be added
To be added
To be added
- Home
- Features
- Supported Hardware
- Download
- Changelog
- FAQ
- Installation:
- Configuration
- Deployment
- Documentation
- Extensions
- Tools
- Examples
- Tutorials
- Publications
- Acknowledgements
- Internal and old