-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 25
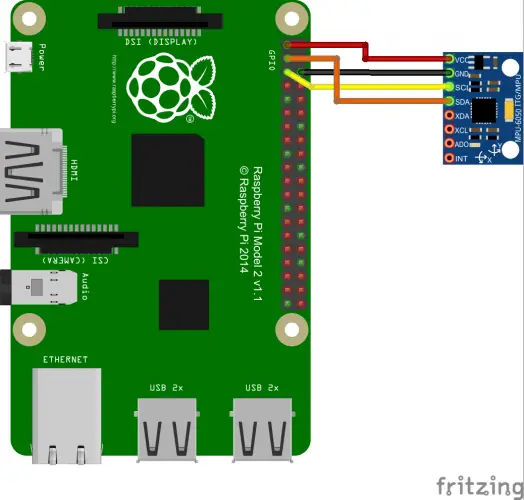
How to connect sensors
As you can see the Raspberry PI and the servo is connected to different power converters. Embedded in ESC of BEC provides an average 2A, that is sufficient to power only the Servo. An additional source > 3A 5V is required to power the RPi.
First we enable I2C.
sudo raspi-config
Here we find the menu for activating services. Under “8. Advanced Options” there is the entry “A7 I2C”, which we activate (This can differ in other Raspbian versions). For older Raspbian versions, the entries in the /etc/modprobe.d/raspi-blacklist.conf file must be excerpted (with #).
We then edit the modules file:
sudo nano /etc/modules
If the following lines are not already included, add them and restart the Pi (sudo reboot):
Shell:
i2c-bcm2708
i2c-dev
Now we can quickly install the necessary tools:
sudo apt-get install i2c-tools python-smbus
Just connect via usb -> uart converter to a free usb port.
For further configuration, use this instruction
1. Installation Instructions (Ubuntu)
2. How to connect sensors
3. Linking of multiple machine in ros (external link)
4. How to remote control
5. Setting TF
6. Created map by using hector_slam
7.1 Autonomous Navigation by using move_base
7.2 Autonomous Navigation by using teb_planner
8. Setup opencv+aruco localisation
9. Swarm control
1. Installation Instructions (Ubuntu)
2. How to connect sensors
3. Linking of multiple machine in ros (external link)
4. How to remote control
5. Setting TF
6. Created map by using hector_slam
7.1 Autonomous Navigation by using move_base
7.2 Autonomous Navigation by using teb_planner
8. Setup opencv+aruco localisation
9. Swarm control