-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 200
Hardware ~ Supported WiFi adapters
Pay attention to the version number of the wifi adapter, manufacturers often use a completely different chipset with a different version number!
| Name | Dual bands 2.4/5.8 | TX Power | Chip | Diversity | RC | Notes | Available in 2018 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CSL 300Mbit | X | 30mW | RT5572 | X | low range on 5g due to stock antenna | X | |
| ALFA AWUS036NHA | 2.4g | 280mW | AR9271 | X | 2.3g capable | X | |
| ALFA AWUS051NH v2 | X | 330mW | RT3572 | stock antenna 5db gain, pattern too flat | |||
| ALFA AWUS052NH v2 | X | 330mW | RT3572 | X | stock antenna 5db gain, pattern too flat | ||
| ALFA AWUS1900 | X | ? | RTL8814 | X | 4 antennas, support coming soon | X | |
| ALFA AWUS036ACH | X | ? | RTL8812 | X | 2 antennas, support coming soon | X | |
| ALFA AWUS036AC | X | ? | RTL8812 | X | 2 antennas, support coming soon | X | |
| Ubiquiti Wifistation | 2.4g | >800mW | AR9271 | X | 2.3g capable | ? | |
| Ubiquiti Wifistation EXT | 2.4g | >800mW | AR9271 | X | 2.3g capable | ? | |
| TPLink TL-WN722N V1 | 2.4g | 60mW | AR9271 | X | 2.3g capable | X | |
| TPLink TL-WDN3200 | X | RT5572 | X | ||||
| Rosewill RNX-N600UBE | X | RT5572 | X | ||||
| AW-NU138 | 2.4g | 50mW | AR9271 | X | 2.3g capable, needs good cooling | ? | |
| AW-NU137 | 2.4g | 70mW | AR9271 | X | I-PEX antenna connection | ? |
This adapter will provide around 280mW output power. Ranges of several kilometers have been reported (with directional antennas though).
This adapter is quite large, but seems to have a good quality amp on it. Useable TXPower is not yet determined, but should be slightly higher than the AWUSH036NHA.
This adapter will provide around 60mW output power. Range should be roughly around 800-1000m with 2.1dbi stock antennas.
NOTE: There have been reports that the TL-WN722N V1 seems to be replaced by V2 and V3 versions. These new versions use a completely different chipset and are not compatible. Consider asking the seller for the version, if it says "V2" or "V3" on the back of the dongle it's the wrong chipset!
NOTE: The PCB antenna causes packetloss and bad reception under certain circumstances. It is recommended to disconnect the antenna by moving the SMD component as shown below:
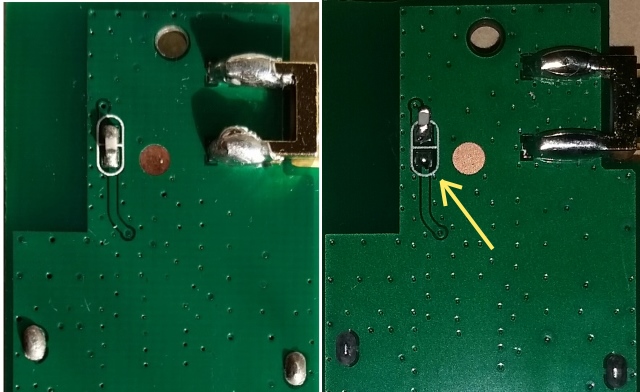
This adapter is very small, output power about 50mW. The internal antenna can be de-soldered and replaced with an external antenna. Since it's very small it runs quite warm, good cooling is needed.
Very similar to the NU138. Reported power is 70mW. I-PEX antenna connector allows for light weight build.
This adapter provides around 30mw output power. Range on 5Ghz is not very high, around 200-300m. Stock antennas are not usable on 5Ghz, as they are simple 2.4Ghz 2.1dbi sleeved-dipole antennas.
When used as an Rx dongle, bad blocks can occur when the received signal strength is higher than -20dbm. This can be worked-around by using more than one adapter and pointing antennas in different directions / polarizations.
This adapter will provide around 330mw output power. Range on 5Ghz is around 800-1000m. Stock antenna is not recommended because they have 5dbi gain, which will give a too-flat radiation pattern.
This adapter will provide around 330mw output power. This is the same adapter as the 051NH, but with two TX chains. Stock antennas are not recommended because they have 5dbi gain, which will give a too-flat radiation pattern.
In general the WiFi dongles with the following chipsets work:
- Atheros AR9271
- Ralink RT2070, RT2770, RT2870, RT3070, RT3071, RT3072, RT3370, RT3572, RT5370, RT5372, RT3573, RT5572
- MediaTek MT7601
For cheap alternatives check out the usual computer stores and maybe consider Aliexpress. Be a little careful, some cards are of questionable quality. However, often, brandname wifi modules or USB sticks originally made for applications like Smart-TVs etc. are offered for a very good price.
A good way to find out more about wifi sticks and modules offered online is to look for product numbers, chipsets, or even better an FCC ID. With those, try to find high-res internal photos of the cards, to find out the chipset and the amps used.
Search the web for those numbers and also these two very helpful sites:
- https://fccid.io/ (FCC documents which contain internal photos)
- https://wikidevi.com/wiki/ (general infos and sometimes photos)
When you have found photos, google for the numbers on the amps to find a datasheet giving a rough estimate about the expectable output power.
It would be nice if you report back your findings in case you tried a wifi card that is not listed here.
Another way to increase output power is to use a low-power wifi stick combined with an external amp like this "2W" amp:
Real output power is around 600mW with a low-power AR9271 stick.
General
Hardware Setup
- Proper Wiring
- Power Supply (BECs)
- Supported Pi models
- Supported Cameras
- Supported WiFi Adapters
- Supported Displays
- Antennas
- DIY builds
Software Setup
- Basic configuration options
- Advanced Options
RC Control
- General
- RC with Ardupilot (MAVlink)
- RC with iNav
- DIY builds
Ground Stations
- Mission Planner (Windows)
- QGroundControl (Windows / Linux / Mac / Android /iOS)
- APM Planner (Windows / Mac / Linux)
- Tower (Android)
- FPV_VR (Android)
- GStreamer (Windows / Mac / Linux)
- Fishing FanCam (iOS)
Expert Settings
- OSD MAVLink message types
- Transmit power settings
- SSH shell
- Raspivid camera settings
- Optimizing-Power-Consumption
Extensions / AddOns
- HDMI-in cards
- WebCams
- Video Switcher
- Thermal (FLIR, Seek)
- 360° cameras
Community-HUB
Developer's Corner
- Room for Improvement
- Mounting Images
- Reducing Images size
- WinSCP (copying files)